* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Unit 5 Study Guide Key
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
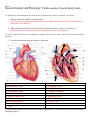
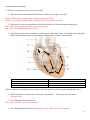
Name _____________________________________________ Honors Anatomy and Physiology Cardiovascular System Study Guide 5.1 Explain the relationship between the structure and function of arteries, capillaries, and veins. 1. Why do arteries have thicker walls than veins? They have thicker walls because the blood pressure is higher in arteries as they deliver blood from the heart to the rest of the body. 2. What would be the difference between blood leaving from an artery versus a vein when cut? Blood from an artery would rush out (fast) but blood from a vein would drip/slow. 5.2 Label a diagram of the heart, including the chambers, blood vessels, valves, and the route of blood through the heart. 1. Label the external and internal structures of the heart. A:Superior Vena Cava B: Pulmonary Vein C:Aortic arch D: Pulmonary Trunk E: Pulmonary Vein F:Inferior Vena Cava G: Aorta H: Pulmonary Artery I: Pulmonary Vein J: Apex K: Right Atria L: Tricuspid Valve M: Right Ventricle N: Chordae Tendineae O: Left Atria P: Pulmonic Valve Q: Mitral Valve R: Aortic Valve S: Left Ventricle **On the internal diagram above, draw arrows with a colored pencil or crayon that show the path of the blood through the heart.** Circulatory System Study Guide 5.3 Outline the mechanisms that control the heartbeat 1. What are systolic and diastolic blood pressure? Which one is higher, and why? Systolic- High number, pressure when ventricles contract (pumping) Diastolic- Low number, pressure when ventricles relax (so the pressure is lower) 2. What activity or process causes heart sounds (the lub-dub you can hear through a stethoscope)? Lub- Closing of bicuspid/tricuspid (Atrioventricular) valves. Dub- aortic valve and pulmonic valve closing 3. Label the parts of the heart’s intrinsic electrical system on the figure below. Word bank: Atrioventricular bundle, atrioventricular node, bundle branches, Purkinje fibers, septum, sinoatrial node A Sinoatrial Node B Atrioventricular Node C Bundle branches D Purkinje Fibers E Bundle Branches F Purkinje Fiber G Septum **With a crayon or colored pencil, draw arrows to show the path of electrical impulses through the heart** 4. Which of the above structures acts as the heart’s “pacemaker”? You can just write the name. Sinoatrial Node 5. List 3 things that increase heart rate. Fear, exercise, sickness, stress, hot temperature, 6. List 3 things that decrease heart rate. Digestion, sleep, medication, cold temperature, 2 Circulatory System Study Guide 5.4 Differentiate the formed elements and define their function 1. Label the following components: Platelet, Red Blood Cell, White Blood Cell 2. __Red Blood Cells___ are essentially bags of hemoglobin and carry ___Oxygen___ from the lungs to the rest of the body 3. _____White Blood Cells_______ are blood cells that are a part of the immune system. They fight pathogens and cancers. 4. ____Platelets_____ are non-cellular blood components that clot together to stop bleeding. 5.5 Investigate and describe ABO and Rh blood groups 1. Based on the results of blood typing agglutination reactions below, what are the blood types of the individuals? Add your answer to the column labeled “Blood Type” in the table below. A filled in circle indicates a positive reaction (clumping). Anti-A Anti-B Anti-Rh Blood Type Antigen Present Antibody Present AB- AB None A+ A, Rh B antibody B- B A antibody O+ Rh A & B antibodies Fill in the blank. 2. Blood types are determined by the presence of protein located on which blood cells? Red Blood Cell 3. Blood type AB+ is considered to be the universal recipient 4. If a person has type A– blood, then they have which proteins? (A antigens) & (B antibodies) 3 Circulatory System Study Guide Complete the following: 1. Diagram how the blood flows through the body. Start with the oxygenated blood entering the left atrium and end with it returning. This can be done through words, pictures, or diagrams. Left Atrium-> Bicuspid (mitral) valve-> Left Ventricle -> Aortic Valve-> Aorta-> Body-> Vena Cava>Right Atrium-> Tricuspid Valve->Right Ventricle-> Pulmonic Valve-> Pulmonary Artery-> Lungs-> Pulmonary Veins-> Left Atrium 2. Describe each of the disease types: Blood Plasma disease, Red Blood Cell disease, Blood Clotting disease, and White Blood Cell disease. Blood Plasma- Problems with parts of the blood other than RBC/WBC. Usually a problem with platelets or antibodies attacking the blood in the body. Red Blood Cell- Problems with the shape of the RBC that cause anemia. Prevents proper oxygen circulation throughout the body. Blood Clot- Problems with the platelets in the body that cause a buildup of clots in the system. Can lead to strokes. White Blood Cell- Usually cancer related, cause too many or too little WBCs. Leads to problems with the immune system. 4