* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Potential Difference - White Plains Public Schools
Speed of gravity wikipedia , lookup
Introduction to gauge theory wikipedia , lookup
Anti-gravity wikipedia , lookup
Gibbs free energy wikipedia , lookup
Work (physics) wikipedia , lookup
Internal energy wikipedia , lookup
Conservation of energy wikipedia , lookup
Aharonov–Bohm effect wikipedia , lookup
Electric charge wikipedia , lookup
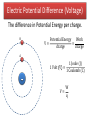
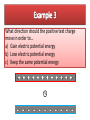
Potential Difference SWBAT calculate the potential difference of a charge in a position in space. 1) 4 2) 2 3) 3 4) 2 5) 1 6) 2 7) 4 8) 4 9) 1 The force felt by a specific object due to it’s mass and the gravitational field strength. Fg = mg Gravitational Field Strength The force per kg of any object in a specific position due to a gravitational field. Fg g= m The potential energy possessed by a specific object due to it’s mass and position. GPE = mgh Gravitational Potential The potential energy per kg of any object in a specific position. GPE W Gravitational Potential = or m m The potential energy possessed by a specific object due to it’s position and charge. 𝑃𝐸𝑒 = qEd The potential energy per Coulomb of any object in a specific position. 𝑃𝐸𝑒 W Electric Potential = or q q B A + + It takes work to move the charge from A to B. This work equals the change in electric potential energy of the charge. The electric potential is higher at point B than point A. A B + + It takes work to move the charge from A to B. This work equals the change in electric potential energy of the charge. The electric potential is higher at point B than point A. Definition: The stored ability to do work per coulomb of charge at a specific point in a field. Unit: Joules/Coulomb (J/C) or Volts (V) Formula: W V= q Work Voltage = charge Electric Potential Difference (Voltage) The difference in Potential Energy per charge. B A + + Potential Energy Work V= = charge charge 1 Joule (J) 1 Volt V = 1 Coulomb (C) W V= q It takes 6 Joules of energy to move 3 Coulombs of charge from position A to position B. What is the potential difference between these two points? B A + + It takes 3.2x10-18 Joules of energy to move a proton from position A to position B. What is the potential difference between these two points? A B + + What direction should the positive test charge move in order to… a) Gain electric potential energy b) Lose electric potential energy c) Keep the same potential energy +q0 The Voltage of a standard household electrical outlet in the US is 120V. If 5C of charge moves from one wire of the outlet to the other, how much energy is released?