* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Cochlear Representation Algorithm (CRA)
Speech perception wikipedia , lookup
Auditory system wikipedia , lookup
Telecommunications relay service wikipedia , lookup
Hearing loss wikipedia , lookup
Hearing aid wikipedia , lookup
Noise-induced hearing loss wikipedia , lookup
Sensorineural hearing loss wikipedia , lookup
Audiology and hearing health professionals in developed and developing countries wikipedia , lookup
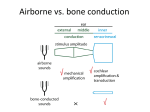
New Technique for Improving Speech Intelligibility for the Hearing Impaired Miriam Furst-Yust School of Electrical Engineering Tel Aviv University 1 The Hearing Aid Problem Current hearing aids are very helpful to severe and profound hearing impairment in quiet environment. Most people with mild-to-moderate hearing loss are unable to understand speech in a noisy background. Current Hearing aids are useless in a noisy background. 2 THE PROBLEM: common noise suppression techniques are not robust and most of the time are not effective 3 Our Approach A single microphone followed by a cochlear model algorithm that improves the signal-tonoise ratio. The algorithm is robust, so speech with high SNRs are not distorted. 4 Cochlear Representation Algorithm A Device that Mimics the Human Hearing and Speech Perception 5 Cochlear Representation Algorithm (CRA) Mimic the cochlear representation of speech signals Identify the speech areas in the cochlear representation and discard the noise areas Reconstruct the speech signal from the modified cochlear representation 6 Cochlear Representations of Tones Cochlear representation 7 Representation of a word Input Signal: The word “SHEN” INPUT OUTPUT Normal Ear Damaged Ear 8 Input Speech Time representation Spectrogram 9 Energy Estimation Energy Estimation Energy Mask 10 Cochlear Representation TIME (sec) 11 Modified Cochlear Representation 12 Speech Reconstruction Time representation Spectrogram 13 CRA Performance Noisy Sentence MELP 2.4 Kb/s Clean Sentence G729 8 Kb/s MELP 2.4 Kb/s G729 8 Kb/s 14 Analysis of Human Performances with CRA: Recognition of CVC words in an open set Subjects: 1. Hearing Impaired with their Cochlear Implants 2. Hearing Impaired with their Hearing Aids 3. Normal Hearing 15 Word database - HAB Hebrew adaptation (Kishon-Rabin,2002) to AB (Arthur Boothroyd) list (Boothroyd,1968) comprising CVC words. Equal distributions in each list of phonemes in the Hebrew language HAB common use in hearing tests. Reduces effect of frequency and/or familiarity on test scores Two speakers: male and female. 15 lists of 10 words (total of 300 words) Recorded at a sampling rate of 44.1 kHz 16 Applied Word database Test subject’s ability to recognize words in noisy environments Gaussian white noise in SNRs of 0 – 30 dB Bandpass filter 500-8000 Hz Apply cochlear model and reconstruction algorithm 17 Normal Hearing Performances in open-set words identification 18 Hearing Aid Users Performances in open-set words identification Percentage Correct (%) 70 60 50 Hearing Aid 40 Hearing Aid+CRA 30 20 10 0 No Noise 30 24 Signal-to-Noise Ratio (dB) 18 No. of Subjects=51 * Hearing Impaired performance were significantly improved by CRA in SNR of 18 dB 19 Cochlear Implant Users Performances in open-set words identification Percentage Correct (%) 60 50 Hearing Aid 40 30 Hearing Aid+CRA 20 10 0 No Noise 30 24 Signal-to-Noise Ratio (dB) 18 No. of Subjects=16 * Hearing Impaired performance were significantly improved by CRA in SNR of 18, 24 and 30 dB 20 Why CRA is Beneficial to the Hearing Impaired but Not Effective to Normal Hearing Subjects? 21 Normal Hearing Recognition rate of 2.5 Oct. Band Limited Speech Center Frequency = 600 Hz 100 90 80 70 60 50 40 30 20 10 0 600 Hz 2500 Center Frequency = 2500 HzHz No filter Clean SNR=0 dB SNR=3 dB 22 Summary & Conclusions: Normal Hearing People Speech is redundant in the frequency domain. Normal Hearing subjects can efficiently recognize speech in noisy environments because they identify the speech in different frequency bands. CRA reduces the speech redundancy. Therefore, CRA that is applied to a wide-band signal is not effective to normal hearing people. 23 Summary & Conclusions: Hearing Impaired People Hearing Impaired people have band limited hearing. The speech redundancy is not very useful to the hearing impaired. Therefore, CRA can be very effective to the hearing impaired. 24 Hardware Solution : Real time Implementation of the Algorithm Implementation of the algorithm as part of common digital hearing aid or Cochlear Implant. 25 Real Time Implementation 26