* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download THE TRANSPORT SYSTEMS
Coronary artery disease wikipedia , lookup
Cardiac surgery wikipedia , lookup
Myocardial infarction wikipedia , lookup
Quantium Medical Cardiac Output wikipedia , lookup
Antihypertensive drug wikipedia , lookup
Lutembacher's syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Dextro-Transposition of the great arteries wikipedia , lookup
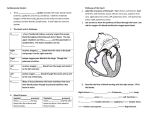
mad17743_ch23.qxd 3/10/06 2:01 PM Page 216 23 THE TRANSPORT SYSTEMS CHAPTER REVIEW If an animal has a transport system, it is either open or closed. In a closed system, as in earthworms, and humans, the blood is always contained within blood vessels and never runs free. Among vertebrates, the circulatory pathway varies from a single loop (fishes) to a double loop (all others). The heart has three chambers in amphibians and most reptiles, but has four chambers in some reptiles, birds, and mammals. In a four-chamber heart, the heart is a double pump and O 2 -poor blood is kept separate from O 2 -rich blood. Even so, during a heartbeat, first the atria contract under stimulation from the SA node and then the ventricles contract under stimulation from the AV node. The beating of the heart creates blood pressure that keeps blood moving in arteries, blood vessels that take blood away from the heart. There follows arterioles, cap- illaries, venules, and weak-walled veins that return blood to the heart. Skeletal muscle contraction pushing in on the walls of a vein, plus respiratory movements, keep blood moving in the veins that have valves that prevent back flow. Blood is composed of plasma plus formed elements, consisting of red blood cells (transport O 2 ), white blood cells (fight infection), and platelets (assist clotting). One of the primary functions of blood is carrying out capillary exchange. During capillary exchange, nutrients diffuse out of and wastes diffuse into the capillary. Water leaves a capillary at the arterial end because of blood pressure and is retrieved at the venule end because of osmotic pressure (created by proteins and salts). Lymphatic capillaries in the vicinity of cardiovascular capillaries pick up excess tissue fluid and return it to cardiovascular veins. CHAPTER KEY TERMS After studying the key terms of this chapter, match the phrases below with the alphabetized list of terms. artery lymphatic vessel blood plasma blood pressure pulmonary circuit capillary pulse diastole systemic circuit heart systole hemoglobin vein lymph a. force of blood pushing against the inside wall of blood vessels _______________________ b. fluid derived from tissue fluid _______________________ c. blood vessel that arises from venules and transports blood toward the heart _______________________ d. blood vessel that transports blood away from the heart _______________________ e. circulatory pathway between the lungs and the heart _______________________ f. circulatory pathway between the tissues and the heart _______________________ g. muscular organ whose contraction causes blood to circulate in the body of an animal _______________________ h. relaxation period of a heart chamber during the cardiac cycle _______________________ i. contraction period of the heart chamber during the cardiac cycle _______________________ j. vibration felt in arterial walls due to expansion of the aorta following ventricle contraction _______________________ k. fluid circulated by the heart through a closed system of vessels _______________________ l. microscopic blood vessel; gases and other substances are exchanged across the walls _______________________ m. liquid portion of blood _______________________ n. iron-containing respiratory pigment occurring in red blood cells _______________________ o. vessel that carries lymph _______________________ 216 mad17743_ch23.qxd 3/10/06 2:01 PM Page 217 S T U DY E X E R C I S E S Study the text section by section as you answer the questions that follow. 23.1 OPEN AND CLOSED CIRCULATORY SYSTEMS (PP. 396–398) • An open circulatory system can be contrasted with a closed circulatory system. • Fishes have a single circulatory loop, whereas the other vertebrates have a double circulatory loop—to and from the lungs and also to and from the tissues. 