* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Treatments For Psychological Disorders
Art therapy wikipedia , lookup
Adherence management coaching wikipedia , lookup
Professional practice of behavior analysis wikipedia , lookup
Methods of neuro-linguistic programming wikipedia , lookup
Primal therapy wikipedia , lookup
Intensive short-term dynamic psychotherapy wikipedia , lookup
Albert Ellis wikipedia , lookup
Gestalt therapy wikipedia , lookup
Transtheoretical model wikipedia , lookup
Behaviour therapy wikipedia , lookup
Dance therapy wikipedia , lookup
Chelation therapy wikipedia , lookup
Residential treatment center wikipedia , lookup
Conversion therapy wikipedia , lookup
The Radical Therapist wikipedia , lookup
Emotionally focused therapy wikipedia , lookup
Dodo bird verdict wikipedia , lookup
Animal-assisted therapy wikipedia , lookup
Equine-assisted therapy wikipedia , lookup
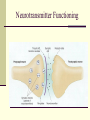
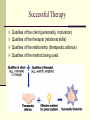
Treatments for Psychological Disorders Biological and Psychological Based Treatments Early Attempts at Biological Intervention Coma and convulsive therapies Insulin coma therapy Electroconvulsive shock therapy (ECT) Bilateral ECT and Unilateral ECT Shock lasting 1.5 Seconds 3 x week (2-4 weeks) Memory Impairment for Months After Neurosurgery Psychosurgery or Neurosurgery The prefrontal lobotomy Very, Very Seldom Today Due to Medications Psychopharmacological Methods of Treatment Note: Keep in mind that the role of neuro- transmitters in mental illness is not well known. The use of medication is based on theory not fact Psychopharmacology- the science of determining which drugs alleviate which mental disorders and why they do so Antipsychotic Medications Neuroleptics or Major Tranquilizers Traditional Antipsychotics included side effects including Tardive Dyskinesia- a disfiguring disturbance of motor control, particularly of the facial muscles Atypical Antipsychotics Zyprexa, Geodon, Risperdal, Clozaril, Seraquil Side Effects Include: Dry Mouth, Motor Disturbances, Sedation, Weight Gain, Damage to Liver (blood levels need to be taken), Risperdal (lactation in females) Effectiveness (20-30% do not respond) Neurotransmitter Functioning Antidepressant Medications Monoamine oxidase (MAO) inhibitors Inhibits breakdown of neurotransmitters Used in depression with hypersomnia Requires Dietary Supplement Tricyclic antidepressants (TCAs) Inhibits reuptake of serotonin & norepinephrine Cause death with overdose Selective serotonin re-uptake inhibitors (SSRI) Prozac, Zoloft, Paxil, Luvox, Lexapro, Celexa Not as selective as once thought Should be taken for minimum of 9-12 months Antianxiety Medications Anxiolytics or Minor Tranquilizers Benzodiazepines Sedative effect Dependency Issues Used to Treat Alcohol Withdrawal High Relapse Rate After Termination of Medication Probably stimulate GABA an inhibitory neurotransmitter Side Effects Include: Drowsiness and Lethargy Lithium for the bipolar mood disorders Long Term Use Side Effects Include: thyroid dysfunction, kidney damage, memory and motor speed problems Medication and Children Do anti-depressants increase suicidality? Natural increase in likelihood to suicide when mood improves Medications do result in an initial adjustment for the body that can be agitating Important to monitor the individuals mood in the first 10 days A client’s response to a medication in the first 10- 14 days is often predictive of how effective the medication will be in alleviating antidepressant Psychologically Based Therapies An Overview of Psychological Treatment Who provides psychotherapeutic services? Psychologists, Psychiatrists, Social Workers Educational Backgrounds Vary Theories of Change Vary (see next slide) Commonalities in Effective Therapists Form a Therapeutic Alliance with Their Clients Focus on Client Goals Use Research Based Interventions Psychotherapy Psychotherapy- the treatment of mental disorders by psychological methods. To Achieve changes a therapist may: Change maladaptive behavior patterns Minimize or eliminate influences from the environmental condition Improve interpersonal skills or other competencies Resolve disabling conflicts among motives Modify dysfunctional beliefs Reduce or remove distressing or disabling emotional reactions. Foster a clear cut sense of identity An Overview of Psychological Treatment Why do people seek therapy? Those in highly stressful situations. Referred by