* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download The Theory of Continental Drift
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
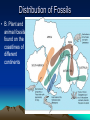
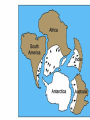
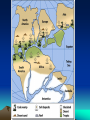
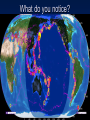
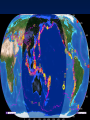
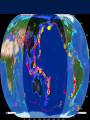
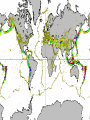
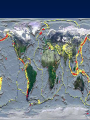
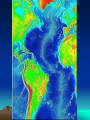
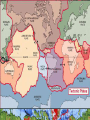
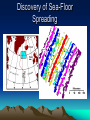
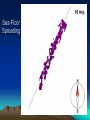
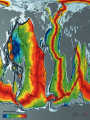
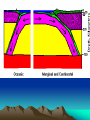
Formation of continental crust • Buoyant Material rises to the surface of a molten Earth, • Continental (Felsic) material is less dense, more buoyant, therefore rises and “floats Higher” 3 bya 2.8-2.5 bya 1.6-1.2 bya 1.2 bya to 700 mya Continental Drift • Proposed by Alfred Wegener in 1912 • Hypothesis: 250 million years ago, all of the continents were combined into one super-continent called “Pangaea”, (all land). • The continents gradually drifted apart to where they are today Alfred Wegener • 1880-1930, German meteorologist • Noticed that South America and Africa look as though they could fit together like pieces of a puzzle. • proposed the hypothesis of continental drift in "On the Origin of Continents and Oceans" (1912) • Died while crossing the Greenland ice cap in 1930, exploring. Evidence for Wegener’s hypothesis. “Puzzle Pieces” • A. Continents look like they could be part of a giant jigsaw puzzle • NOTE: Shorelines don’t match perfectly, but the continental shelves do. Distribution of Fossils • B. Plant and animal fossils found on the coastlines of different continents Tie-in to Sequence of Rocks • C. Same rock patterns found in South America, India, Africa, Antarctica and Australia Geological Evidence for Continental Drift • D. geological matches – mountain belts (AppalachiansCaledonians) – age similarities (matching Archean cratons) – – stratigraphic similarities, matching layers of rock (e.g., Nova Scotia and Morocco) igneous provinces, chemical imprints (Mesozoic basalts, Precambrian anorthosites) Ancient Climates • E. Tropical plant remains (coal deposits) found in Antarctica • E(2). Glaciation in Africa, South America, India, and Australia during the same time Paleoclimate evidence Glacial striations Ice sheets covered big areas of southern hemisphere ~ 220-300 million years ago E(3). Climate Evidence Coal deposits and fern fossils in Antarctica Glacial deposits in India, S. America, Africa, Australia hint: These locations must have once been at a different latitude (further north or south!) Problems With The Hypothesis • No mechanism for movement of continents. What force could possibly drive them? • Wind and water currents could possibly move fossils. Some animals could migrate / swim. • Biblical Stories explained marine fossils on mountain peaks, as well as the existence of tropical fossils in Antarctica. • Theory was not accepted by scientists. • Glacial evidence and geologic matches, however, were stumpers. Wegener’s Hypothesis Confirmation of Continental Drift • World War II technology – mapping the ocean floor with sonar – Discovery of the match of continental shelves. They matched up better than previously thought. • Worldwide Standardized Seismic Network 1963- What do you notice? Worldwide Standardized Seismic Network Discovery of Sea-Floor Spreading Sea-Floor Spreading Seafloor Spreading: What does this mean for the evidence of the theory? Now we have a theory. What is the difference between a theory and a hypothesis? • A hypothesis is an idea, an educated guess, or a possible solution derived from logic or common sense. • A theory is an explanation that fits ALL of the facts, observations, and data. • Scientists realized there was a relationship between seafloor spreading, volcanic activity, earthquakes, mountain formation, mid-ocean ridges, the continental shelves, and deep ocean basins. The Plate Tectonics Model