* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Heat Transfer Tab
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
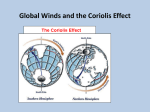
Heat Transfer Tab: (Use the textbook or the ScienceSaurus book) Box 1: Radiation: • Define (on the colored tab) • Draw a picture (on the white tab directly below it) Box 2: Convection: • Define (on the colored tab) • Draw a picture (on the white tab directly below it) Box 3: Conduction: • Define (on the colored tab) • Draw a picture (on the white tab directly below it) Hurricanes Tab: (Use the Weather Patterns or Hurricanes section of the packet) Box 1: Tropical Cyclone: • List the Oceans that hurricanes can form in. (There should be 4) • Describe the shape of the winds and the direction that they spin. Box 2: Conditions: • Describe the speeds and the direction (Qualitative) that winds blow when hurricanes start forming. (This is general) • List the latitudes that hurricanes form between. • Describe the surface temperature and how deep those temperatures extend when hurricanes form. • Describe the characteristics of the lower atmosphere when hurricanes form. Box 3: Formation: • Describe the air mass’ properties (temperature and humidity) and where it acquires those properties. • Describe the wind direction (qualitative). • Describe what happens to the air (hint: sounds a lot like cloud formation). • Describe the wind direction above the storm. Box 4: Movement: • Describe the direction that the hurricanes turn in regards to the equator. Air Masses Tab: (use What is an Air Mass – Ch.26 packet) Box 1: Humidity (Global Winds packet, Moisture in the Air section) • Define • What type of tool is used to measure humidity • Discuss what affects the density of the air (hint: look at your definition of density) • Discuss how air temperature affects the density of air. Box 2: Air Mass • Define Box 3: Formation • What are the characteristics that indicate how an air mass will form? • Define Air mass Formation (this is not in your notes or book, this is in your head – use the definition of air mass and the information from the first bullet in this box. Box 4: Location At the following locations, describe the air masses temperature at the locations indicated. • Equator • Polar Region Of the following air mass origins, describe its formal name and the amount of humidity that area has. • Land • Water Box 5: Labels What are the 2 types of air masses and describe where they form. Box 6: Classification Write what each abbreviation stands for • mT • cT • mP • cP • cA (hint: think of where Santa lives) Box 7: Characteristics Describe the following air masses in terms of temperature and moisture content. • mT • cT • mP • cP • cA Box 8: Convection • Define a convection current • Describe how a convection current moves. • What 2 types of currents does a convection current form? • Describe what happens to air as density increases and decreases. Global Winds (Tab #1) Box 1: Wind: • Define Box 2: What Causes Wind: • Uneven heating causes…. • Where is the Sun’s Energy more concentrated on Earth? • At the Equator, warm air is _______ dense and has ________pressure. • At the Poles, cold air is _______ dense and has ________pressure. • What kind of currents cause wind? (These kind of currents drive everything on Earth.) • How does air pressure move? (low to high or high to low) Box 3: Global Convection Currents: • When density changes as a result of temperature changes, _______ cells are created. (These kind of currents drive everything on Earth.) • Global Convection Currents cause ______________ pattern of air that circulate over the whole global pattern. Box 4: Global Wind Belts: • Where the Convection Cells meet, ___________winds and ______Streams form. • Global Wind Belts blow from ______________ (Julio’s Fav band) over a certain area of the Earth’s surface • The winds from the _______ blow toward the __________ (really hot belt on the Earth.) • The winds from the Equator blow towards ___________(where Santa lives.) Global Winds (Tab #2) Box 5: Jet Stream – Use the Winds Packet • Define • Describe where it forms • Describe the temperature & the wind speed. • The Polar Jet dips ____________(which direction) when _________ (describe how cold the wind is) polar air masses move _______ (direction). They tend to stay North in the summer months. Box 6: Prevailing Winds (Use the What Causes Climate section) • Define o Define Polar Easterlies o Define Westerlies o Define Easterlies (Trade Winds) • Pressure belts form in between _________ belts. (what are we studying?) Box 7: Coriolus Effect (Use the Global Winds Packet) • Define • Describe the wind direction in the Northern Hemisphere • Describe the wind direction in the Southern Hemisphere • Draw Fig 1-15 pg. 24 Box 8: Equilibrium • Write “Our Earth is always seeking balance.” • Write “In an effort to find balance, there is a continuous cycle of patterns.” Ocean Currents (Tab #1) – Use the Weather Folder Info. Box 1: Ocean Currents • Describe the direction that warm currents flow. • Describe the direction that cold currents flow. Box 2: Factors Influencing Currents: • Sun: Describe what type of currents the Sun creates. • Wind: Describe the gradient that winds flow. Describe what is created when wind blows across the surface of the water. Water piles up because _____ _______ flows _____ (speed – qualitatively) than the wind blows. • Gravity: Water piles up because _____ _______ pulls it down in a _____ (horizontal or vertical) direction. Describe what