* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Current and Voltage in Series and Parallel Circuits
Power electronics wikipedia , lookup
Operational amplifier wikipedia , lookup
Schmitt trigger wikipedia , lookup
RLC circuit wikipedia , lookup
Voltage regulator wikipedia , lookup
Power MOSFET wikipedia , lookup
Switched-mode power supply wikipedia , lookup
Current source wikipedia , lookup
Surge protector wikipedia , lookup
Current mirror wikipedia , lookup
Network analysis (electrical circuits) wikipedia , lookup
Rectiverter wikipedia , lookup
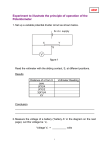
Worksheet: Current and Voltage in Series and Parallel Circuits Name:___________________ 1. Go to http://www.explorelearning.com/ 2. Click on enroll in a class (top right hand) 3. Enter your class code Section 03 – LX6TEWBUBW Section 04 - GJWGSWDRBW 4. Create an explore learning account – use your school username and password so that you don’t forget 5. Click on the launch gizmo button for the advanced circuit gizmo 6. In the window titled “Meters” change the precision to 1. Simple Circuit Construct a simple circuit with 1 battery (10 volt), 1 switch and 1 light bulb, connected in series. Draw a schematic diagram of the circuit you built below. Measuring Voltage Measure the voltage drop across the battery and the light bulb. To measure the voltage drop across a light bulb place the positive end of the voltmeter ( + ) on the side of the light bulb connected to the positive end of the battery and the negative end of the voltmeter (-) on the side of the light bulb connected to the negative end of the battery. (you should get a positive number) Voltage across battery:__________________________________ Voltage across light bulb:_________________________________ Measuring Current Use the ammeter to measure the current in several places around the circuit, by placing the ammeter (A) on a wire. Current after battery:______________________________________ Current after switch:_______________________________________ Current after light bulb:_____________________________________ Fill in the blank The _______________________(voltmeter/ammeter) measures the flow rate of electrons (the number of electrons that pass a point in the circuit each second). It is connected in _________________ (series – in the circuit/parallel – around something), which forces all of the current to pass through the meter for measurement. The _______________________ (voltmeter/ammeter) measures the energy used by each load. It is connected in ____________________ (series – in the circuit/parallel – around something) which creates an alternate path for the electrons to follow. Series Circuits Construct a series circuit with 1 battery, 1 switch, and 4 lights connected in series. Draw a schematic diagram of the circuit you built below. Measuring Voltage Measure the voltage rise across the battery. Record the voltage below. Move the voltmeter to each light bulb and record the voltage drop across each. Location Voltage (V) Battery (Vs) Light bulb #1 (V1) Light bulb #2 (V2) Light bulb #3 (V3) Light bulb #4 (V4) Add up V1 + V2 + V3 + V4 = __________ How does this number relate to Vs? _____________________________ In a series circuit, the voltage at the source (battery) is ___________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________________ Measuring Current Use the ammeter to measure the current flowing from the battery and out of each light bulb. measure only current flowing out of each lamp. Record all data in the table below. Location Be careful to Current (A) Battery (flowing out) Is Light bulb #1 (flowing out) I1 Light bulb #2 (flowing out) I2 Light bulb #3 (flowing out) I3 Light bulb #4 (flowing out) I4 How does Is relate to I1, I2, I3, and I4? ________________________________________________________ In a series circuit the current at the source is ___________ to the current at each point in the circuit. Summary for Series Circuits: A series circuit has ____________ path(s) for the charge to flow through. If one light bulb burns out what happens to the other light bulbs? ____________________________________ The total current in a series circuit is _____________________ (equal or shared) as lights are added. Light bulbs each have a voltage drop. How does their voltage compare to the battery voltage? Are the light bulbs in your home wired in series with each other? _________ Explain how you know how they are wired. Parallel Circuits Construct a parallel circuit with 1 battery, and 1 switch connected in series, and 4 light bulbs connected in parallel. Draw a schematic diagram of the circuit you built below. Measuring Voltage Measure the voltage across the battery, and record the voltage below. Measure the voltage drop across each light bulb and record your data. Location Voltage (V) Battery (Vs) Light bulb #1 (V1) Light bulb #2 (V2) Light bulb #3 (V3) Light bulb #4 (V4) How does Vs relate to V1, V2, V3, and V4? ________________________________________________ In a parallel circuit the voltage at the source is ___________ to the voltage at each point in the circuit. Measuring Current Use the ammeter to measure the current flowing from the battery and out of each light bulb. Be careful to measure only the flow out of each light bulb. Record all data in the table below: Location Current (A) Battery (flowing out) Is Light bulb #1 (flowing out) I1 Light bulb #2 (flowing out) I2 Light bulb #3 (flowing out) I3 Light bulb #4 (flowing out) I4 Add up I1 + I2 + I3 + I4 = __________ How does this number relate to Is? ______________________________ In a parallel circuit, the current at the source (battery) is __________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________________ Summary for Parallel Circuits: A parallel circuit has _________________ path(s) for the charge to flow through. If one light bulb burns out what happens to the other light bulbs? ____________________________________ The total current in a parallel circuit is _____________________ (equal or shared) through the light bulbs. How does the light bulb voltage compare to the battery voltage? ____________________________________ OVERAL SUMMARY Fill in the following table to compare series circuits and parallel circuits: Series Number of paths Parallel Voltage Is the voltage shared between loads or equal to the source? Current Is the current shared between loads or equal to the source? If one light bulb burns out, will the other bulbs stay on? On a separate piece of paper, draw the following circuit diagrams: 1. One cell, one light bulb, and one motor wired in parallel. A switch is connected in series with the light bulb so that it can be turned on and off without affecting the rest of the circuit. 2. One battery (four cells) with two lights in parallel and a resistor is in series with both light bulbs. 3. Two cells, two lights (if one burns out the other will stay on), and a switch controlling each light. HAND IN AND BEGIN REVIEWING FOR YOUR CURRENT ELECTRICITY QUIZ.