* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Transferring Thermal Energy
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
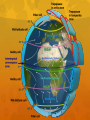
Transferring Thermal Energy Physical and Geo Content Before the video… Get out a sheet of paper. Write an example of each type of thermal energy transfer discussed in the video. Bill Nye Clip After the video Draw a diagram of each type of thermal energy transfer that you listed from the video. Include the heat source, where it is going, and what it is heating up. Thermal Energy Thermal Energy: sum of the kinetic and potential energy of all the molecules in an object Thermal Energy increases as temperature increases Heat is thermal energy that flows from high temperatures to low temperatures How is thermal energy transferred? Three Mechanisms Conduction Convection Radiation Conduction Transfer of thermal energy through matter by the direct contact of particles Ex: Holding snow/ice in your hand Holding a cup of coffee Convection Transfer of energy by the motion of heated particles in a fluid Energetic particles move from one spot to another, carrying energy with them Fluid expands as temperature increases What does this imply about the density? Convection currents are a rising and sinking action Convection Examples Lava Lamp Convection Currents on Earth Global Circulation Video Overall, the Sun heats the surface of the Earth, and Earth radiates back to space about as much energy as it receives over the course of a year. (300) Day vs. Night, Poles vs. Tropics Balancing the budget! (301) Tropics and other places maintain fairly constant average temps bec heat energy is redistributed around the world. The continual motion of air and water reallocates heat energy among Earth’s surface, oceans, and atmosphere and brings it into balance. Energy Transfer in Atmosphere: Global Wind Systems (305-6) and refer to video http://www.mhhe.com/biosci/genbio/tlw3/eBrid ge/Chp29/animations/ch29/global_wind_circulat ion.swf Wind (282) – air moves in response to density imbalances created by the unequal heating and cooling of Earth’s surface, works like air conditioned building, H L Air Masses (303) – large body of air that takes on characteristics of the area over which it forms, cP cT mP mT, air masses move transferring heat from one area to another to establish heat balance Salinity Graph Thermocline Energy Transfer in Oceans: Vertically – Water Masses (397-8) – sea ice forms, salt ions are left, cold salty water becomes denser and sinks, (H – density current) arctic, salty water migrates toward the equator along the ocean floor Upwelling (405) – upward motion of ocean water, water originates from the bottom of the ocean and are cold, surface water is displaced by winds and replaced by upwelling deep water, waters are rich in nutrients which support marine life Energy Transfer in Oceans: Horizontally – Density currents - arctic, salty water migrates toward the equator along the ocean floor, move slowly in deep ocean waters (403) Surface currents – wind driven and follow wind patterns, relatively salty midlatitude / subtropical water carried into polar regions and become colder and denser and sink (403) Gyres – closed, circular current systems, five major ones, northern hemisphere = clockwise, southern hemisphere = counterclockwise --Read page 404 and view the figure Gyres Radiation Transfer of energy by electromagnetic waves Travel through space regardless of matter being present or not AKA radiant energy Ex: Standing by a fire to warm your hands Sun heating the Earth Radiation In a solid, liquid, or gas radiant energy can travel through the space between molecules Molecules absorb the radiation, and re- radiate some of the absorbed energy Solids and liquids, molecules are much closer, causing them to collide more often This means gases absorb less radiant energy, and transmit more, than solids and liquids Controlling Heat Flow Insulators A material that does not allow the flow of heat Wood, plastic, and fiberglass Some insulators contain trapped air pockets which are poor conductors of heat Fleece jackets Building insulation