* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Pancreas
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
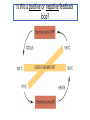
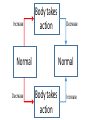
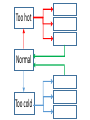
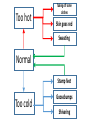
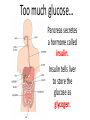
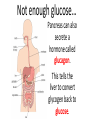
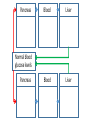
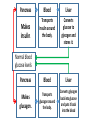
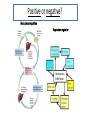
Essential Question How do the body systems work together in a functional human organism? Standard B.10A - describe the interactions that occur among systems that perform the functions of regulation, nutrient absorption, reproduction, and defense from injury or illness in animals Collect Today Body Systems Slideshow Assigned Plant Systems Test Analysis (TOMORROW) Protist/Fungi MAKEUP Quiz (TOMORROW) Page 122 – Notecard Defintions (Tuesday – after SB) Plant Systems Vocabulary MAKEUP Quiz (Thursday – after SB) Plant Systems Essay MAKEUP (Thursday-after SB) Late Page 118 – Photosynthesis/Cellular Respiration Foldable (-50%) Page 119 – Photosynthesis/Cellular Respiration Coloring (-50%) Page 121 - Plant Systems Test Review (-50%) Unit 10 – Body Systems Definitions Due Tuesday (3/22/16) All Parts Due Monday(3/28/16) 1. Digestion 2. Absorption 3. Respiration 4. Antibody 5. Stimuli 6. Response 7. Interdependence 8. Pathogen 9. Gamete 10. Hydrolysis 11. Circulatory System 12. Digestive System 13. Endocrine system 14. Epidermis 15. Excretion 16. Excretory System 17. Integumentary System 18. Muscular System 19. Nervous System 20. Pancreas 21. Reproductive System 22. Ovary PG 122 23. Respiratory System 24. Skeletal System 25. Lymphatic System 26. Immune System 27. Organ 28. Neuron Talk to your table group: What are some things that your body regulates? (regulate = control) What is homeostasis? …its all about BALANCE What does it mean? Homeostasis comes from the Greek and means “staying the same” Maintaining a constant internal environment. Claude Bernard (1813-1878) What happens when there is an imbalance in the internal environment? Jog on the spot for 60 seconds. Start Timer 60 Seconds 60 45 30 15 0 How’s your breathing? Are you getting warmer? Start Timer 60 Seconds 60 45 30 15 0 FEEDBACK LOOP: how the body maintains homeostasis when something goes wrong Negative feedback A decrease in function in response to a stimulus. (Removes the stimulus) The OPPOSITE thing is added to return to the original condition examples: shivering when you’re cold, blood sugar regulation Positive feedback An increase in function in response to a stimulus. (adds the stimulus) The SAME thing is added to return to the original condition examples: contractions before child birth, blood clotting Is this a positive or negative feedback loop? Increase Body takes action Normal Normal Decrease Decrease Body takes action Increase Why do we need to maintain a constant temperature? Enzymes work best at normal o body temperature (approx. 37 C) Too hot and we can get o hyperthermia (40 C). Too cold and we can get hypothermia (35oC). Too hot Normal Too cold Too hot Taking off some clothes Skin goes red Sweating Normal Stamp feet Too cold Goosebumps Shivering Task. Define homeostasis. Define negative feedback? Start Timer 5 Minutes 5 4 Evaluate and describe the effect of the exercise on your body – what did it do to return to normal. 3 2 1 0 Food for the cells… Glucose. Cells need a healthy diet of glucose. Not too much…not too little Body needs to control level of sugar (glucose) in the blood. This is done by the pancreas. Too much glucose… Pancreas secretes a hormone called insulin. Insulin tells liver to store the glucose as glycogen. Not enough glucose… Pancreas can also secrete a hormone called glucagon. This tells the liver to convert glycogen back to glucose. Normal blood glucose levels Pancreas Blood Liver Blood Liver Normal blood glucose levels Pancreas Pancreas Blood Liver Makes insulin. Transports insulin around the body. Converts glucose to glycogen and stores it. Pancreas Blood Liver Makes glucagon. Transports glucagon around the body. Converts glycogen back into glucose and puts it back into the blood Normal blood glucose levels Diabetes. With diabetes (type I) the pancreas does produce insulin. It used to be called the wasting disease as you died very slowly, becoming weaker and weaker, until you entered a coma. Diabetes. Fortunately it is now treatable and diabetics can lead virtually normal lives by taking regular injections of insulin. This was thanks to the pioneering work of Banting and Best. Diabetes video Task. In your own words, explain how blood sugar level is controlled by the pancreas and the cause of diabetes. Words to help: hormone, insulin, glucose, glycogen, liver, glucagon. Insulin and the control of blood sugar levels. After a meal blood ……….. levels increase. As a result the pancreas releases ……………. This enables the cells to absorb ………….., required for respiration, and also causes the ………. to convert excess glucose to insoluble …………… for storage. When blood sugar levels run low the ……………… releases glucagon instead. This causes the ………….. to breakdown the glycogen back into …………….. to give the cells energy. A person with ……………. does not produce the insulin required for absorbing and storing the glucose. As a result the person feels tired, is constantly thirsty, urinates a lot and their body slowly wastes away. Diabetes is treatable through injections of ………………... Insulin and the control of blood sugar levels. sugar glucose liver diabetes insulin pancreas glycogen After a meal blood sugar levels increase. As a result the pancreas releases insulin. This enables the cells to absorb glucose, required for respiration, and also causes the liver to convert excess glucose to insoluble glycogen for storage. When blood sugar levels run low the pancreas releases glucagon instead. This causes the liver to breakdown the glycogen back into glucose to give the cells energy. A person with diabetes does not produce the insulin required for absorbing and storing the glucose. As a result the person feels tired, is constantly thirsty, urinates a lot and their body slowly wastes away. Diabetes is treatable through injections of insulin. Positive or negative? Blood glucose regulation Temperature regulation For the rest of today… 1. Draw a feedback loop of your own! 2. Think about how your body responds when: • • • • you get dehydrated you get scared you cut your finger you get tired 3. Use your own example for extra credit. • You MUST get approval before you begin. • Requirements: 1. 2. 3. 4. Your feedback loop must be titled You must have at least 4 steps in your loop You must write the steps and draw them (they should be colored, too!) These will go up in the hallway…so make them school appropriate and neat! • This is for a daily grade.