* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Extended Questions- The Answers
Conservation of energy wikipedia , lookup
Quantum electrodynamics wikipedia , lookup
Photon polarization wikipedia , lookup
Nuclear physics wikipedia , lookup
Density of states wikipedia , lookup
Electrical resistivity and conductivity wikipedia , lookup
Theoretical and experimental justification for the Schrödinger equation wikipedia , lookup
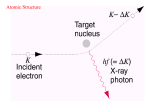
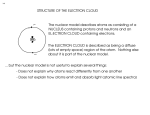
Extended QuestionsThe Answers Higher Physics What is meant by “coherent” waves? Same speed Same frequency In Phase Explain in detail what “photoelectric emission” is? Photoelectric emission is when an electron is ejected from the surface of a material by a photo of light which has frequency greater than the threshold frequency of the material, or energy greater than the work function. What is a “photoelectric current”? Is when an electric field ( or Potential difference ) is applied across the area where a photoelectron has been ejected. This electron experiences a force and accelerates. This moving charge is a photoelectric current. What is meant by the “work function”? Work function is the minimum energy required to release an electron for the surface of a metal Explain what is meant by “quantised energies”? Discrete energy or packets of energy. Explain in detail how an emission spectrum is produced. When an electron is in an excited state it will spontaneously make a transition to a lower energy state and release a photon of light. The difference in energies will be equal to the energy of the photon. From E=hf the corresponding frequency can be gained. This transition would appear as line of colour against a black back. Explain in detail how an absorption spectrum is produced. When a material receives a continuous spectrum of light, some of the frequencies of light (and the energies E=hf) may correspond to energy levels within the atom. If an electron absorbs a photon of a particular energy it makes an upward transition to a higher energy level. The absence of this photon would be noticeable as a black band on the full spectrum. What does “laser” stand for? Light Amplification Stimulated Emission Radiation of due to the What is meant by the term “population inversion” When most (or all) of the electrons are excited to an energy level above the ground state. Explain in detail how a laser works? Pump laser to excite electrons to desired energy level (population inversion) Release photon with equal energy. This causes electrons to make downward transition. Releasing more photons All photons in Phase and moving in the same direction. What is meant by the term “doping”? The process of adding impurities to a semiconductor material. Explain in detail how a n-type semiconductor material is formed Silicon, 4 outer electrons, tight covalent bond. No free charge carriers. Dope with Arsenic, 5 outer electrons 4 bond allowing 1 free charge carrier. As charge carrier is electron, n-type material formed Nb. Overall charge not changed What is the depletion layer and how is it formed? In this region there are no free charge carriers. Formed when electrons fill up holes around the p-n junction. A diode is connected forward bias. Explain in detail if and how it conducts. In forward bias(n type to neg end of bat) electrons given enough energy to overcome the depletion layer. This allows for a current to flow through the depletion layer, remove it. A diode is connected reverse bias. Explain in detail if and how it conducts. In reverse bias the (n-type to pos end) the potential causes a movement of charge carriers away from the depletion layer, making it larger. This makes it even more difficult to get a current to flow through it.