* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Unit 13 - Treatment of Psychological Disorders
Intensive short-term dynamic psychotherapy wikipedia , lookup
Adherence management coaching wikipedia , lookup
Attachment therapy wikipedia , lookup
Gestalt therapy wikipedia , lookup
Art therapy wikipedia , lookup
Psychoanalysis wikipedia , lookup
Albert Ellis wikipedia , lookup
Primal therapy wikipedia , lookup
Behaviour therapy wikipedia , lookup
Residential treatment center wikipedia , lookup
Chelation therapy wikipedia , lookup
Dodo bird verdict wikipedia , lookup
Dance therapy wikipedia , lookup
Conversion therapy wikipedia , lookup
Emotionally focused therapy wikipedia , lookup
Reality therapy wikipedia , lookup
The Radical Therapist wikipedia , lookup
Equine-assisted therapy wikipedia , lookup
Relationship counseling wikipedia , lookup
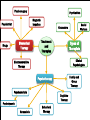
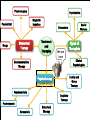
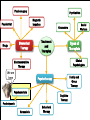
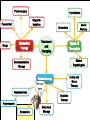
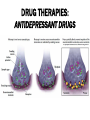
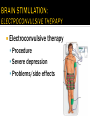
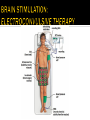
UNIT 13 Psychosurgery Psychiatrists Magnetic Impulses Psychiatrist Biomedical Therapy Drugs Treatment and Therapies Types of Therapists Clinical Psychologists Electroconvulsive Therapy Family and Group Therapy Psychotherapy Psychoanalysis Psychodynamic Humanistic Social Workers Counselors Cognitive Therapy Behavioral Therapy The Psychological Therapies Evaluating Psychotherapies The Biomedical Therapies Preventing Psychological Disorders Maltreatment of the insane throughout the ages was the result of irrational views. Many patients were subjected to strange, debilitating, and downright dangerous treatments. Philippe Pinel in France and Dorthea Dix in America founded humane movements to care for the mentally sick. Philippe Pinel (1745-1826) Dorthea Dix (1802-1887) About 15% of population in a given year Most common: anxiety and depression Women more willing than men Stigma surrounding mental health Psychotherapy involves an emotionally charged, confiding interaction between a trained therapist and a mental patient. Biomedical therapy uses drugs or other procedures that act on the patient’s nervous system, treating his or her psychological disorders. An eclectic approach uses various forms of healing techniques depending upon the client’s unique problems. Psychosurgery Psychiatrists Magnetic Impulses Psychiatrist Biomedical Therapy Drugs Treatment and Therapies We are here Electroconvulsive Therapy Psychoanalysis Humanistic Cognitive Therapy Behavioral Therapy Types of Therapists Clinical Psychologists Family and Group Therapy Psychotherapy Psychodynamic Social Workers Counselors Psychosurgery Psychiatrists Magnetic Impulses Psychiatrist Biomedical Therapy Drugs Treatment and Therapies Types of Therapists Clinical Psychologists Electroconvulsive Therapy We are here Family and Group Therapy Psychotherapy Psychoanalysis Psychodynamic Humanistic Social Workers Counselors Cognitive Therapy Behavioral Therapy The first formal psychotherapy to emerge was psychoanalysis, developed by Sigmund Freud. Sigmund Freud's famous couch Since psychological problems originate from childhood repressed impulses and conflicts, the aim of psychoanalysis is to bring repressed feelings into conscious awareness where the patient can deal with them. When energy devoted to id-ego-superego conflicts is released, the patient’s anxiety lessens. Dissatisfied with hypnosis, Freud developed the method of free association to unravel the unconscious mind and its conflicts. The patient lies on a couch and speaks about whatever comes to his or her mind. During free association, the patient edits his thoughts, resisting his or her feelings to express emotions. Such resistance becomes important in the analysis of conflict-driven anxiety. Eventually the patient opens up and reveals his or her innermost private thoughts, developing positive or negative feelings (transference) towards the therapist. 1. 