* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Audiological Evaultions
Survey
Document related concepts
Noise-induced hearing loss wikipedia , lookup
Sound from ultrasound wikipedia , lookup
Audiology and hearing health professionals in developed and developing countries wikipedia , lookup
Sound localization wikipedia , lookup
Auditory system wikipedia , lookup
Transcript
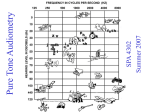
Audiological Evaultions Sarah Woolford Basics of Hearing Testing • Audiometry: The testing and measuring of hearing. • Audiometers: measures hearing • Transducers: how sound is delivered from a device to the person being evaluated. - Circumaural headphones, supra-aural headphones, inserts (earbuds), speakers, and bone oscillators (All definitions provided by class discussions and PowerPoints) Transducers Other Terms • • • • • Monaural – Sound in one ear only Binaural – Sound in both ears simultaneously Unilateral – One-sided hearing loss Bilateral – Hearing loss on both sides If there is no hearing loss, it is referred to as hearing that is “Within Normal Limits” or “WNL” (All definitions provided by class discussions and PowerPoints) What is there to test? • Air conduction (AC): sound travelling through the outer and middle ear leading to the inner ear. • Bone Conduction (BC): sound travelling through the bones of the skull straight to the inner ear, thereby bypassing the middle and outer ear Each type of conduction plays a major role in how one hears. And both types have their own battery of tests to determine how good the conduction is. (All definitions provided by class discussions and PowerPoints) Air Conduction Testing Typically, a standard pure tone test will be administered to determine if air conduction is WNL. The patient will be tested in a booth and can wear any of the previously mentioned transducers (with the exception of the bone oscillator) but circumaural headphones are regularly used. The paitent then will either response verbally, press a button, or raise a hand when they hear a sound from the transducer. Pure tone testing can be done monaurally or binaurally, but standard practice is that one ear will be tested, followed by the other. (All information provided by class discussions and PowerPoints) Air Conduction Testing Measurements: The pure tones are played at 250, 500, 1000, 2000, 4000, and 8000 hertz for each ear. Other hertz ranges that can be tested are 3000 and 6000 if needed. At any hertz range, the audiologist will be able to see at which decibel the individual can hear the pure tone. Purpose for testing: The aim of the testing is to find an individual’s lowest threshold, meaning the lowest intensity level that a person can accurately hear the tone. In order to hear the tone accurately, the patient must be able to response to the tone 2/3 of the times the tone is played. Bone Conduction Testing Bone Conduction testing, also, uses pure tones to determines an individual’s bone conduction. Testing is also done in a booth and once again the patient response to sounds verbally, pressing a button, or raising a hand when they hear a sound from the transducer. A major difference is that the only transducer that can be utilized is the bone oscillator. The bone oscillator is placed behind the ear and vibrates the skull, transferring sound through the bones of the skull. (All information provided by class discussions and PowerPoints) Bone Conduction Testing Measurements: Bone conduction testing plays pure tones at 500, 1000, 2000, and 4000 hertz and is done on both sides of the head. At any hertz range, the audiologist will be able to see at which decibel the individual can hear the pure tone. Purpose for testing: Bone conduction testing is used to determine if sound can be and how well it is transferred via the bones of the skull into the inner ear. Pure Tone Average • The average air conduction threshold value at the 500, 1000, 2000 hertz levels. This give an overall perspective in someone’s able to determine speech. Speech Testing • SRT – Speech Reception Threshold The purpose of speech testing is to find the lowest level in which an individual can repeat an easy, spondee word. A spondee is a two syllable word with equal stress, i.e. a compound word. The patient can be test with any transducer but typically not a bone oscillator. This is done monaurally and in both ears. A patient’s threshold should be within 6 dBs of their PTA (pure tone average) for both ears. SPONDEES Speech Testing • WRS – Word Recognition Score (a discriminatory score, percentage) The goal of this test is to see how many words an individual can correctly repeat a word in an ideal listening environment. By understanding the percentage of words correctly heard in an ideal listening environment, an audiologist can better be able to help the patient understand how much he or she is actually receiving in daily life. The patient is excepted repeat single syllable words that are heard using any transducer other than a bone oscillator. This can be tested monaurally, and with noise if so needed. Words can be spoken or played on a CD. Visual References • Slide 3: headphones: (http://www.bhphotovideo.com/images/images500x500/Sennheiser_HDA2 80_HDA280_Stereo_Hearing_Test_539203.jpg: • Slide 3: Ear buds: (http://azbalanceandhearing.com/wpcontent/uploads/2010/07/oae-teoa.png) • Slide 3: Bone Oscillator: (http://aisforadelaide.com/wpcontent/uploads/2013/01/bone-conductor.jpg) • Slide 7: Left picture: (http://www.ushersyndrome.nih.gov/join/images/audiology.jpg) Visual Reference • Slide 7: Right Picture: (http://www.linksfieldaudiology.co.za/images/testbooth.jpg) • Slide 10: Image: (http://www.hhclinics.com/images/Bone_Conduction_Threshold.jpg) • Slide 14: Spondee: (http://2.bp.blogspot.com/-6FIpghFvTRo/UYMLUlW3lI/AAAAAAAAAis/i60GDGSXD9g/s1600/Slide6.JPG)