major Earth System causes water to curve. • Coriolis Effect: Describe what happens in the Northern Hemisphere. Describe what happens in the Southern Hemisphere. • Continental Deflection: Describe what happens to the ocean currents in regards to the continents (land masses). Box 3: Surface Currents: • Describe the percentage of the ocean that surface currents make up. • Describe the depth (in meters) of surface currents. • Describe what causes surface currents. Box 4: Gyres: • Define • Describe what they produce (in terms in currents) • Describe the 5 locations that Gyres occur in and the direction that they turn (clockwise or counter-clockwise) Ocean Currents (Tab #2) – Use the Weather Folder Info. Box 1: Gulf Stream • Describe its strength in terms of surface currents. • Describe where (the state) the Gulf Stream begins. • Describe that it where it flows before it crosses the Atlantic Ocean. • What ocean does it cross? • Describe the kind of climate does it cause in NW Europe. Box 2: Great Ocean Conveyor Belt • Write “Helps maintain Earth’s balance.” • What type of current regulates the climates. Box 3: Upwelling • Define. Box 4: Deep Water Currents • Describe the percentage of the ocean that surface currents make up. • Describe what causes Deep Water Currents. • Write “Differences in _______ (same thing that causes Deep Water Currents) are related to temperature and ____________.” • Describe what happens to Deep Water Currents at high latitudes. • Describe what happens to density and temperature of Deep Water Currents. Atmospheric Movement Tab– Use the Winds Packet and/or What Happens When Air masses Meet? – Ch. 27 and What Are Some Other Kinds of Fronts? – Ch. 28 and/or pages 37-40 in the Weather Folder. Box 1: Fronts • Define Box 2: Land Breeze • Define • Draw a land breeze and number where the wind starts throughout its circular pattern. Box 3: Sea Breeze • Define • Draw a land breeze and number where the wind starts throughout its circular pattern. Box 4: Cold Front • Define • Describe qualitatively the speed of the storm and what the weather will be like. • Describe qualitatively the temperature at the boundary compared to the rest of the air mass. • What type of weather will occur after the Cold Front comes through and what type of pressure will result. Box 5: Warm Front • Define • Describe qualitatively the speed of the storm and what the weather will be like. • Describe qualitatively the temperature at the boundary compared to the rest of the air mass. Box 6: Stationary Front • Define • Describe the length of time it remains in an area. • What type of weather will occur after the Cold Front comes through and what type of pressure will result. Box 7: Occluded Front • Define • What type of weather will occur after the Cold Front comes through and what type of pressure will result. Weather Maps Symbols Tab – Use the “Predicting the Weather” section. Box 1: Weather Maps • Define (You will need to use your definition of weather and maps to come up with this definition) • Define Isotherm • Define Isobar Box 2: High Pressure • What symbol is used to show high pressure? • Describe the air temperature qualitatively and the density of the air in regards to where it is located to the Earth’s surface. • Describe the direction the winds flow. Draw Arrows showing their pattern of movement. • What type of weather will occur after the High Pressure Cell comes through. • Describe the gradient (the increase/decrease or movement that characterizes what you are describing) that a High Pressure Cell moves to. Box 3: Low Pressure • What symbol is used to show Low pressure? • Describe the air temperature qualitatively and the density of the air in regards to where it is located to the Earth’s surface. • Describe the direction the winds flow. Draw Arrows showing their pattern of movement. • What type of weather will occur after the Low Pressure Cell comes through. • Describe the gradient (the increase/decrease or movement that characterizes what you are describing) that a Low Pressure Cell moves to. Box 4: Cold Front • Draw the symbol used to indicate Cold Fronts. Color it with a blue colored pencil. Draw the arrow in the direction that the wind moves. Box 5: Warm Front • Draw the symbol used to indicate Warm Fronts. Color it with a red colored pencil. Draw the arrow in the direction that the wind moves. Box 6: Stationary Front • Draw the symbol used to indicate Stationary Fronts. Color it with red and blue colored pencils. Draw arrows in the direction that the winds are moving. Box 7: Occluded Front • Draw the symbol used to indicate Occluded Fronts. Color it with a purple colored pencil. Draw an arrow in the direction that the wind moves. El Niño/ La Niña Tab – Use the “Predicting the Weather” section and the El Niño/ La Niño handout. Box 1: El Niño • Describe the water surface temperature that occurs and where (in relation to a continent) this occurs. • Describe the type of weather patterns that is globally causes. • Describe the wind patterns when El Niño begins. Describe what happens to the water, include qualitative descriptions of the temperature and quantitative descriptions of the direction and what continents it moves towards. • Write “It changes where the convection current occurs.” • Describe the unusual weather patterns that might occur as a result. Box 2: La Niña • Describe the water surface temperature that occurs and where (in relation to a continent) this occurs. • Describe the unusual weather patterns that might occur as a result.