1. Match the items to the following types of circulation: 1. gastrovascular cavity 2. open circulatory system 3. closed circulatory system a. planarian b. vertebrate c. insect d. hemolymph instead of blood e. each cell exchanges with external fluid f. blood transports oxygen 2. Match the items with these types of vertebrate hearts: 1. one atrium and one ventricle 2. two atria and one ventricle 3. two atria and two ventricles a. amphibian (frog) b. fish c. mammal d. no mixing of O 2 -poor blood with O 2 -rich blood e. reduction in pressure following respiratory organ 3. What is the difference between the pulmonary circuit and the systemic circuit? 23.2 TRANSPORT IN HUMANS (PP. 399–404) • In humans, the right side of the heart pumps blood to the lungs, and the left side pumps blood to the tissues. • The heartbeat results from the contraction of the heart’s chambers. The pulse can be used to measure the heart rate. 4. To label the following diagram of the heart place the letters next to the appropriate terms. _____ aorta _____ aortic semilunar valve _____ bicuspid valve _____ inferior vena cava o. _____ left atrium _____ left ventricle n. _____ pulmonary arteries _____ pulmonary semilunar valve _____ pulmonary trunk m. _____ pulmonary veins _____ right atrium _____ right ventricle l. _____ septum _____ superior vena cava _____ tricuspid valve k. j. a. b. c. d. e. f. g. h. i. 217 mad17743_ch23.qxd 3/10/06 2:01 PM Page 218 5. a. Which blood vessel is an artery but carries O 2 -poor blood? __________________________________________ b. What is the correct definition of an artery? ________________________________________________________ c. What is the correct definition of a vein? ___________________________________________________________ 6. Trace the path of blood through the heart: a. from the vena cava to the lungs: __________________________________________________________________ b. from the lungs to the aorta: 7. Complete the following table with the words systole and diastole to show what occurs during the 0.85 second of one heartbeat: Time Atria Ventricles 0.15 sec 0.30 sec 0.40 sec 8. The heart beats about 70 times a minute. The the b. _________________________ a. _________________________ (chambers). This stimulus is picked up by the node, which initiates the contraction of the d. _________________________ not contracting, they are relaxing. Contraction is scientifically termed resting is termed node initiates the contraction of f. _________________________ g. _________________________ valves into the c. ________________________ (chambers). When the chambers are e. _________________________, and the . Contraction of the atria forces the blood through the h. _________________________. The closing of these valves is the lub sound. Next, the ventricles contract and force the blood into the arteries. Now the i. ____________________ valves close; this is the dub sound. BLOOD VESSELS (PP. 401–403) • Arteries take blood away from the heart to the capillaries where exchange occurs, and veins take blood to the heart. • The pulmonary circuit moves blood from the heart to the lungs and back, while the systemic circuit moves blood from the heart to all regions of the body and returns it to the heart. 9. Label the artery, capillary, and vein in the following diagram of the systemic circuit: Which of these vessels: d. has the thinnest walls? __________________ e. has the strongest walls? _________________________ f. has flabby walls? a. _________________________ heart g. moves blood due to blood pressure? _________________________ h. moves blood due to skeletal muscle b. contraction? _________________________ i. contains valves pointing toward the heart? _________________________ 218 Closed circulatory system c. mad17743_ch23.qxd 3/10/06 2:01 PM Page 219 10. Trace the path of blood in the pulmonary circuit from the heart to the lung and return. 11. Trace the path of blood in the systemic circuit to the kidneys and return. 12. How does the hepatic portal system differ from the pulmonary and systemic circuits? LYMPHATIC SYSTEM (P. 403) • The lymphatic vessels form a one-way system that transports lymph from the tissues and fat from the digestive tract to certain veins. 