* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download When Plates Collide:
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
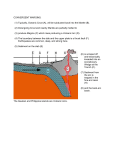
When Plates Collide: Imaging the roots of Cascadia’s volcanoes Berkeley University of California Seismological Laboratory Richard Allen Professor, Director William Hawley Robert Porritt Berkeley University of California Seismological Laboratory Sponsored by Cascadia: Cascadia: why Cascadia: Subduction, Destruction and Warning Risk: People Seattle Portland Earth dynamics: Subduction Blue slab Surface: Earthquakes and Volcanoes Data Deploying seismometers 1. Onshore …easy 2. Offshore …hard Earthscope - USArray •! Seismometers deployed across the US Cascadia Initiative •! 70 ocean bottom seismometers •! Deployed each year for 4 years •! ~280 deployment locations !! Six cruises per year, 3 to recover + 3 to redeploy Our cruise objectives Year 4, Leg 3, June 22 - July 6, 2014 1.! Recover 10 OBS (blue) 2.! Recover 22 with ROV Jason (orange/red) The science team 2 Chief Scientists 2 Graduate students 7 Undergraduates 6 OBS team 10 ROV Jason team Loading ROV Jason onto the R/V Thompson The science team 2 Chief Scientists 2 Graduate students 7 Undergraduates 6 OBS team 10 ROV Jason team Student Video Blog Search for “Cascadia Tom Cruise” Student Video Blog Search for “Cascadia Tom Cruise” FN14A recovery Student Video Blog Search for “Cascadia Tom Cruise” J29C rescue Lost instrument ROV Jason search Student Video Blog 500 m Search for “Cascadia Tom Cruise” J29C rescue Student Video Blog Search for “Cascadia Tom Cruise” FN15C loss – shipwreck Student Video Blog Search for “Cascadia Tom Cruise” Data coverage Data coverage Data coverage to constrain •! Juan de Fuca plate •! Subducting slab Juan de Fuca plate Data coverage to constrain •! Juan de Fuca plate •! Subducting slab •! Earthquakes Data coverage to constrain •! Juan de Fuca plate •! Subducting slab •! Earthquakes •! Volcanoes Data coverage to constrain •! Juan de Fuca plate •! Subducting slab •! Earthquakes •! Volcanoes •! Newberry track Data coverage to constrain •! Juan de Fuca plate •! Subducting slab •! Earthquakes •! Volcanoes •! Newberry track Teleseismic body-wave imaging Seismic array Geologic object with a velocity anomaly inner core outer core mantle Teleseismic body-wave imaging Geologic object with a velocity anomaly Hot feature = slow velocity Event 1 Teleseismic body-wave imaging Similar methods used in CAT scan Event 2 Event 1 Beneath Cascadia? Hot geologic objects ! slow velocity Cold geologic objects ! fast velocity DNA15-P 100 km depth Continuous slab at shallow depths Low velocities beneath Newberry DNA15-P 150 km depth Continuous slab at shallow depths Low velocities beneath Newberry DNA15-P 200 km depth Continuous slab at shallow depths Low velocities beneath Newberry DNA15-P 250 km depth Continuous slab at shallow depths Low velocities beneath Newberry Gap in slab as it passes below Newberry DNA15-P 300 km depth Continuous slab at shallow depths Low velocities beneath Newberry Gap in slab as it passes below Newberry DNA15-P 350 km depth Continuous slab at shallow depths Low velocities beneath Newberry Gap in slab as it passes below Newberry Gap widens with depth DNA15-P 100 km depth Continuous slab at shallow depths -122° S N 100km depth (km) DNA15-P S-N at -122° DNA15-P 250 km depth -121° S Gap in slab as N it passes below Newberry 250km depth (km) DNA15-P S-N at -121° Slab destruction by the Newberry volcanic source What is the origin of the Newberry track? Yellowstone Caldera Yellowstone Caldera Yellowstone supervolcano …a hotspot track • age-progressive track • high gravity anomaly • high 3He/4He ratio …with a deep source? …a plume? Yellowstone Caldera The origins of Yellowstone plate motion SW NE Lowry, Ribe & Smith, 2000 Yellowstone Snake River Plain SW 75 km DNA13-SH NE NW Yellowstone SE asthenospheric window remnant slab Farallon slab DNA13-SH DNA13-SH -2% +2% Porritt et al 2014 The role of the Yellowstone plume Obrebski et al 2010 Yellowstone Snake River Plain SW NE NW Yellowstone SE asthenospheric window remnant slab Farallon slab DNA13-SH DNA13-SH -2% +2% Porritt et al 2014 The role of the Yellowstone plume Newberry gap Gorda 0km Juan de Fuca Yellowstone The reason for so few earthquakes? 1000km DNA13-SH Farallon slab Summary: Cascadia Geophysical adventure – data is king: instrumentation around the globe – expanding to more challenging environments ! Are smartphones next? Slab fragmentation – subducting oceanic slabs can be broken – Newberry volcanism is slicing through the slab today ! Is this the reason for so few earthquakes? Yellowstone supervolcano – lower mantle source for this hot upwelling: a mantle plume – plumes can destroy subducting oceanic lithosphere ! How big is the area of influence for Yellowstone?