* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Completeness
Voltage optimisation wikipedia , lookup
Flip-flop (electronics) wikipedia , lookup
Power inverter wikipedia , lookup
Mains electricity wikipedia , lookup
Solar micro-inverter wikipedia , lookup
Switched-mode power supply wikipedia , lookup
Buck converter wikipedia , lookup
Opto-isolator wikipedia , lookup
Control system wikipedia , lookup
Curry–Howard correspondence wikipedia , lookup
3. Logic Gate
• 3.1 Introduction
static, fully complementary CMOS
psudo-nMOS, domino logic
• 3.2 Combinational Logic Functions
combinational logic ---- specification
expression
logic gate networks ---- implementation
area, delay, power ---- costs
literal
[Completeness]
•Function {|}=NAND function: complete
•1:
a|(a|a) = a|a’ = 1
•0:
{a|(a|a}|{a|(a|a)} = 1|1 = 0.
•a’:
a|a = a’.
•ab:
(a|b)|(a|b) = ab
•a+b:
(a|a)|(b|b) = a’|b’=a+b
•NOR function: complete
•AND and OR function: not complete
[Irredundant] no literal can be removed.
redundant Ab+ab’=a
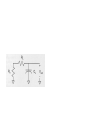
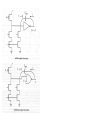
3.3 Static Complementary Gates
3.3.1 Gate Structure
VDD
Pullup network (pMOS)
•output is connected to VDD
Pulldown network (nMOS)
•Output is connected to VSS
VSS
CMOS NAND
VDD
Pullup network (pMOS)
•output is connected to VDD
when ab=0.
Pulldown network (nMOS)
•Output is connected to VSS
when ab=1.
VSS
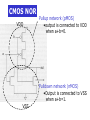
CMOS NOR
VDD
Pullup network (pMOS)
•output is connected to VDD
when a+b=0.
Pulldown network (nMOS)
•Output is connected to VSS
when a+b=1.
VSS
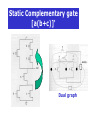
Static Complementary gate
[a(b+c)]’
Dual graph
And Or Inverter (AOI) gate
(ab+c)’
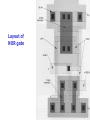
3.3.2 Basic Gate Layouts
Layout of
Inverter
Layout of
NAND gate
Layout of
NOR gate
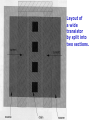
Layout of
a wide
transistor
by split into
two sections.
3.3.3 Logic Levels
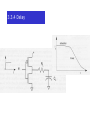
VOH: minimum voltage output for logic 1.
VOL: maximum voltage output for logic 0.
VIH: minimum voltage input
for logic 1.
VIL: maximum voltage input
for logic 0.
VOL < VIL
VOH > VIH
Minimum size
transistors
VOH
Noise Margin
NML = VIL-VOL
NMH = VOH-VIH
VIH
VOL
VIL
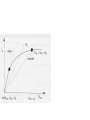
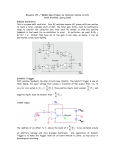
3.3.4 Delay
3.3.5 Power Consumption
3.3.6 The Speed-Power Product
• Speed-power product
= power-delay product
SP=(1/f)P=CV2
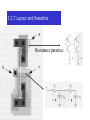
3.3.7 Layout and Parasitics
Resistance parastics
3.3.8 Driving Large Loads
Alpha=(Cbig/Cg)(1/n)
Ttot =
Nopt=
3.4 Wires and Delay
3.4.1 Elmore Delay Model
Delta1=r1 x (C1+---+Cn) =n rc
Delta2=r2 x (C2+----+Cn) =(n-1)rc
DeltaN=rn x Cn
=rc
total=Delta1+ ----- + DeltaN
=n(n+1)/2 x rc
3.4.2 Wire Sizing
Optimum-shaped wire
3.4.3 RC Trees
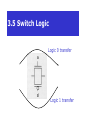
3.5 Switch Logic
Logic 0 transfer
Logic 1 transfer
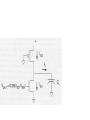
3.6 Alternative Gate Cirucits
3.6.1 Pseudo-nMOS Logic
3.6.2 DCVS (Differential Cascaded voltages
switch logic) Logic
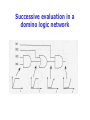
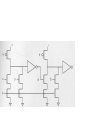
3.6.3 Domino Logic
Successive evaluation in a
domino logic network
Charge sharing