13. Explain the following statements: a. The lymphatic system is a one-way system. _____________________________________________________ b. Lymphatic vessels are like cardiovascular veins. _________________________________________________ c. Lymph begins as tissue fluid. __________________________________________________________________ CARDIOVASCULAR DISORDERS (PP. 403–404) • Although the human cardiovascular system is very efficient, it is still subject to degenerative disorders. 14. Associate the following: a. hypertension with stroke: ______________________________________________________________________ b. hypertension with heart attack: _________________________________________________________________ c. blocked arteries with two treatments: ___________________________________________________________ 23.3 BLOOD: A TRANSPORT MEDIUM (PP. 405–408) • In humans, blood is composed of cells and a fluid called plasma that contains proteins and various other molecules and ions. • Blood clotting is a series of reactions that produce a clot consisting of fibrin threads in which red blood cells are trapped. • Exchange of substances between blood and tissue fluid across capillary walls supplies cells with nutrients and removes wastes. 15. Plasma is mostly a. _____________________ 16. The red blood cells, scientifically called and b. _____________________. a. _____________________, Upon maturation, they are small, biconcave disks that lack a d. _____________________. and are made in the c. _____________________ After about 120 days, red blood cells are destroyed in the f. _____________________. characterizes the condition of b. _____________________. and contain e. _____________________ An insufficient number of red blood cells or not enough hemoglobin g. _____________________. 17. What is erythropoietin? 18. White blood cells, scientifically called a. _____________________, are made in the b. _____________________. 19. Three differences between red blood cells and white blood cells are that white blood cells are a. _____________ in size than red blood cells, have a(n) b. ___________________, and do not contain c. ___________________. 219 mad17743_ch23.qxd 3/10/06 2:01 PM Page 220 20. Match the descriptions with these types of white blood cells: 1. lymphocyte 2. monocyte 3. neutrophil a. an agranular leukocyte with a large, round nucleus; the B cells produce antibodies and the T cells destroy cells that contain viruses b. an abundant granular leukocyte with a multilobed nucleus that phagocytizes pathogens c. a large, spherical cell that transforms into a macrophage 21. The following shows the reactions that occur as blood clots: platelets → prothrombin activator prothrombin → thrombin fibrinogen → fibrin threads a. Does the left side or the right side list substances always present in the blood? __________________ b. Which substances are enzymes? _________________________ c. Which substance is the actual clot? _________________________ 22. Label the following diagram of capillary exchange: a. Key: Net blood pressure Net osmotic pressure around cells b. of capillary c. tissue cell d. water oxygen glucose amino acids wastes carbon dioxide water e. of capillary 23. Match the phrases below with the numbered conditions/events. The numbers can be used more than once. 1. osmotic pressure 2. blood pressure 3. gas exchange 4. nutrients for waste exchange 5. diffusion a. oxygen out, carbon dioxide in b. Water is retrieved. c. pressure at arterial end, represented by arrowheads pointing out d. pressure at venous end, represented by arrowheads pointing in e. amino acids out, waste in 24. What happens to excess tissue fluid? 