* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Bile
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
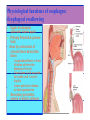
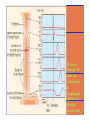
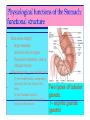
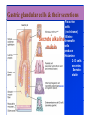
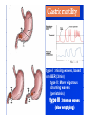
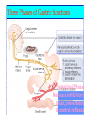
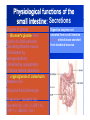
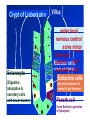
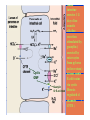
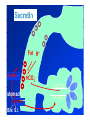
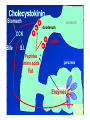
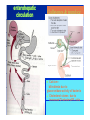
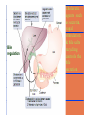
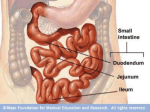
By: M.H.Dashti Lecture 3 Physiological functions of esophagus: Esophageal sw allow ing Upper esophageal sphincter closes again Primary Peristalsis pushes food down by contraction of circular fibers behind the bolus longitudinal fibers in front of bolus shorten the distance of travel Travel time is 4-8 seconds for solids and 1 sec for liquids Lower sphincter relaxes as food approaches Secondary peristaltic: central or enteric reflexes Pressure changes in pharynx pharynx ,esophagus & esophageal sphincters during swallowing LES is controlled by : Parasympathetic preganglionic fibers via ENS stimulatory & inhibitory neurons Vagal nucleus Post ganglionic Sympathetic Neurons Cholinergic sympathetic which inhibit Vagal neurons ENS neurons + -+ and directly stimulate lower ENS + + esophageal Cholinergic sphincter NANC neur Neuron L.E.S. MUSCLE VIP,ATP,NO 1:Achalasea : LES fails to open distension of esophagus feels like chest pain or heart attackTreatment :Air balloon ,Myotomy sympathectomy 2 : GERD/ hiatus hernia: LES fails to close post- prandial heart burn, regurgitation at 1 hour Avoiding a large meal (fatty foods) and lay down or Bending, smoking , alcohol & coffee, tomatoes, onions & mint taking H2 blocker 60 minutes before eating neutralize existing stomach acids with Digel Size when empty? large sausage stretches due to rugae Receptive relaxation due to oblique muscle Physiologically, it is divided into (1) the orad portion, comprising about the first two thirds of the body, (2) the caudad portion, comprising the remainder of the body plus the antrum. Two types of tubular glands: 1- oxyntic glands (gastric Gastric glandular cells & their secretions Paracrine cells (not shown) 1-Entrochromafin cells produce Histamine 2- D cells secretes Somatostatin Secrete alkaline mucin ,rennin Regulation of gastrin secretion Stimuli that increase gastrin secretion Luminal: Peptides and amino acids, Distention, Neural: Increased vagal discharge via GRP Blood-borne: Calcium, Epinephrine Stimuli that inhibit gastrin secretion Luminal: Acid, Somatostatin Blood-borne: Secretin, GIP, VIP, Glucagon, calcitonin Functions of the gastrin stimulation of gastric acid and pepsin secretion stimulation of the growth of the mucosa of the stomach and small and large intestines (trophic action). Stimulation of gastric motility Stimulation of insulin & glucagon secretion; however, only after a protein meal, and not after a carbohydrate meal (Glucagon stimulating intestinal factor ) Helicobacter pylori & Gastritis cytokines Stimulated by: Prostaglandins & parasympathetic vagal stimulation Inhibited by : Sympathetic nerve stimulation, Bile salts , Alcohol & Citric acid Secretin , VIP & -adrenergic agonists act via CAMP Ach Gastrin & cck act via IP3 & Ca2+ Mechanism for Potentiation effect of H+ is not known Pepsinogen & Gastric lipase type I type IItypeIII type I : mixing waves, based on BER (3/min) type II : More vigorous churning waves (peristalsis) type III :Intense waves (slow emptying) Intestinal Phase Nervous inhibition by local, prevertebral & central reflexes Myenteric plexus duodenum antrum Pyloric sphincter Sub mucosal plexus Regulation of Gastric Emptying Rates of gastric emptying depends on: 1- Gastetic motility 2- Pyloric sphincter