* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Electronics - Deans Community High School
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
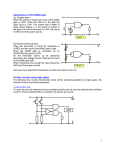
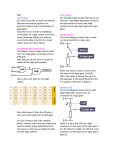
Electronics Input, process, output All electronics systems consist of three parts, the input, process and output. We can show these as a block diagram. Input Process Output It is possible to draw up a block diagram for any electronics system. Some are shown below. keypad aerial tuner, decoder, amp. speaker chip display Input devices Input devices detect some form of energy and cause a change in the electrical signal going to the process device. Microphone Changes sound energy into electrical energy. Thermistor The resistance of the thermistor changes with change in temperature. This changes the input signal to the process. LDR The resistance of the thermistor changes with change in light level. The brighter the light the smaller the resistance. This changes the input signal to the process. Switch The switch sends a signal to the process device when it is opened or closed. Examples: Input devices required Baby monitor: needs to pick up sound so microphone. Automatic night light: needs to detect light and dark so LDR. Electronic thermometer: needs to detect temperature differences so thermistor. Output Devices Output devices in electronics systems change electrical energy from the process device into some other form of energy. Loudspeaker: changes electrical energy into sound energy Buzzer [alarm]: changes electrical energy into sound energy Lamp: changes electrical energy into light energy LED: changes electrical energy into light energy Motor [in mixer]: changes electrical energy into kinetic energy Examples: Possible uses of output devices Loudspeaker: any situation where you want voice or music sounds Tannoy, public address system at railway station, Hi-Fi Buzzer : any situation where you just want to produce a noise Clock alarm, burglar alarm, warning buzzer Lamp : any situation where you want to light up an area Automatic night light, lighthouse LED : any situation where you want to indicate something is on Hi-Fi display, on/off indicator on a computer Motor : any situation you want to produce movement Food mixer, fan, vacuum cleaner Digital Logic Gates Logic gates are the basic components in many different electronics systems. It is important that you learn the names and shapes of three of the basic gates. These are shown below. AND OR NOT Digital signals can only have two values: High voltage which is usually called logic 1 Low voltage which is usually called logic 0 Logic gates are a bit like the advert for Ronseal on telly. The only difference is that they do exactly as their name says [instead of what it says on the tin] What goes in is NOT what comes out So if a logic 1 goes in a logic 1 can NOT come out, this means that a logic 0 comes out. input A input B output To get a logic 1 out, input A must be logic 1 AND input B must be logic 1. input A input B output To get a logic 1 out, input A must be logic 1 OR input B must be logic 1. Examples of logic gate systems A light that comes on automatically at night: light sensor lamp The light sensor gives a logic 0 when it gets dark. The lamp needs a logic 1 to light. The NOT gate changes the logic 0 into a logic 1 and the lamp comes on when it gets dark. An alarm for a drawer that can be switched off when required. light sensor buzzer on/off switch If the switch is on [logic 1], then opening the drawer will give another logic 1 into the AND gate. Two logic 1 inputs will give a logic 1 out and the buzzer will sound. If the switch is off [logic 0] it does not matter what the input from the light sensor is, the output cannot be logic 1 and the buzzer will not sound. A warning system if it is hot or dark: light sensor buzzer temp. sensor If it is dark the light sensor will give out a logic 0. The NOT gate will change this to a logic 1. If it is hot the temp. sensor will give out a logic 1. If either input to the OR gate is logic 1 the output will go to logic 1 and the buzzer will sound. Learning Outcomes An electronic system has 3 parts InputProcessOutput Draw and recognise block diagrams of electronic systems. keypad chip display Calculator Input devices change a form of energy into electrical energy microphone Input devices can change the size of the input voltage. Thermistor, LDR, Switch The resistance of a thermistor changes with changes in temperature The resistance of an LDR reduces as the light level increases You should be able to choose an appropriate input device for a given situation An output device changes electrical energy into another useful energy A loudspeaker, buzzer, lamp, LED and electric motor are all output devices. Know the energy changes: electrical loudspeaker sound buzzer sound lamp light LED light electric motor kinetic You should be able to choose an appropriate output device for a given situation Digital Logic Gates You should be able to draw the symbol for a NOT, an AND and an OR gate. There are only two possible values for logic gate input and output High voltage is the same as a logic 1 Low voltage is the same as a logic 0 The output from a NOT gate is the opposite of the input The output from an AND gate is only logic 1 when both inputs are logic 1 The output from an OR gate is logic 1 if either input is logic 1 You should be able to explain how simple logic gate circuits work. You should be able to design simple logic gate circuits for given situations. Questions 1. Draw a block diagram showing the three parts of an electronics system. 2. The list below gives three input devices. Copy and complete the sentences. (a) A microphone is affected by changes in ___________ level. (b) A thermistor is affected by changes in ___________ level. (c) An LDR is affected by changes in ___________ level. 3. The list below gives three output devices. Copy and complete the sentences. (a) A ____________ changes electrical energy to kinetic energy. (b) A ____________ changes electrical energy to light energy. (c) A ____________ changes electrical energy to sound energy. 4. Which input device would be used for the following applications: (a) A frost warning device for a gardener. (b) An early morning sunrise alarm for a keen angler. (c) A mobile phone. 5. Which output device would be used for the following applications: (a) A frost warning device for a gardener. (b) An on/off indicator for a computer. (c) Automatic curtain closer. (d) A security light for a driveway 6. Draw the symbols for a NOT, an AND and an OR gate 7. Copy the diagrams below and state the missing signal for each one. logic 0 logic 1 logic 1 logic 1 logic 1 logic 1 logic 0 logic 0 logic 0 logic 1 8. A keen angler who wanted to know when it was light in the morning and warm enough to go fishing set up the following system. light sensor buzzer gate A temperature sensor The light sensor gives a logic 1[‘high’] when light and a logic 0 [‘low’] when dark. The temp. sensor gives a logic 1[‘high’] when warm and a logic 0 [‘low’] when cold. (a) What gate would have to be used for this circuit to work? (b) Explain why did you chose this gate. (c) What change would have to be made to the circuit if the angler wanted to fish when it was light and cold?