220 mad17743_ch23.qxd 3/10/06 2:01 PM Page 221 K E Y WO R D C RO S S WO R D Review key terms by completing this crossword puzzle, using the following alphabetized list of terms: 1 artery blood pressure capillary cardiovascular system diastole heart hemoglobin plasma portal system pulmonary circuit systemic circuit systole vein 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 Across 1 circulatory pathway between the lungs and the heart (two words) 3 blood vessel that transports blood away from the heart 6 blood vessel that arises from venules and transports blood toward the heart 7 contraction period of a heart during the cardiac cycle 9 microscopic blood vessel; gas and nutrient exchange occurs across its walls 11 force of blood pushing against the inside wall of an artery (two words) 12 circulatory pathway of blood flow between the tissues and the heart (two words) Down 1 pathway of blood flow that begins and ends in capillaries, such as the one found between the small intestine and liver (two words) 2 series of blood vessels that distributes blood under the pumping action of the heart (two words) 4 liquid portion of blood; contains nutrients, wastes, salts, and proteins 5 red respiratory pigment of erythrocytes for transport of oxygen 8 relaxation period of a heart during the cardiac cycle 10 muscular organ that pumps the blood, propelling it through blood vessels 221 mad17743_ch23.qxd 3/10/06 2:01 PM Page 222 CHAPTER TEST OBJECTIVE QUESTIONS Do not refer to the text when taking this test. 1. Which one does NOT apply to a hydra and planarian? a. They both have a cardiovascular system. b. Cells carry out gas exchange independently. c. They both have a gastrovascular cavity. d. Nutrients diffuse from cell to cell. 2. Indicate the correct pathway of blood flow. a. arteries, capillaries, veins b. arteries, veins, capillaries c. veins, arteries, capillaries d. veins, capillaries, arteries 3. The function of the heart valves is to a. prevent the backward flow of blood. b. pump the blood. c. separate the two sides of the heart. d. signal the chambers to contract. 4. When the atria contract, the ventricles are in a. diastole. b. systole. 5. Which chamber has the thickest walls because it pumps blood into the systemic system? a. right atrium b. right ventricle c. left atrium d. left ventricle 6. The heart sounds are due to a. atria recoiling. b. the closing of the valves. c. the heart muscle contracting. d. Both a and c are correct. 7. The chamber of the heart that receives blood from the pulmonary veins a. is the right atrium. b. is the left atrium. c. contains O 2 -rich blood. d. contains O 2 -poor blood. e. Both a and d are correct. f. Both b and c are correct. 8. The SA node a. works only when it receives a nerve impulse. b. is located in the left atrium. c. initiates the heartbeat. d. All of these are correct. 9. Arteries a. carry blood away from the heart. b. carry blood toward the heart. c. have valves. d. Both b and c are correct. 10. All arteries carry O 2 -rich blood, and all veins carry O 2 -poor blood. a. true b. false 222 11. Which of these vessels have the weakest walls? a. arteries b. veins c. Both are the same. 12. The venae cavae a. carry blood to the right atrium. b. carry blood away from the right atrium. c. join with the aorta. d. have a high blood pressure. 13. The coronary arteries carry blood a. from the aorta to the heart tissues. b. from the heart to the brain. c. directly to the heart from the pulmonary circuit. d. from the lungs directly to the left atrium. 14. At the capillary, fluid is forced out of the vessel by the a. blood pressure. b. osmotic pressure. 15. Gas exchange occurs in a. pulmonary capillaries. b. renal capillaries. c. coronary capillaries. d. all capillaries. 16. Select the incorrect statement about red blood cells. a. contain hemoglobin b. contain iron c. respond during inflammation d. transport oxygen 17. Select the incorrect statement about white blood cells. a. involved in blood clotting b. exist in agranular and granular forms c. Lymphocyte is one type. d. Neutrophil is one type. 18. For the coagulation of blood, fibrinogen is converted to a. calcium. b. fibrin threads. c. prothrombin. d. thrombin. 19. In tracing the path of blood to the liver and back to the heart, you would not mention the a. hepatic portal vein. b. aorta. c. pulmonary veins. d. inferior vena cava. mad17743_ch23.qxd 3/10/06 2:01 PM Page 223 CRITICAL THINKING QUESTIONS The introduction to this chapter is about the cardiovascular system. 