* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Name - Prosper ISD
Coriolis force wikipedia , lookup
Rigid body dynamics wikipedia , lookup
Fictitious force wikipedia , lookup
Faster-than-light wikipedia , lookup
Classical mechanics wikipedia , lookup
Length contraction wikipedia , lookup
Newton's theorem of revolving orbits wikipedia , lookup
Hunting oscillation wikipedia , lookup
Centrifugal force wikipedia , lookup
Mass versus weight wikipedia , lookup
Classical central-force problem wikipedia , lookup
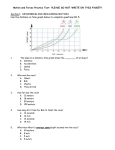
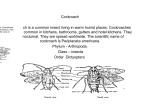
Name _______________________________________________ Date____________ Period_____ Review Sheet for Physics Test – OL Test Date: _________________________ ******************************************************************************************** Part 1: Measuring Motion 1. What is the math formula used to calculate AVERAGE SPEED? ___________________ Distance Time 10 meters 5 seconds 30 meters 10 seconds 45 meters 15 seconds 80 meters 20 seconds 2. What is the speed of the cockroach after 5 seconds? ____________ 15 seconds? _____________ 10 seconds? ___________ 20 seconds? _____________ 3. Fill in the blanks with the words “accelerates”, “decelerates” or “constant speed” ______________What happens to the speed of the cockroach between 5 and 10 seconds ______________What happens to the speed of the cockroach between 10 and 15 seconds ______________What happens to the speed of the cockroach between 15 and 20 seconds 4. In 5 minutes, you ride your bike 265 meters toward the north. What is your average speed while riding your bike? (show your work) ___________________________ What is your velocity?___________________________________________ 5. What is the difference between speed & velocity? Part II: What is a Force? Use your notes or the internet to define the following terms and answer the questions that follow. 6. Force— A _______________ or _________________. Force and be described based on ________________ and direction. 7. Newton—The _______________ in which force is measured or expressed 8. Net force-The ___________________ of all forces being exerted on an object. 9.When finding net force, forces that are in the SAME direction should be ______________, while forces in DIFFERENT directions should be _______________. pulling 48 N left pushing 40 N left 10. What is the net force shown in the picture above? __________________. 11. In what direction will the box move?_________________________. 12. If net force is equal to ZERO, then forces are __________________. 13. If net force is NOT equal to ZERO, then forces are ________________. 14. How much work does an elephant do while moving a circus wagon 20 meters with a pulling force of 200N? 15. Angela uses a force of 25 Newton’s to lift her grocery bag while doing 50 Joules of work. How far did she lift the grocery bags? Part III: Line Graphs 16. On a speed graph what does a horizontal line represent?________________ 17. On a speed graph, what label goes on the x axis?: ______________ What label goes on the y axis?: ________________________ Look at the graph to the right to answer questions 18-20. 18. How far had the object traveled at 3pm? ______________________________ 19.What time was it once the object traveled 60 km? ________________________ 20.Describe the motion from point B to point C. _____________________________ Use the graph below to answer questions 21-23. 600 cruising jet speeding race car DISTANCE (m) 500 flying eagle 40 0 galloping horse 30 0 20 0 wheelchair racer walking person 10 0 0 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 1 0 1 1 1 2 TIME (s) 21. The graph above shows distance-time data for various objects. What can be concluded from the data in the graph? a. The graph of the fastest-moving object is steepest. b. The racecar is traveling the fastest. c. The graph of the slowest-moving object is the steepest. d. The horse and the eagle are traveling at the same speed. 22. According to the graph above, which of the objects traveled the furthest distance? a. the cruising jet b. the galloping horse c. the wheelchair racer d. the flying eagle 23. Did any of the objects stop to take a break? (yes or no) How do you know? Use the graph to the right to answer questions 24-27. Choose from the following words: Accelerating, Decelerating, or Constant Speed. 24. Describe the object’s movement from Point A to Point B. _______________________ 25. Describe the object’s movement from Point B to Point C. ______________________ 26. Describe the object’s movement from Point E to point F. _____________________________ 27. Between what two points is the object traveling the fastest? ___________________ Part VI: Newton’s Laws Match each example with one of Newton’s Laws. Law: Examples: ________ 28. An object at rest stays at rest; an object in motion remains in motion with the same direction and at the same speed. a. ________ 29. An object’s acceleration depends on its mass and the force exerted on the object b. ________ 30. For every action there is an equal and opposite reaction. c. An empty wagon moves faster than a wagon full of potatoes when equal force is applied. When a rocket’s exhaust fumes push down, the rocket moves up. A soccer ball is kicked, rolls to the sideline, then comes to a stop. 31. A 50 kg skater pushed by a friend accelerates 5 m/sec2. How much force did the friend apply? 32. An object of mass 30 kg is falling in air and experiences a force due to air resistance of 50 Newton’s. Determine the net force acting on the object and calculate the acceleration of the object. 33. Explain the difference between potential and kinetic energy. Then draw and label a diagram showing the difference in position of an object with potential and kinetic energy.