* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Welcome! 3/12/14
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
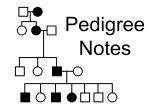
Welcome! 3/12/14 OBJECTIVE—Students will analyze and interpret Punnett Squares and Pedigrees of autosomal and sex-linked traits by showing 80% mastery on Quiz 5.3 CATALYST— Aliens from Mars have 2 eyes (dominant) or 4 eyes (recessive). This gene is carried on the Xchromosome. Show the cross of a heterozygous 2-eyed female with a 4-eyed male. HOMEWORK/REMINDERS— All missing work DUE 3/28/14 END OF 3rd Quarter Let’s Review The 44 non sex chromosomes are called autosomes ◦ Genes found on these chromosomes are called autosomal traits The other 2 chromosomes are sex chromosomes ◦ They are X and Yà females are XX and males are XY Review The genes found on the sex chromosomes are called sex-linked ◦ They are found on the X chromosome Females have 2 copies of these alleles, males only have 1 ◦ This is how females can be a carrier of recessive sex-linked disorders Review Practice Hemophilia is a sex-linked recessive disorder. ◦ What is the genotype of a male with hemophilia? ◦ What is the genotype of a female carrier? ◦ SHOW the cross (Punnett Square) Pedigrees • Pedigrees are maps of inheritance • Help us determine if a trait is dominant, recessive, or sexlinked. • Pedigrees are just like maps and can trace the path of a trait through many generations and marriages. #1-2 Generations numerals are noted with Roman ◦ The generations start at the top and go down. Each individual in a generation is labeled with a regular number How many generations are in this pedigree? I II III IV #3 In a pedigree, males are represented by squares ◦ If a square is colored in, it means that male has the trait that is being discussed How many males are there on your worksheet? ____ How many of the males have hemophilia?____ #4 Females are represented by circles ◦ If a circle is colored in, the female has the trait ◦ SOMETIMES, the circles will be half coloredin. This means that the female is a CARRIER, she is heterozygous for the trait. #4 Carriers Many times, Pedigrees will make it easy and show the carriers by giving them a half colored-in circle on the pedigree. How many females are there on your pedigree? __ How many have hemophilia? __ How many of the females are carriers? __ #5 Helpful hint If there are more affected individuals than unaffected, the trait in question is DOMINANT! If there are fewer affected individuals, the trait is RECESSIVE! (Carriers are not affected) Is the trait on our pedigree dominant or recessive? #6 Marriages are noted by a horizontal line connecting a circle and a square ◦ How many marriages are there in your pedigree? #7 A line perpendicular to a marriage line indicates the offspring. ON YOUR PEDIGREE: ◦ How many children did the first couple in generation I have? ____ ◦ How many children did the couple in generation III have? ____ Determining the genotypes in a pedigree for Sex-Linked Traits Determining genotypes from pedigrees is EASY Sex-linked traits: ◦ Step 1: Determine the genotypes of the males first. Determine if the trait is dominant or recessive, then give the appropriate allele to their X chromosome. Step 2: Determine the female’s genotypes ◦ If the trait is recessive, any female with the trait must have 2 recessive alleles attached to her X chromosomes ◦ How many females have genotype XnXn ?_____ ◦ If the female has the dominant trait, she can either be homozygous dominant, or a carrier (heterozygous) The easiest way to determine this, is to look at her offspring. If ANY offspring have the trait, male or female, the mother MUST be a carrier, WHY? ◦ What is the genotype of individual III.4? ___ Determining the genotypes in a pedigree for Sex-Linked Traits HINT: Sex linked traits often show passing from MOTHER TO SON. More MALES are affected than females. Determining the genotypes in a pedigree for Autosomal Traits What trait is colored in? Look Look at the parents… at the kids… ◦ Dominant usually appears more often ◦ Recessive will appear less often ◦ If both parents do NOT show the trait, but a child does…the trait is RECESSIVE Sometimes you might not be able to determine if a dominant genotype is BB or Bb If it is an autosomal trait, it will usually affect males and females equally. Pedigree Practice Complete Pedigree Practice. Stay focused! Look for clue words. Ask yourself ◦ Is it showing the dominant or recessive? ◦ Is it sex-linked or autosomal? ◦ Who does it affect? More males or females? ◦ Whose genotype is easiest to figure out? Pedigree Practice Pedigree Practice Pedigree Practice Pedigree Practice Your Turn! Goal: Create a pedigree to show the passing of hitchhiker’s thumb. (HINT: the “affected” individuals will have a hitchhiker thumb). Directions: 1. 2. 3. Read the following family clues out loud as a group. Review the key for making pedigrees... Draw the pedigree for this family on a piece of chart paper. DRAW IN PENCIL FIRST. You may also want to make a rough draft on a piece of scratch paper. 4. Read the following description and color in the squares or circles for the affected individuals. 5. Once you’re pedigree has been approved by Mrs. Reigel, you can make a final draft on your chart paper, add colors and a KEY! Don’t forget to add Roman Numerals for each generation, and numbers to each person in a generation. 6. Now look back at your pedigree, add GENOYPES to each person! (If an individual is dominant, you might have to write “Rr or RR”) *** BONUS: If you finish early, complete the analysis questions found on the back of your directions.*** Quiz 5.3—Sex Linked Traits and Pedigrees Stay focused ANNOTATE genotypes and phenotypes Eliminate answers Ask yourself ◦ Is it dominant or recessive? ◦ Is it sex-linked or autosomal? ◦ Who does it affect? ◦ Whose genotype is easiest to figure out? Exit Slip 1. 2. 3. How many school days until the HSA? When does 3rd Quarter end? What do YOU need to do before the end of 3rd Quarter to make sure you are on track? (List at least 3 things)