physician or other professional. Forced by spouse, parent, or court. Who has the best prognosis? (YAVIS) Young, Attractive, Verbal, Intelligent, and Successful Individuals. Why YAVIS? Motivation, Cognitive Abilities, Malleable The client’s contribution to the success of treatment includes his or her motivation and expectation Successful Therapy Qualities of the client (personality, motivation) Qualities of the therapist (relational skills) Qualities of the relationship (therapeutic alliance) Qualities of the method being used. Stages of Change Prochaska’s Levels of Change Pre-contemplation Contemplation Preparation Action Maintenance Termination Customer or not a customer Psychodynamic Therapies: Freudian psychoanalysis Four Basic Techniques Free association Analysis of dreams Manifest content Latent content Analysis of resistance An unwillingness or inability to talk about certain thoughts, motives or experiences Analysis of transference Transference- the process whereby clients project onto the therapist attitudes and feelings they had in a past relationship with a parent or other person close to them Countertransference- the process in which the therapist reacts in accord with the client’s transferred attributions rather than objectively Psychodynamic Therapies: Since Freud Interpersonal therapy Object relations Self psychology Other interpersonal variations Psychodynamic therapies tend to be time consuming and expensive They suggest that past issues need to be resolved for change to occur Efficacy vs Effectiveness of of Psychodynamic Approaches Behavior Therapy Guided exposure Systematic desensitization Graduated scenes Require an inconsistent bx from the client while exposed (real or imagined) to the feared stimuli In Vivo Exposure Aversion therapy Use of Punishment (antabuse) Driving Movie Pornography and Children Walking In Modeling, Imitation, and Role Playing Behavior Therapy Systematic Use of Reinforcement Also referred to as Contingency Management Response Shaping- a behavior therapy technique using positive reinforcement to establish by gradual approximation a response that is actively resisted or is not initially in a person’s behavioral repertoire Remove Reinforcements or Add Reinforcements Super-Nanny Token Economies Behavioral Contracting (marital tx and social exchange) Biofeedback Treatment Monitor Physical, Convert to Signal, Prompt Feedback Cognitive & Cognitive-Behavioral Tx Rational emotive behavior therapy (REBT) Focus on changing core irrational beliefs See table 3.5 Stress-inoculation therapy (SIT) Three stages include: cognitive preparation, skill acquisition & rehearsal, and application and process. Beck’s cognitive therapies Focus on illogical thinking about self, world, and future. Humanistic-Experiential Therapies Client-Centered (person-centered) therapy Nondirective Unconditional Positive Regard Self-actualization Existential Therapy The human predicament Focus on here and now Therapist is to be authentic Gestalt Therapy Integration of thought, feeling, and action into one’s self-awareness Therapy for Interpersonal Relationships Couples Counseling (Marital Therapy) Family Systems Therapy Systemic Recursiveness Identified Patient Homeostasis Structural Family Therapy (Salvador Minuchin) Family Rules and Boundaries Eclecticism and the Integration of the Psychotherapies How do they all fit together? How Does One Measure Success in Psychotherapy? Objectifying and quantifying change Would change occur anyway? Can therapy be harmful? Psychotherapy and Society Social values and psychotherapy Psychotherapy and cultural diversity EVALUATING PSYCHOTHERAPIES Is psychotherapy effective Client perceptions indicates that 3 out of 4 are satisfied while 1 in 2 are very satisfied. Reports may be inaccurate due to crisis effect, effort effect, and liking the therapist Clinician’s Perceptions Most testify to therapy success (big surprise) Outcome Research Indicates that the average therapy outcome for clients who receive treatment surpasses that of the client who remains untreated. “Those not undergoing therapy often improve, but those undergoing therapy are more likely to improve.” On average psychotherapy is somewhat effective (it depends on the diagnosis obviously) Psychotherapy has been shown to decrease medical costs. Contrary to Myer’s presentation, some treatment approaches have been proven to be more effective than others. UNRESOLVED ISSUES Efficacy versus effectiveness