* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download CHAPTER 5 CIRCULATION
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
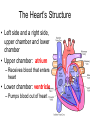
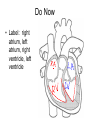
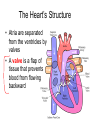
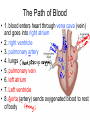
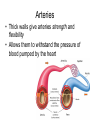
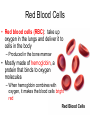
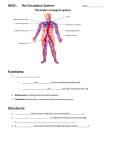
Do Now • What is the strongest muscle in your body? CHAPTER 5 CIRCULATION Miss Sabia https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=EtLKuUdMk5I Standards • 1.2f-circulatory system moves materials from one cell to another, responding to changing demands • 1.2j-disease??? • LE Skill #8-ID pulse points and pulse rates Chapter Project • Write a story from the point of view of a red blood cell as it travels through the body. Section 1 THE BODY’S TRANSPORTATION SYSTEM Essential Question • 1. What is the function of the cardiovascular system? • 2. What is the path taken by red blood cells in the body? Cardiovascular System • The cardiovascular system, or circulatory system, carries needed substances to cells and carries waste away from cells. • Composed of: – Heart – Blood vessels (veins & arteries) – blood Movement of Materials • Needed materials: – Oxygen – Glucose – Nutrients (from digestion) • Waste materials: – Carbon dioxide The Heart • The heart is a hollow, muscular organ that pumps blood throughout the body • Each time it pumps, it pushes blood through the blood vessels The Heart’s Structure • Left side and a right side, upper chamber and lower chamber • Upper chamber: atrium – Receives blood that enters heart • Lower chamber: ventricle – Pumps blood out of heart Do Now • Label: right atrium, left atrium, right ventricle, left ventricle The Heart’s Structure • Atria are separated from the ventricles by valves • A valve is a flap of tissue that prevents blood from flowing backward How the Heart Works • Contract—pumps blood forward • Relax—heart fills with blood • A heartbeat (lub-dub) is heard during the pumping phase – Lub—valves close between ventricles and atria – Dub—valves close between ventricles and blood vessels Blood Vessels • Arteries: blood vessels that carry blood away from the heart • Veins: blood vessels that carry blood back to the heart • Capillaries: tiny vessels where substances are exchanged between the blood and body cells (located between veins and arteries) The Path of Blood • 1. blood enters heart through vena cava (vein) and goes into right atrium • 2. right ventricle • 3. pulmonary artery • 4. lungs • 5. pulmonary vein • 6. left atrium • 7. Left ventricle • 8. Aorta (artery) sends oxygenated blood to rest of body Section 2 A CLOSER LOOK AT BLOOD VESSELS Essential Question • How do the structures of the different blood vessels aid in their functions? Arteries • Thick walls give arteries strength and flexibility • Allows them to withstand the pressure of blood pumped by the heart Veins • Thinner walls than arteries – don’t need to withstand as much pressure, because they are not receiving blood directly from the heart • Blood flows through veins by… – Contraction of nearby muscles helps push blood along in veins – Contain valves that prevent backflow of blood – Breathing movements force blood towards the heart (squeezing pressure) Capillaries • Recall… – Capillaries: tiny vessels where substances are exchanged between the blood and body cells (located between veins and arteries) • Blood Cells: – Oxygen – Glucose • Cells Blood: – Cellular waste Pulse • You can feel your pulse on the inside of your wrist or on your neck • Caused by expansion and relaxation of the artery wall Section 3 BLOOD AND LYMPH Red Blood Cells • Red blood cells (RBC): take up oxygen in the lungs and deliver it to cells in the body – Produced in the bone marrow • Mostly made of hemoglobin, a protein that binds to oxygen molecules – When hemoglobin combines with oxygen, it makes the blood cells bright red White Blood Cells • White blood cells (WBC): fight disease – Some recognize disease-causing agents – Some produce chemicals to fight the invaders – Some surround and engulf (and kill) the invaders