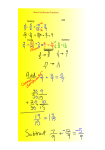
* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download 2.3 Solving Linear Equations Involving Fractions and
Eigenvalues and eigenvectors wikipedia , lookup
Signal-flow graph wikipedia , lookup
Linear algebra wikipedia , lookup
Cubic function wikipedia , lookup
Quartic function wikipedia , lookup
Quadratic equation wikipedia , lookup
System of polynomial equations wikipedia , lookup
Elementary algebra wikipedia , lookup
History of algebra wikipedia , lookup
2.3 Solving Linear Equations Involving Fractions and Decimals; Classifying Equations Learning Objectives: 1. Use the least common denominator to solve a linear equation containing fractions. 2. Solve a linear equation containing decimals. 3. Classify a linear equation as an identity, conditional, or a contradiction. 4. Use linear equations to solve problem. 1. Solve a linear equation containing parentheses, fractions and decimals Steps for solving a Linear Equations 1. If the equation contains fractions, multiplying both sides of the equation by the least common denominators. This will clear the equation of fractions. 2. If the equation contains decimals, multiplying both sides of the equation by the power of ten depending on the number of the decimal digits. This will clear the decimal. 3. If the equation contains parentheses, use distributive property to remove grouping symbols and combine like terms. Distributive Property: For any real numbers a, b and c a (b + c ) = ab + ac and − a (b + c ) = − ab − ac 4. Verify that the result is the solution of the equation. Example 1. Solve the linear equations: 4 7 5 1. x − x = − 3 4 4 2. 3n + 5 4n + 2 = 4+ 2 4 3. 0.04 x + 0.06(10000 − x ) = 480 1 2. Classify a linear Equation as an Identity, conditional or a contradiction Definitions: 1. An _______________________ equation is an equation that is satisfied for all values of the variable for which both sides of the equation are defined. 2. A __________________________ equation is an equation that is true for some values of the variable and false for other values of the variable. 3. A ___________________________ equation is an equation that is false for every value of the variable. Example 2. Solve the linear equations. State whether the equation is an identity, conditional or a contradiction equation. 1 2 14 1. x+ x= 2 3 3 1 2. 3(2 − 4n ) + 1 = − (24n − 6) 2 3. − (4a + 5) + 2a = 8a − 5 − 10a 2