20. An artificial pacemaker mimics the action of which part of the heart? ________________________________________ 21. The heart is autorhythmic. What does that mean? ____________________________________________________________ 22. The body often has layers of control. What outside influences can affect the beating of the heart? _____________ ____________________________________________________________________________________________________________ 23. If the beat of the heart is irregular, how might it be detected? ________________________________________________ Test Results: ______ number correct ÷ 23 = ______ × 100 = ______ % EXPLORING THE INTERNET ARIS, the Essentials of Biology website: http://www.mhhe.com/maderessentials ARIS, the website for Essentials of Biology, offers access to a wide variety of tools to help students learn biological concepts and to reinforce their knowledge. Online study aids such as practice quizzes, interactive activities, animations, labeling exercises, flashcards, and much more are organized according to the major sections of each chapter. There is even an online tutorial service! ANSWER KEY CHAPTER KEY TERMS a. blood pressure b. lymph c. vein d. artery e. pulmonary circuit f. systemic circuit g. heart h. diastole i. systole j. pulse k. blood l. capillary m. plasma n. hemoglobin o. lymphatic vessel STUDY EXERCISES 1. a. 1 b. 3 c. 2 d. 2 e. 1 f. 3 2. a. 2 b. 1 c. 3 d. 3 e. 1 3. pulmonary blood to the lungs and systemic blood to the tissues 4. a. aorta b. pulmonary trunk c. pulmonary arteries d. pulmonary veins e. left atrium f. bicuspid valve g. septum h. left ventricle i. inferior vena cava j. right ventricle k. tricuspid valve l. right atrium m. pulmonary semilunar valve n. aortic semilunar valve o. superior vena cava; see also Figure 23.4, page 399, in text 5. a. pulmonary artery b. carries blood away from the heart c. carries blood toward the heart 6. a. vena cava, right atrium, atrioventricular valve, right ventricle, pulmonary semilunar valve, pulmonary trunk, pulmonary arteries, lungs b. lungs, pulmonary veins, left atrium, atrioventricular valve, left ventricle, aortic semilunar valve, aorta 7. Atria Ventricles Systole Diastole Diastole Systole Diastole Diastole 8. a. SA b. atria c. AV d. ventricles e. systole f. diastole g. atrioventricular h. ventricles i. semilunar 9. a. vein b. capillary c. artery d. capillary e. artery f. vein g. artery h. vein i. vein 10. right ventricle, pulmonary artery, lungs, pulmonary vein, left atrium 11. left ventricle, aorta, renal artery, kidneys, renal vein, inferior vena cava, right atrium 12. The hepatic portal system begins and ends in the capillaries. A pulmonary circuit carries blood to the lungs, and from the lungs back to the heart. The systemic circuit takes blood throughout the body. 13. a. It begins at lymphatic capillaries and goes to cardiovascular veins in shoulders. b. Vessel walls are flabby and have valves. c. Lymphatic capillaries take up excess tissue fluid. 14. a. increased blood pressure can cause a cranial arteriole blood vessel to burst. b. Hypertension leads to plaque and blockage of a coronary artery. c. coronary bypass operation and use of a stent 15. a. water b. plasma proteins 16. a. erythrocytes b. red bone marrow c. nucleus d. hemoglobin e. liver f. spleen g. anemia 17. a molecule that stimulates production of red blood cells 18. a. leukocytes b. bone marrow 19. a. larger b. nucleus c. hemoglobin 20. a. 1 b. 3 c. 2 21. a. left side b. prothrombin activator and thrombin c. fibrin threads 22. a. tissue fluid b. arterial end c. salt d. plasma protein e. venous end 23. a. 3, 5 b. 1 c. 2 d. 1 e. 4, 5 24. taken up by lymphatic vessels 223 mad17743_ch23.qxd 3/10/06 2:01 PM Page 224 KEYWORD CROSSWORD 1 P U L M O N A R 2 Y C I R C U T E R Y E I N A P I P R CHAPTER TEST 1. a 2. a 3. a 4. a 5. d 6. b 7. f 8. c 9. a 10. b 11. b 12. a 13. a 14. a 15. d 16. c 17. a 18. b 19. c 20. SA node 21. It beats on its own without the need for nervous stimulation. 22. nervous stimulation and certain hormones 23. listening to the heart and taking an electrocardiogram I T L L A R Y S S U R E C I R C U A O 3 A R R D T 4 5 A P H L L E I O 6 A V M 7 S Y S T O L E A Y M G S A L D C T O I U E B A L M I S A S 8 9 10 N T R H 11 B L O O D L E E S A Y R S T T E 12 S 224 Y S T E M I C I T