2. Psychoanalysis is hard to refute because it cannot be proven or disproven. Psychoanalysis takes a long time and is very expensive. Psychodynamic therapy Influenced by Freud Similarities with psychoanalysis ▪ Focus on common themes in relationships across life Differences with psychoanalysis ▪ Face to face ▪ Much shorter in duration – Interpersonal psychotherapy https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=QV6DpJKW6a0 Psychosurgery Psychiatrists Magnetic Impulses Psychiatrist Biomedical Therapy Drugs Treatment and Therapies Types of Therapists Clinical Psychologists Electroconvulsive Therapy Psychoanalysis Psychodynamic Humanistic Social Workers Counselors Family and Group Therapy Psychotherapy We are here Cognitive Therapy Behavioral Therapy Insight therapies focus more on: the present rather than the past conscious rather than the unconscious taking immediate responsibility promoting growth instead of curing Client-centered therapy – Carl Rogers Nondirective therapy Genuineness, acceptance, and empathy Active listening ▪ Paraphrase ▪ Invite clarification ▪ Reflect feelings Unconditional positive regard Active listening Paraphrase ▪ Summarize in own words Invite clarification ▪ “What might be an example of this?” Reflect feelings ▪ What you’re sensing from speaker’s body language and intensity Unconditional positive regard In stark contrast to psychoanalysis, humanistic therapists assume that people are generally good and healthy, but can be negatively affected by pressure from oneself and society. Humanistic therapists accomplish treatment through genuineness, empathy, and unconditional regard and acceptance for their clients. Psychosurgery Psychiatrists Magnetic Impulses Psychiatrist Biomedical Therapy Drugs Treatment and Therapies Types of Therapists Clinical Psychologists Electroconvulsive Therapy Psychotherapy Psychoanalysis Psychodynamic Humanistic Social Workers Counselors We are here Cognitive Therapy Behavioral Therapy Family and Group Therapy Therapy that applies learning principles to the elimination of unwanted behaviors. To treat phobias or sexual disorders, behavior therapists do not delve deeply below the surface looking for inner causes. The behaviors are the problem, so we must change the behaviors! Counterconditioning is a procedure that conditions new responses to stimuli that trigger unwanted behaviors. It is based on classical conditioning and includes exposure therapy and aversive conditioning. https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=t9Av2l4t0U4 - Sheldon The Far Side © 1986 FARWORKS. Reprinted with Permission. All Rights Reserved. Expose patients to things they fear and avoid. Through repeated exposures, anxiety lessens because they habituate to the things feared. A type of exposure therapy that associates a pleasant, relaxed state with gradually increasing anxiety-triggering stimuli commonly used to treat phobias. Extreme form: Flooding A type of counterconditioning that associates an unpleasant state with an unwanted behavior. With this technique, temporary conditioned aversion to alcohol has been reported. BEHAVIOR THERAPIES: AVERSION THERAPY BEHAVIOR THERAPIES: AVERSION THERAPY BEHAVIOR THERAPIES: AVERSION THERAPY Operant conditioning procedures enable therapists to use behavior modification, in which desired behaviors are rewarded and undesired behaviors are either unrewarded or punished. A number of withdrawn, uncommunicative 3-year-old autistic children have been successfully trained by giving and withdrawing reinforcements for desired and undesired behaviors. In institutional settings, therapists may create a token economy in which patients exchange a token of some sort, earned for exhibiting the desired behavior, for various privileges or treats. How durable are the behaviors? Will people become dependent upon extrinsic rewards? Is it right for one human to control another’s behavior? Psychosurgery Psychiatrists Magnetic Impulses Psychiatrist Biomedical Therapy Drugs Treatment and Therapies Types of Therapists Clinical Psychologists Electroconvulsive Therapy Family and Group Therapy Psychotherapy Psychoanalysis Psychodynamic Humanistic Social Workers Counselors Cognitive Therapy Behavioral Therapy We are here Teaches people adaptive ways of thinking and acting based on the assumption that thoughts intervene between events and our emotional reactions. Aaron Beck (1979) suggests that depressed patients believe that they can never be happy (thinking) and thus associate minor failings (e.g. failing a test [event]) in life as major causes for their depression. Beck believes that cognitions such as “I can never be happy” need to change in order for depressed patients to recover. This change is brought about by gently questioning patients. GOAL IS TO REVERSE CATASTROPHIZING BELIEFS Stress inoculation training Cognitive therapists often combine the reversal of self-defeated thinking with efforts to modify behavior. Cognitive-behavior therapy aims to alter the way people act (behavior therapy) and alter the way they think (cognitive therapy). Psychosurgery Psychiatrists Magnetic Impulses Psychiatrist Biomedical Therapy Drugs Treatment and Therapies Types of Therapists Clinical Psychologists Electroconvulsive Therapy Family and Group Therapy Psychotherapy Psychoanalysis Psychodynamic Humanistic Social Workers Counselors Cognitive Therapy Behavioral Therapy We are here Group therapy normally consists of 6-9 people attending a 90-minute session that can help more people and costs less. Clients benefit from knowing others have similar problems. Family therapy treats the family as a system. Therapy guides family members toward positive relationships and improved communication. COMPARISION OF PSYCHOTHERAPIES Regression toward the mean Client’s perceptions Clinician’s perceptions Outcome research Meta-analysis Placebo treatments Evidence-based practice Eye movement desensitization and reprocessing (EMDR) Light exposure therapy Seasonal affective disorder (SAD) Hope for demoralized people A new perspective An empathic, trusting, caring relationship Similarities between cultures Differences between cultures Psychosurgery Psychiatrists Magnetic Impulses Psychiatrist Biomedical Therapy Drugs Treatment and Therapies We are here Family and Group Therapy Psychotherapy Psychoanalysis Humanistic Types of Therapists Clinical Psychologists Electroconvulsive Therapy Psychodynamic Social Workers Counselors Cognitive Therapy Behavioral Therapy TYPES OF THERAPISTS TYPES OF THERAPISTS TYPES OF THERAPISTS TYPES OF THERAPISTS TYPES OF THERAPISTS Psychosurgery Psychiatrists Magnetic Impulses Psychiatrist Biomedical Therapy Drugs Treatment We are and here Therapies Types of Therapists Clinical Psychologists Electroconvulsive Therapy Family and Group Therapy Psychotherapy Psychoanalysis Psychodynamic Humanistic Social Workers Counselors Cognitive Therapy Behavioral Therapy Biomedical therapy Drugs - psychopharmacology Electroconvulsive therapy – shock treatment Magnetic impulses - rTMS Psychosurgery - lobotomy Psychiatrists Psychosurgery Psychiatrists Magnetic Impulses Psychiatrist Biomedical Therapy Drugs Treatment and Therapies Types of Therapists We are here Electroconvulsive Clinical Psychologists Therapy Family and Group Therapy Psychotherapy Psychoanalysis Psychodynamic Humanistic Social Workers Counselors Cognitive Therapy Behavioral Therapy Psychopharmacology Factors to consider with drug therapy Normal recovery rate of untreated patients Placebo effect ▪ Double blind procedure DRUG THERAPIES Antipsychotic drugs Psychoses Chlorpromazine (Thorazine) Dopamine Tardive dyskinesia Atypical antipsychotics (Clozaril) ▪ Positive and negative symptoms Antianxiety drugs Xanax, Ativan, D-cycloserine Physiological dependence Antidepressant drugs Use with mood and anxiety disorders Fluoxetine (Prozac), Paxil ▪ Selective-serotonin-reuptake inhibitors (SSRIs) ▪ Neurogenesis Side effects of antidepressants DRUG THERAPIES: ANTIDEPRESSANT DRUGS DRUG THERAPIES: ANTIDEPRESSANT DRUGS DRUG THERAPIES: ANTIDEPRESSANT DRUGS Mood-stabilizing Lithium Depakote medications Psychosurgery Psychiatrists Magnetic Impulses Psychiatrist Biomedical Therapy Drugs Treatment and We areTherapies here Types of Therapists Clinical Psychologists Electroconvulsive Therapy Family and Group Therapy Psychotherapy Psychoanalysis Psychodynamic Humanistic Social Workers Counselors Cognitive Therapy Behavioral Therapy Electroconvulsive therapy Procedure Severe depression Problems/side effects We are here Psychosurgery Magnetic Impulses Psychiatrist Biomedical Therapy Drugs Psychiatrists Treatment and Therapies Types of Therapists Clinical Psychologists Electroconvulsive Therapy Family and Group Therapy Psychotherapy Psychoanalysis Psychodynamic Humanistic Social Workers Counselors Cognitive Therapy Behavioral Therapy Magnetic Stimulation Repetitive transcranial magnetic stimulations (rTMS) Deep-Brain Stimulation BRAIN STIMULATION: ALTERNATIVE NEUROSTIMULATION THERPAIES Psychosurgery We are here Psychiatrist Biomedical Therapy Drugs Psychiatrists Magnetic Impulses Treatment and Therapies Types of Therapists Clinical Psychologists Electroconvulsive Therapy Family and Group Therapy Psychotherapy Psychoanalysis Psychodynamic Humanistic Social Workers Counselors Cognitive Therapy Behavioral Therapy Psychosurgery Lobotomy ▪ History ▪ Procedure ▪ Side effects ▪ Use today Resilience Preventing psychological disorders Integrated biopsychosocial system Therapeutic life-style change Aerobic exercise Adequate sleep Light exposure Social connection Anti-rumination Nutritional supplements