* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download TRANSFORMERS A transformer changes electrical energy of a
Stepper motor wikipedia , lookup
Ground (electricity) wikipedia , lookup
Wireless power transfer wikipedia , lookup
Electrical ballast wikipedia , lookup
Spark-gap transmitter wikipedia , lookup
Current source wikipedia , lookup
Variable-frequency drive wikipedia , lookup
Power inverter wikipedia , lookup
Resistive opto-isolator wikipedia , lookup
Power engineering wikipedia , lookup
Electric machine wikipedia , lookup
Electrical substation wikipedia , lookup
Capacitor discharge ignition wikipedia , lookup
Surge protector wikipedia , lookup
Stray voltage wikipedia , lookup
Three-phase electric power wikipedia , lookup
Schmitt trigger wikipedia , lookup
Buck converter wikipedia , lookup
Voltage optimisation wikipedia , lookup
Voltage regulator wikipedia , lookup
History of electric power transmission wikipedia , lookup
Galvanometer wikipedia , lookup
Mains electricity wikipedia , lookup
Ignition system wikipedia , lookup
Opto-isolator wikipedia , lookup
Alternating current wikipedia , lookup
Switched-mode power supply wikipedia , lookup
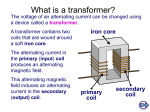
1 K Hinds | 2012 TRANSFORMERS A transformer changes electrical energy of a given voltage into electrical energy at a different voltage level. It consists of two coils which are not electrically connected, but which are arranged in such a way that the magnetic field surrounding one coil cuts through the other coil. When an alternating voltage is applied to (across) one coil, the varying magnetic field set up around that coil creates an alternating voltage in the other coil by mutual induction. A transformer can also be used with pulsating dc, but a pure dc voltage cannot be used, since only a varying voltage creates the varying magnetic field which is the basis of the mutual induction process. A transformer consists of three basic parts, as shown below. These are an iron core which provides a circuit of low reluctance for magnetic lines of force, a primary winding which receives the electrical energy from the source of applied voltage, and a secondary winding which receives electrical energy by induction from the primary coil. 2 K Hinds | 2012 Types of Transformers Transformers either Step up or step down the input voltage. The function of the transformer is determined by the number of windings on the input coil compared to the output coil windings. The diagram below shows two types of transformers: The ratio of the transformer input voltage to the output voltage is the same as the turn’s ratio if the transformer is 100 percent efficient. Thus, when 10 volts are applied to the primary of the transformer shown in A , two volts are induced in the secondary. If 10 volts are applied to the primary of the transformer in B of figure, the output voltage across the terminals of the secondary will be 40 volts. Turns Ratio (n) This is the ratio of turns in the input coil compared to the number of turns on the output coil n = Input and Output Voltage in transformer Input and Output Current 3 K Hinds | 2012 Np = # windings on primary coil Ns = # windings on Secondary coil Vp = Input Voltage Vs = Output Voltage Is = Input Current Is = Secondary Current No transformer can be constructed that is 100 percent efficient, although iron core transformers can approach this figure. This is because all the magnetic lines of force set up in the primary do not cut across the turns of the secondary coil. A certain amount of the magnetic flux, called leakage flux, leaks out of the magnetic circuit. 4 K Hinds | 2012 Ideal power equation The ideal transformer as a circuit element If the secondary coil is attached to a load that allows current to flow, electrical power is transmitted from the primary circuit to the secondary circuit. Ideally, the transformer is perfectly efficient. All the incoming energy is transformed from the primary circuit to the magnetic field and into the secondary circuit. If this condition is met, the input electric power must equal the output power: Efficiency of a Transformer No transformer is 100% efficient. Therefore, the efficiency of a transformer is given by the equation: Efficiency = (Vs Is / Vp Ip) x 100 Losses in a transformer In actual practice output is not equal to input therefore actual transformers are not 100% efficient. However commercial transformers have very high efficiency in the range of 95% to 99%. EDDY CURRENTS Due to variation in magnetic flux eddy currents are induced on the surface of iron core which in turn produce heating and therefore reduce the amount of power to the secondary coil. In order to avoid eddy currents , the core is laminated, made of thin sheets of soft iron. Each sheet is separated from the next by a layer of insulating varnish HYSTERESIS LOSS Each time the direction of magnetization is reversed, some useful energy is wasted in overcoming internal friction. This is known as "hysteresis loss" and it also produces heating in the core. Hysteresis loss is minimized by using special alloys known as "perm alloy" for core material. 5 K Hinds | 2012 HEATING Some energy is dissipated as heat in the coil. This is reduced by using suitably thick wire. FLUX TRANSPORT FAILURE Some loss of useful energy occurs because a small amount of the flux associated with the primary coil fails to pass through the secondary Questions 1. When the turns ratio of a transformer is 20 and the primary ac voltage is 12 V, what is the secondary voltage? 2. A certain transformer has 400 turns in the primary winding and 2,000 turns in the secondary winding. What is the turn ratio for this transformer? a. If the input current is 5A, what is the Output current? b. How efficient is this transformer?