* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Lecture 7-3 Phasor Domain Analysis
Crystal radio wikipedia , lookup
Electrical engineering wikipedia , lookup
Distributed element filter wikipedia , lookup
Schmitt trigger wikipedia , lookup
Power electronics wikipedia , lookup
Mathematics of radio engineering wikipedia , lookup
Switched-mode power supply wikipedia , lookup
Opto-isolator wikipedia , lookup
Power MOSFET wikipedia , lookup
Operational amplifier wikipedia , lookup
Two-port network wikipedia , lookup
Wilson current mirror wikipedia , lookup
Resistive opto-isolator wikipedia , lookup
Valve RF amplifier wikipedia , lookup
Electronic engineering wikipedia , lookup
Surge protector wikipedia , lookup
Current source wikipedia , lookup
Rectiverter wikipedia , lookup
Current mirror wikipedia , lookup
Antenna tuner wikipedia , lookup
Standing wave ratio wikipedia , lookup
Network analysis (electrical circuits) wikipedia , lookup
Zobel network wikipedia , lookup
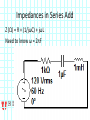
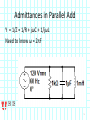
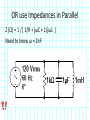
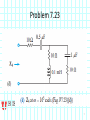
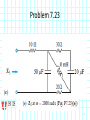
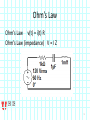
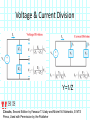
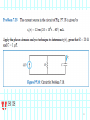
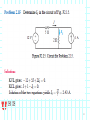
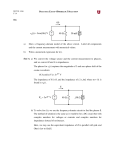
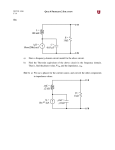
Introduction to Electrical & Computer Engineering Phasor Domain Analysis Dr. Cynthia Furse University of Utah Dr. Cynthia Furse University of Utah 1 Impedance & Phasor Domain Analysis • Impedance (Z) (ch 7-2) – Resistance R – Capacitance 1/jωC – Inductance jωL • Ohm’s Law Z = V/ I (ratio of voltage to current, including phase shifts) • Phasor Domain Analysis (ch 7-3) • Impedance Transformation (ch 7-4) 2 Impedance and Admittance Impedance is voltage/current Admittance is current/voltage R = resistance = Re(Z) X = reactance = Im(Z) G = conductance = Re(Y) B = susceptance = Im(Y) Resistor ZR Y 1/ R Inductor Z j L Y 1 / j L Z 1 / j C Y j C Capacitor Circuits, Second Edition by Fawwaz T. Ulaby and Michel M. Maharbiz, © NTS rights reserved. Do notby copythe or distribute. © 2013 National Technology and Science Press Press, Used withAllPermission Publisher Impedances in Series Add Z (Ω) = R + (1/jωC) + jωL Need to know ω = 2πF 4 Admittances in Parallel Add Y = 1/Z = 1/R + jωC + 1/jωL Need to know ω = 2πF 5 OR use Impedances in Parallel Z (Ω) = 1 / [ 1/R + jωC + 1/jωL ] Need to know ω = 2πF 6 Problem 7.23 7 Problem 7.23 8 Ohm’s Law Ohm’s Law v(t) = i(t) R Ohm’s Law (impedance) V = I Z 9 Voltage & Current Division Y=1/Z reserved.by Do not copy or distribute. © 2013 National and Science Press Circuits, SecondAll rights Edition Fawwaz T. Ulaby andTechnology Michel M. Maharbiz, © NTS Press, Used with Permission by the Publisher 11 12 13 Introduction to Electrical & Computer Engineering Antelope Island, Great Salt Lake, Utah Dr. Cynthia Furse University of Utah 14