* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download DC Fundamentals, 9-2 - Lab-Volt
Transistor–transistor logic wikipedia , lookup
Immunity-aware programming wikipedia , lookup
Index of electronics articles wikipedia , lookup
Integrating ADC wikipedia , lookup
Flexible electronics wikipedia , lookup
Integrated circuit wikipedia , lookup
Power electronics wikipedia , lookup
Josephson voltage standard wikipedia , lookup
Regenerative circuit wikipedia , lookup
Valve RF amplifier wikipedia , lookup
Electrical ballast wikipedia , lookup
Operational amplifier wikipedia , lookup
Switched-mode power supply wikipedia , lookup
Voltage regulator wikipedia , lookup
Power MOSFET wikipedia , lookup
Current source wikipedia , lookup
Current mirror wikipedia , lookup
Resistive opto-isolator wikipedia , lookup
Rectiverter wikipedia , lookup
Schmitt trigger wikipedia , lookup
Surge protector wikipedia , lookup
Opto-isolator wikipedia , lookup
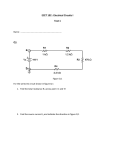
DC Fundamentals Series/Parallel Resistive Circuits Exercise 2: Voltage in a Series/Parallel Circuit EXERCISE OBJECTIVE Ohm’s law. You will verify your results with a multimeter. DISCUSSION In a series/parallel circuit, voltage across each circuit branch is distributed in proportion to the resistive value of each branch. In this circuit, the applied voltage equals the voltage across R1 plus the voltage across the parallel branch (R2 or R3). In this circuit, the voltage across R2 (VR2) equals a. VR3. b. VR1. c. VA. In this circuit, IT R1 = IT x R1 or IR1 x R1. We may use the value of IT for IR1 because the amount of current through any series element of the circuit is identical to the total current of the circuit. Student Manual FACET by Lab-Volt 183 Series/Parallel Resistive Circuits DC Fundamentals a. VA = VR3 + VBC b. VA = VR1 + VR2 c. VA = VR1 + VR2 + VBC PROCEDURE Locate the SERIES/PARALLEL CIRCUIT circuit block, and connect the circuit shown. Measure the value of the circuit source voltage. VA = Vdc (Recall Value 1) Student Manual 184 FACET by Lab-Volt DC Fundamentals Measure the voltage drop of R1. VR1 = Vdc (Recall Value 2) Measure the voltage drop of R2. VR2 = Series/Parallel Resistive Circuits Vdc (Recall Value 3) Measure the voltage drop of R3. VR3 = Vdc (Recall Value 4) Student Manual FACET by Lab-Volt 185 Series/Parallel Resistive Circuits DC Fundamentals Based on your data recalled below, which statement properly relates the voltage drops of your circuit? a. The voltage drops are not related because of the series/parallel combination. b. The voltage drop of R1 indicates a circuit problem because its value is not equal to that of VR2 or VR3. c. The voltage drops are correct because the sum of the series and parallel combination voltage drops equals VA. VA = Vdc (Step2, Recall Value 1) VR1 = Vdc (Step3, Recall Value 2) VR2 = Vdc (Step4, Recall Value 3) VR3 = Vdc (Step5, Recall Value 4) To calculate the voltage drop of R1, a. multiply either IR2 or IR3 with the value of R1. b. subtract the sum of VR1 and VR2 from VA. c. multiply IT by the value of R1. Place CM switch 12 in the ON position to put R4 in the circuit. What is the relationship of the circuit voltages with resistor R4 added? a. VA = VR1 + VRE + VR4 b. VA = VR1 + VR4 c. VR1 = VR3 and VR2 = VR4 With CM 12 still in the ON position, VR4 equals a. IR4 x R4. b. IT x R4. c. (IR2 + IR3) x R4. With CM 12 still in the ON position, what are the voltage drops of R2 and R3? a. about 15 Vdc b. about 4.45 Vdc c. about 9.7 Vdc Make sure all CMs are cleared (turned off) before proceeding to the next section. Student Manual 186 FACET by Lab-Volt DC Fundamentals Series/Parallel Resistive Circuits CONCLUSION • In a series/parallel circuit, the sum of the branch voltage drops equals the source voltage of the circuit. • • In a series/parallel circuit, the voltage drops across each resistor of a parallel element are equal. REVIEW QUESTIONS 1. a. b. c. d. E = I/R E = IR E = R/I E = E/RI 2. In a series/parallel circuit consisting of three equal 5 k: resistors, the voltage drop is a. greatest across the parallel branch. b. greatest across the series branch resistor. c. equal across all the branches. d. None of the above. 3. What information do you need to calculate the voltage drop across a parallel branch of a series/ parallel circuit? a. total circuit current (IT) and equivalent resistance (RE) b. equivalent resistance (RE) c. applied voltage (VA) d. None of the above. 4. In this circuit, what would be the effect if R3 were shorted? a. VR1 would decrease. b. VR2 would increase. c. VRE would increase. d. VR1 would equal VA. 5. Locate the SERIES/ PARALLEL CIRCUIT circuit block, and connect the circuit shown above. Place a. b. c. d. A 600: resistor was placed in the parallel branch. A 1 k: resistor was placed in parallel with R1. A 2.7 k: resistor was placed in parallel with R2. A 4.7 k: resistor was placed in parallel with R3. NOTE: Make sure all CMs are cleared (turned off) before proceeding to the next section. Student Manual FACET by Lab-Volt 187