status 3- Type of ingested meals Chem ical Digestion & absorp tion in the Stom ach Protein digestion begins HCl denatures (unfolds) protein molecules HCl transforms pepsinogen into pepsin that breaks peptides bonds between certain amino acids (aromatics) Rennin in infants digests casein Fat digestion continues gastric lipase ( tributirase ) splits the triglycerides in milk fat most effective at pH 5 to 6 (infant stomach) Absorption of Water ( especially if it is cold ) , Electrolytes , Some drugs (especially aspirin) By: M.H.Dashti Lecture 4 Secretions 2 types of glands 1- Brunner s glands- from pyloric to Oddi sphincter Secreting Alkaline mucus -Stimulated by parasympathetic -Inhibited by sympathetic -?stress related ulceration 2- crypts/glands of Lieberkuhn between villi Exocrine from Enterocyte Endocrine: Gasterin (G), Secretin (S) , cck ( I ),GIP ( K ) ,VIP ( v ) ,Motilin ( mo ) Digestive enzymes not secreted from small intestine except enterokinase secreted from duodenal mucosa Crypt of Lieberkuhn Enterocyte (Digestive , absorptive & secretary cells with brush border) Villus under local nervous control some minor hormonal control cells (VIP Mucous (simple goblet cells) ,secretin, CCK ) Endocrine cells (secrete hormones for control of gut function) Paneth cell (have Secretory granules of lysozyme) Cyclic GMP GC Guanylin Or E-coli toxin Small intestine secretes 1 L/ day of day ofiso iso osmotic alkaline secretion stimulated by guanylin ( secreted by enterocytes from pylorus to the rectum ) & heat stable E-coli toxins via cystic fibrosis regulated cl channels ( CFTR ) Fat H+ S cells stomach Secretin Bile S.I. HCO3- Stomach stomach duodenum CCK I cells Bile S.I. Peptides + Amino acids , pancreas Fat Enzymes Insulin Glucagon GIP (Gastric Inhibitory peptide ) from k cells Stimulated by carbohydrates in duodenum Stimulate insulin secretion (E. I. S. F ) VIP ( Vasoactive Intestinal Peptide ) Stimulated by H+ in duodenum Inhibits gastric acid secretion & Stimulates intestinal secretions VIPoma Motilin Stimulated by H+ in duodenum Co-related to Migratory Myoelextric Complex ( MMC ) Mixing (Segmentation) Contractions BER ( 12-9/min), influenced by local local mixing of chyme with intestin Weak peristalsis in comparison to the stomachtraveling 3-5 cm, chyme remains in SI for 4 to 5 hours a local reflex influenced by gastroenteric reflex & hormones( enhanced by gastrin, CCK, insulin, motilin, and serotonininhibited by secretin and glucagon ) Peristaltic rush: a local reflex highly influenced by the central reflex due to intense irritation. Interdigestive ( migratory ) myoelectric complexes ( MMC ): An intense central reflex ,slowly propagated from the stomach to the terminal ileum every 75-90 minutes in fasting associated with the release of moyilin Controlled by pressure differences and Neural events Ileo -colic & colonoileal reflexes Ileo- gastricic & gastro-ileal reflexes Ileal break Ileo- gastricic reflex along with the secretion of Oxyntomodulin & neurotensin from the ileum Components: water& eledtrolytes Cholesterol , TG, FA & PL (Lecithin ) bile salts = Na & K salts of bile acids ( 50% cholic acid, 30% chenodesoxycholic acid, 15% desoxycholic acid & 5% lithocholic acid all conjugated to glycine or taurine ) bile pigments (bilirubin) Alkalinephosphatase 0.5-1 Lof bile/day is secreted yellow--green in color yellow & pH 7.6 to 8.6 Bile p rod u ction & secretion ~ enterohepatic circulation Gallstones & jau nd ice Calcium bilirobinate due to glucoronidase activity of bacteria Cholesterol stones due to increased Cholesterol/PL ratio Bile regulation Choleretic agents su ch as secretin, vagal stim u lation & bile salts recycling controls the bile secretion cholagogu es agents e.g. CCK & Ach controls the gallblad d er em p tying This document was created with Win2PDF available at http://www.daneprairie.com. The unregistered version of Win2PDF is for evaluation or non-commercial use only.