* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download How systems work together
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
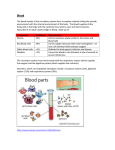
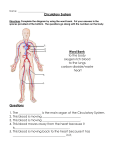
HOW SYSTEMS WORK TOGETHER LIFE SCIENCE UNIT 3 LESSON 8 Attendance Link: http://goo.gl/forms/3L8JsZBBf6 OBJECTIVES • Compare major features and functions of plant and animal systems. • Give an example of how a problem in one part of a body system can affect the entire system. All multicellular organisms have to grow, develop, move, reproduce, and function day to day. How is this done? All of the body’s systems have to work together. Let’s look to see how this is done. Code Word: Green NUTRIENTS COMING INTO THE BODY • Every cell needs oxygen. • Which system brings oxygen into the body? • The respiratory system • Which system bring food in and makes it available to cells? • The digestive system • Do plants have a digestive system? • No, plants make their own food so they don’t need a digestive system like us. HOW ARE NUTRIENTS TRANSPORTED THROUGH THE BODY? • The circulatory system! • Remember that the circulatory system is the transportation system of the body. • So, the respiratory and the digestive systems bring in the nutrients and let out waste that is carried through the body by the circulatory system. WHAT WOULD HAPPEN… • If there is damage to part of the circulatory like the heart? • If the heart is damaged, the circulatory system will not be able to move waste or nutrients around the body. • If the damage is great it could be fatal. Heart attacks damages cardiac muscle. If the muscle cannot pump the blood, other cells in the body become oxygenstarved. This can lead to brain damage. HOW ARE THE EXCRETORY AND CIRCULATORY SYSTEMS CONNECTED? • The excretory system removes waste. It gets the waste from the circulatory system via the kidneys. HOW OTHER ORGANISMS REMOVE WASTE? • Plants • Oxygen and excess water exit through the stomata of the leaves. • Fish • Carbon dioxide exits through the gills. • Amphibians • Carbon dioxide exits through the skin. THE IMMUNE SYSTEM AT WORK • Think about how bacteria and viruses enter the body. • They enter via the respiratory and digestive systems. • How do these system help out the immune system? • Sneezing, runny nose, and stomach acid help get rid of bacteria and viruses. WHEN THE IMMUNE SYSTEM GOES BAD • Sometimes the immune system attacks the body’s own cells. • The resulting immune response can cause problems in systems throughout the body. • Rheumatoid arthritis is when the immune system attacks the joints and other connective tissues in the body. • This makes movements painful and limited. • It can lead to serious joint damage and disability. WHICH SYSTEMS ARE USED WHEN WE MOVE? • The skeletal and muscular systems are two systems that are used when we move. • Does this movement help out other systems in the body? • When muscles move, they interact with the lymph nods, which are part of the immune system. WHICH SYSTEM IS THE CENTRAL CONTROL OF THE BODY? • The nervous system. • All organ systems need some kind of central control to coordinate so many functions all at once. • The information goes to the central nervous system. The system operates with great speed and efficiency. OTHER SYSTEMS • The endocrine system produces and secretes hormones that help control many of the body’s functions. • This includes growth, metabolism, sexual development, and reproduction. • The reproductive system makes it possible for an organism to pass its genes on to new organisms. The organs of this system also help produce some hormones. • Skeletal system • Provides a structural framework for the organism • Nervous system • Controls other systems and processes information • Digestive system • Takes in and breaks down food • Excretory system • Filters and gets rid of undigested food and waste products • Respiratory system • Takes in oxygen; gets rid of the carbon dioxide • Circulatory system • Transports nutrients and other materials to and from the cells • Immune system • Protects the organism against invasion from harmful substances. • Reproductive system • Muscular system • Produces new organisms • Allows the organism to move. NAME THE SYSTEM THAT TRANSPORTS NUTRIENTS TO THE CELLS OF THE BODY? •The circulatory system OUT OF THE FOLLOWING ORGAN SYSTEMS, WHICH ARE FOUND IN BOTH ANIMAL AND PLANTS? A. B. C. D. Immune system Circulatory system Digestive system Skeletal system IF THE HEART BECOMES DAMAGED OR WEAKENED, HOW WILL THIS AFFECT THE BODY’S SYSTEMS? • If the heart becomes damaged the circulatory system will not function well, which will affect all other body systems. NAME THE BODY SYSTEM PROTECTS THE BODY AGAINST INVASION BY PATHOGENS? • The immune system! WHAT IS THE REASON THAT PLANTS DON’T NEED A DIGESTIVE SYSTEM? • They use energy from the sun to make their own food. ASSIGNMENT • OLS • Master this lesson assessment in the OLS. • There are 5 questions.