* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Unit One: Introduction to Physiology: The Cell and General Physiology
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
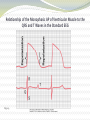
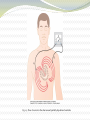
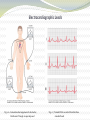
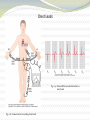
Chapter 11: The Normal Electrocardiogram Guyton and Hall, Textbook of Medical Physiology, 12th edition Characteristics of the Normal ECG Fig. 11.1 The Normal Electrocardiogram (ECG) Characteristics (cont.) • P-Wave-electrical potentials generated when the atria depolarize before atrial contraction • QRS Complex-potentials generated when the ventricles depolarize before contraction • T wave-caused by repolarization of the ventricles Fig. 11.2 Recording the depolarization wave (A and B) and the repolarization wave (C and D) from a cardiac muscle fiber Relationship of the Monophasic AP of Ventricular Muscle to the QRS and T Waves in the Standard EEG Fig. 11.3 Characteristics of the Normal EEG (cont.) • From Figure 11.1 a. Relationship of atrial and ventricular contraction to the waves of the EEG b. Voltage and time calibration of the EEG c. Normal voltages in P-Q or P-R interval d. Normal voltages in the Q-T interval e. Rate of Heartbeat Flow of Current Around the Heart During the Cardiac Cycle Fig. 11.4 Instantaneous potentials develop on the surface of a cardiac muscle mass that has been depolarized in its center Fig. 11.5 Flow of current in the chest around partially depolarized ventricles Flow of Current (cont.) • The average current flow occurs with negativity toward the base of the heart and with positivity toward the apex. • In normal hearts, the current flows from negative to positive in the direction from the base to the apex. Electrocardiographic Leads Fig. 11.6 Conventional arrangement of electrodes; Einthoven’s Triangle is superimposed Fig. 11.7 Normal EEG’s recorded from the three standard leads EEG Leads (cont.) • Lead I-Negative terminal to the right arm and positive terminal to the left arm • Lead II-Negative terminal to the right arm and positive terminal to the left leg • Lead III-Negative terminal to the left arm and positive terminal to the left leg • Einthoven’s Triangle-depicts how the arms and left leg form the apices of a triangle around the heart Chest Leads Fig. 11.9 Normal EEGs recorded from the six chest leads Fig. 11.8 Connections for recording chest leads Augmented Unipolar Limb Leads Fig. 11.10 Normal EEGs from the three augmented unipolar limb leads