* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download A mole - MSE125
X-ray fluorescence wikipedia , lookup
X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy wikipedia , lookup
Molecular orbital wikipedia , lookup
Quantum electrodynamics wikipedia , lookup
Electron scattering wikipedia , lookup
Rutherford backscattering spectrometry wikipedia , lookup
Hydrogen atom wikipedia , lookup
Atomic orbital wikipedia , lookup
Tight binding wikipedia , lookup
Chemical bond wikipedia , lookup
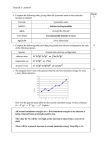
Recitation_1 Chapter 2 1 Q1. (a) How many grams are there in one amu of a material? (b) Mole, in the context of this book, is taken in units of grammole. On this basis, how many atoms are there in a gram-mole of a substance? 2 The Mole A mole is defined as the quantity of matter that contains as many objects (atoms, molecules, or whatever objects we are considering) as the number of atoms in exactly 12 g of 12C. The number of atoms in a 12 g of sample of 12C to be 6.0221421x1023 which is named as Avogadro's number (which has a symbol of NA). 1 mol 12C atoms = 6.02 x1023 12C atoms 1 mol H2O molecules = 6.02 x 1023 H2O molecules 1 mol NO3- ions = 6.02 x 1023 NO3- ions Molar mass is the mass in grams of one mole of a substance. The molar mass (in grams) of any substance is always numerically equal to its formula weight (in amu): One 12C atom weighs 12 amu = 1 mol 12C weighs 12 g One 24Mg atom weighs 24 amu = 1 mol 24Mg weighs 24 g One H20 molecule weighs 18.0 amu = 1 mol H20 weighs 18.0 g One NO3- ions weighs 62.0 amu = 1 mol NO3- ions weighs 62.0 g Q.2 (a) Cite two important quantum mechanical concepts associated with the Bohr model of the atom. (b) Cite two important additional refinements that resulted from the wave-mechanical atomic model. Q3. Give the electron configurations for the following ions: Fe2+, Fe3+, Al3+, Cu+, Ba2+, Br−, O2− and S2-. 6 40 Atomic number 91.224 Atomic symbol Atomic weight Zr - Elements on the left side and in the middle of the periodic table (except for hydrogen) are metallic elements or metals. - Nonmetals are separated from metals. - Metalloids exist between metals and nonmetals. 7 7 Electron Configurations and the Periodic Table Atom Expected Electron Configuration Experimental Electron Configuration 24Cr 1s2 2s2 2p6 3s2 3p6 4s2 3d4 1s2 2s2 2p6 3s2 3p6 4s1 3d5 29Cu 1s2 2s2 2p6 3s2 3p6 4s2 3d9 1s2 2s2 2p6 3s2 3p6 4s1 3d10 8 Q4. Without consulting Periodic Table, determine whether each of the electron configurations given below is an below is an inert gas, a halogen, an alkali metal, an alkaline earth metal, or a transition metal. Justify your choices. (a) 1s2 2s2 2p6 3s2 3p6 3d7 4s2 (b) 1s2 2s2 2p6 3s2 3p6 (c) 1s2 2s2 2p5 (d) 1s2 2s2 2p6 3s2 (e) 1s2 2s2 2p6 3s2 3p6 3d2 4s2 (f) 1s2 2s2 2p6 3s2 3p6 4s1 9 Electron Configurations and the Periodic Table • Elements in any given group in the periodic table have the same type of electron arrangements in their outermost shells. • The outer shell electrons those that lie outside the orbitals occupied in the next lowest noble gas element are called its valence electrons, whereas the electrons in the inner shells are called the core electrons. 10 Electron Configurations and the Periodic Table The periodic table is partitioned in to different elements based on their electron configurations. Block diagram of the periodic table showing the groupings of the elements according to the type of orbital being filled with electrons. 11 Q5. (a) Briefly cite the main differences between ionic, covalent, and metallic bonding. (b) State the Pauli exclusion principle. 12 Q6. Determine the number of covalent bonds that are possible for atoms of the following elements: germanium, phosphorus, selenium, and chlorine. 13 14 14 Q7. Compute the percent ionic character of the interatomic bonds for TiO2 compound. 15 Electronegativity - Tells us whether a given bond will be nonpolar covalent, polar covalent or ionic. - The ability of an atom in a molecule to attract electrons to itself. - Ranges from 0.7 to 4.0. Smaller electronegativity Larger electronegativity 16 Q8. (a) What type(s) of bonding would be expected for each of the following materials: brass (a copper-zinc alloy), rubber, barium sulfide (BaS), bronze (a copper-tin alloy), nylon, and aluminum phosphide (AlP)? 17