* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download vegetative organs - NWIC Blogs
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
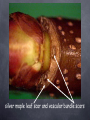
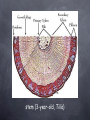
Welcome to Northwest Plants Northwest Indian College ENVS 201 Spring Quarter 2012 Plant Parts vegetative organs: reproductive components: stems flowers roots fruits leaves seeds Today: Stems Stem Features & Functions above ground axis of vascular plants, as well as anatomically similar below ground portions (e.g., rhizomes, bulbs & corms) trunks & branches are stems may be photosynthetic (e.g., cacti) may store food (in some species) etc. Stem Regions & Other Features node (region where leaves may be borne) internode (region between nodes) apical (or terminal) bud (at tip of stem) axillary (or lateral) bud (in axil, on side of stem) flower bud bud scale & bud scale scar epidermis, bark lenticels (in some species, also in some roots, fruits, etc.) leafy branch (silver maple), showing nodes, internodes and buds) apical (terminal) bud silver maple with buds lateral buds flower buds (silver maple) stems of silver maple with bud scales, bud scale scars, bark & lenticels Stem Features Associated with Leaves leaf scar (site of leaf abscission) vascular bundle scar stipular spine (in some species, e.g., black locust) silver maple leaf scar and vascular bundle scars black locust stipular spines Stem Modifications stolon (runner) - aerial, horizontal, often root at nodes (e.g., strawberry) rhizome - +/- horizontal, underground (e.g., bamboo, irises, ferns) tuber - end of underground stem, fleshy, food storage (e.g., potato) corm - shortened, usu. below ground, enclosed by dry scalelike leaves (e.g., gladiolus) stolon (Fragaria, strawberry) rhizome (Polypodium, fern) tuber (Solanum, potato) corm (Gladiolus) Stem Modifications (continued) bulb - short, underground stem with fleshy leaf bases (e.g., onion) cladophyll (also: cladode, phylloclad) - leaflike stem (e.g., cactus) tendril - long, slender, coiling stem (e.g., grape) in climbing plants (or a leaf or other structure in other species) thorn - hard, sharp-pointed, modified branch (e.g., honey locust) prickle - sharp-pointed superficial outgrowth (e.g., Rubus) spur (spur branch/shoot, or short shoot) - short stem on a branch with very short internodes (e.g., ginkgo) bulb (Allium, onion) cladophyll (Opuntia, prickly pear) tendril (Vitis, grape) thorn (Gleditsia, honey locust) prickle (Rubus) Ginkgo spur branch or shoot Betula (birch) Stem Anatomy—Lateral Meristems vascular cambium - thin region of cells that give rise to (secondary) xylem, (secondary phloem) and parenchyma cork cambium (phellogen) - thin region of cells that give rise to phellum (cork) outwardly and phelloderm inwardly cambial zone—> vascular cambium (Tilia) <—cambial region cork cambium (Tilia) Stem Anatomy— Tissues xylem (wood) - main water- & mineraltransporting tissue (in vascular plants) phloem - main food-conducting tissue (in vascular plants) periderm (bark) everything outside vascular cambium: phelloderm, phellogen & phellum (bark sometimes said to also include secondary phloem) Stem Anatomy— Cultural Considerations “sap” - edible region from vascular cambium outward, including cambial cells, phloem and possibly some phelloderm (inner layer of the bark); mainly the softest parts (e.g., of cottonwood) “inner bark” - region possibly as described above (e.g., of red cedar) stem (3-year-old, Tilia) Questions & Comments? Stems are cool. Hy’shqe!