* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download large intestine
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
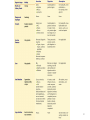
GIT HORMONES Lecture Physiology Dr. Mujeeb Ahmed Shaikh Dr.Mohammed Sharique Ahmed Quadri 1 2. OVERVIEW OF GASTRO-INTESTINAL HORMONES • - We will discuss the following hormones: Gastrin Secretin CCK Motilin Somatostatin GIP VIP 2 GASTRIN • Produced by G-cells in the stomach. • Stimulates the release of HCL and Pepsinogen in the stomach. • Increases gastric motility. • Increases ileal motility . • Relaxes Ileocecal Sphincter. • Induces mass movements in colon [because to help the contents moving through GIT on arrival of new meal in the stomach]. 3 SECRETIN • Secretin is released from small intestine when stomach acid contents come to duodenum. Functions • It inhibits gastric emptying to delay the acid contents of stomach to enter in the duodenum. • It inhibits gastric secretion. • It acts on pancreatic duct to produce large volume of watery, NaHCO3 secretion. • It stimulates the secretion of NaHCO3 rich bile in the liver by acting on the bile ducts. 4 CCK [Cholecystokinin] • CCK is released from the duodenum in response mainly to fat, to a lesser extent to protein products. • Actions of CCK I. Inhibition of gastric motility and secretion II. Stimulates pancreatic Acinar cells to secrete pancreatic enzymes [amylase, lipase, Trypsinogen, Chymotrypsinogen]. III. It causes contraction of gall-bladder and relaxation of sphincter of Oddi. IV. Regulator of food intake (key role in satiety) 5 MOTILIN • It is polypeptide and secreted by entrochromaffin cells and Mo cells in the stomach, small intestine and colon. • It causes contraction of smooth muscles in the stomach and intestine. • It level increases during inter-digestive state and controls GIT motility between the meals. 6 SOMATOSTATIN • It is secreted by D-Cells in pancreatic islets and by similar D-cells in GIT mucosa. • Somatostatin inhibits secretion of Gastrin, VIP, GIP, Secretin and Motilin. • Somatostatin secretion is stimulated by acid in the lumen of intestine. • It acts probably in a paracrine fashion. 7 GIP [Glucose Dependent Insulinotorphic Peptide] • GIP is released from the duodenum. • GIP stimulates release of insulin. – Stimulated by presence of meal specially glucose GIP stimulates insulin release . • Inhibits gastric motility – before it was called Gastric Inhibitory Peptide [this role is minimum]. 8 VIP [Vasoactive Intestinal Peptide] • VIP is found in nerves in the GIT. • It stimulates intestinal secretion of electrolytes and water. • Other action – relaxation of intestinal smooth muscle including sphincters. • Inhibition of gastric acid secretion. • It potentiates the action of acetylcholine in salivary glands. • VIP is also found in brain, blood, autonomic nerves. 9 10 REMINDER REGARDING GIT ENZYMES 11 Thank you 12 References • Human physiology by Lauralee Sherwood, seventh edition • Text book physiology by Guyton &Hall,11th edition • Text book of physiology by Linda .s contanzo,third edition 13