* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Circulatory System - Mahtomedi Middle School
Blood transfusion wikipedia , lookup
Autotransfusion wikipedia , lookup
Schmerber v. California wikipedia , lookup
Blood donation wikipedia , lookup
Plateletpheresis wikipedia , lookup
Jehovah's Witnesses and blood transfusions wikipedia , lookup
Men who have sex with men blood donor controversy wikipedia , lookup
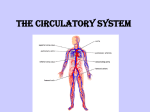
The Circulatory System Chapter 16 Blood moves like this. . . . Right side of the heart Lungs (here it gets oxygen) Left side of the heart Body (here it drops off the oxygen) Cardiovascular System Also called the Circulatory System Made up of: Heart Blood Blood vessels How Do Blood and Air Travel? Blood is liquid tissue. The heart is the main organ that makes up the circulatory system. You’re not writing anything from this slide. It is the job of the Circulatory System to move blood through blood vessels to the body’s cells. You’re not writing anything from this slide. Blood Carries these things to your body’s cells… Food Oxygen Water Interesting Facts…..(no you don’t have to write this)… Sponges and cnidarians don’t have a circulatory system. Insects and other invertebrates have open circulatory systems. Each time the heart beats… It pushes blood through the blood vessels of the cardiovascular system Upper Chambers Left and right atrium There are two Their job is to receive blood that comes from the body Lower Chambers •Left and right ventricle •There are two •Their job is to pump blood out of the heart More Parts of the Heart VALVES – flaps of tissue that prevent blood from flowing backward PACEMAKER – group of cells that adjusts the speed of the heart beat Found in the right atrium When blood flows through the heart, the force that pushes blood out of the heart and into the arteries is . . . the contraction of the ventricles Two Loops The three kinds of blood vessels are: Veins Arteries Capillaries What about the capillaries? •This is what connects the arteries and the veins. It is where diffusion happens. •Remember diffusion??? The movement of molecules from more to less We’ll talk about this more later. crowed areas. Pathway of non-oxygenated blood Blood without oxygen enters the : Vena Cava → Right atrium → Tricuspid Valve → Right ventricle → Pulmonary Valve → Artery → Lungs In lungs, blood picks up O2 and releases CO2. Then O2 rich blood returns to the heart Arteries Arteries carry blood away from the heart Arteries Made of Three Layers inner layer --epithelial cells middle layer -- muscle tissue outer wall -- flexible connective tissue. Major Arteries Aorta – largest artery in the body. Carries blood from the heart to the rest of the body. Coronary Arteries – bring blood to the heart More Artery Info Pulse is caused by the expanding and narrowing of artery walls. When you count pulse beats, you are also counting heartbeats. Arteries control the amount of blood that different organs receive. Capillaries In capillaries, CO2 and O2 are exchanged between the blood and the body’s cells This happens by diffusion Main Job of the Veins… Veins carry blood back to the ♥ Since most are carrying waste they are purplish/bluish in color The walls are very thin which is why you can see the color through your skin. Main Job of the Veins… Veins carry blood back to the ♥ Walls of veins are generally thinner than arteries. Because of this… you can see the color through your skin •Since most are carrying waste they are purplish/bluish in color. What keeps blood moving? – 3 things… contraction of nearby skeletal muscles valves that prevent blood from flowing backward The vein valves are necessary to keep blood flowing toward the heart, but they’re also necessary to allow blood to flow against the force of gravity. For example, blood that is returning to the heart from the foot has to be able to flow up the leg. Generally, the force of gravity would discourage that from happening. The vein valves, however, provide footholds for the blood as it climbs its way up. breathing movements that squeeze veins in the chest Blood Pressure Blood pressure is the pressure that blood exerts against the walls of the blood vessels. As blood moves away from the heart, the blood pressure decreases. The instrument that measures blood pressure is a sphygmomanometer. Superior vena cava Inferior vena cava septum Pulmonary veins & valves aren’t shown here