* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download ANSWER SHEET for SHORT CIRCUITS SCIENCE OLYMPIAD IT`S
Regenerative circuit wikipedia , lookup
Electronic engineering wikipedia , lookup
Resistive opto-isolator wikipedia , lookup
Index of electronics articles wikipedia , lookup
Rectiverter wikipedia , lookup
Electric battery wikipedia , lookup
Surge protector wikipedia , lookup
Rechargeable battery wikipedia , lookup
RLC circuit wikipedia , lookup
Integrated circuit wikipedia , lookup
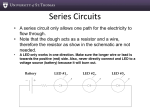
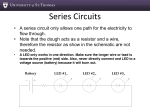
ANSWER SHEET for SHORT CIRCUITS SCIENCE OLYMPIAD IT’S ELEMENTARY MAY 22ND , 2010 A. 1. _____ 2. _____ 3. _____ B. 4. _____ 5. _____ 6. _____ C. 7-8. Tape your wire here _________________________________________________ D. 9. _________________ 10. ._________________ 11. _________________ 12. _________________ 13. _________________ 14. _________________ 15. _________________ 16. _________________ E. 17. F. G. 18. 20. 21. 22. 23. 24. _________ _________ _________ _________ _________. . 25. 26. 27. 28. 29. 30. 31. 32. 33. _________ _________ _________ _________ _________ _________ _________ _________ _________ 19. NOTE! YOU MAY KEEP A COPY OF STATION F QUESTIONS AND CONTINUE TO WORK ON UNTIL THE END OF THE EVENT! 34. 35. 36. 37. 38. _________ _________ _________ _________ _________ Names of Competitors __________________________________ School Team __________________________________________ H. 39. 40. 41. 42. 43. 44. 45. ANSWER SHEET for SHORT CIRCUITS SCIENCE OLYMPIAD IT’S ELEMENTARY MAY 22ND , 2010 _______________ _______________ _______________ _______________ _______________ _______________ _______________ I. 46. 47. 48. 49. _____ _____ _____ _____ J. 50 -55 K. 56. (second tie-breaker) 57. Total voltage = ___________ L. 58. 59. Total voltage = _____________ Show work on sheet provided. (1st tie breaker and bonus!) Names of Competitors __________________________________ School Team __________________________________________ Short Circuits Station B Questions About Bulbs and Batteries in Circuits 1. Two identical bulbs, A and B, are connected in series to a single D-cell battery. The same bulbs are then connected in parallel to the same D-cell battery. Which statement below best describes the brightness of the bulbs in the circuits? A. Bulbs A and B will be brighter in the parallel circuit. B. Bulbs A and B will be brighter in the series circuit. C. Bulbs A and B will be the same brightness in either the series or parallel circuit. 2. Imagine a circuit with a 1.5 volt battery and one bulb. Imagine a similar circuit with a 3.0 volt battery and two bulbs connected in series. Which circuit has the brighter bulbs? A. Circuit with 1.5 volt battery and one bulb. B. Circuit with 3.0 volt battery and two bulbs. C. Bulbs in both circuits are at the same brightness levels. 3. As you add more light bulbs in parallel with a battery of constant voltage, what happens to the brightness of each bulb? A. Each bulb gets dimmer. B. Each bulb gets brighter. C. Each bulb will have the same brightness. Short Circuits Station B Questions About Bulbs and Batteries in Circuits 4. Which circuit will drain the battery the quickest? A. Series circuit with one bulb and one battery. B. Series circuit with two bulbs and one battery. C. Parallel circuit with two bulbs and one battery. 5. Why is a bulb brighter when it is powered by two batteries rather than one battery? A. Because the flow of electric current in the circuit is less. B. Because the flow of electric current is the same. C. Because the flow of electric current is more. 6. What is the effect of changing the wire in a circuit from a straight thick wire to a straight thin wire of the same length? A. Bulbs become dimmer. B. Bulbs become brighter. C. Bulbs remain the same level of brightness. Short Circuits Station C Wire Stripping 7 and 8. Take one piece of wire from the bag and strip approximately 1 cm from EACH end of the wire using the wire stripper provided. Use the scotch tape provided to tape the wire in the appropriate box on your answer sheet. Scoring: + 1 point for correctly stripping each end of the wire. Short Circuits Station D Schematic Diagram Symbols Identify the following symbols commonly found on schematic diagrams. Short Circuits Station E Lighting a Light Bulb Draw three ways you can light a light bulb using only one D-cell battery, one piece of wire (stripped on both ends) and one small light bulb. (You may use the materials supplied to help answer this question). 17. Here is one way …. 18. Here is another way … 19. Here is another way … Short Circuits Station F General Questions about Circuits and Electricity Electricity: in each set, circle the Odd One Out and explain why it does not fit with the others. (NOTE! – you may continue to work on this sheet at any time during the event.) Which is the Odd One? 20. D cell battery Filament Metal jacket Electrical tip Why it is the Odd One Out? Which is the Odd One? 21. Rubber eraser Plastic paper clip Copper penny Wood ruler Why it is the Odd One Out? Which is the Odd One? Why it is the Odd One Out? Which is the Odd One? Why it is the Odd One Out? Which is the Odd One? Why it is the Odd One Out? 22. Heat Sound Light Color 23. Battery Switch Wire Bulb 24. A G C D Short Circuits Station G Electrical Terms and Vocabulary Match the following terms with their definitions: 25. Circuit A. energy caused by the flow of electrical charges 26. Electric Motor B. a circuit in which the current must flow through each electrical device in order to complete the circuit 27. Conductor C. a complete path that electricity can flow through 28. Current Electricity D. a broken or incomplete path that electricity cannot flow through 29. D-Cell E. property of a material through which electricity has difficulty flowing 30. Electricity F. device that keeps too much electric current from flowing through wires 31. Grounded G. a material through which heat or electricity flows easily 32. Insulator H. a circuit in which each electrical device is independently connected to the electrical source 33. Open Circuit I. device that can open or close an electrical circuit 34. Parallel Circuit J. a battery that changes chemical energy into electrical energy 35. Resistance K. device that changes electrical energy into mechanical energy 36. Series Circuits L. when an electrical charge flows into the ground or surface of the earth 37. Fuse M. a moving electrical charge 38. Switch N. a material through which heat or electricity does not flow very well Short Circuits Station H Insulators and Conductors Look at each item in the list below. Identify each item as a conductor of electric current or as a non-conductor (insulator) of electric current. Item 39. House Key 40. Rubber Band 41. Coin 42. Wooden Toothpick 43. Metal Fork 44. Plastic Spoon 45. Aluminum Foil Conductor of Electric Current Non-conductor (Insulator) of Electric Current Short Circuits Station I For questions 46 – 49 below, select the one word that best completes the sentence. 46. The filament of a light bulb produces light and _____________ A. B. C. D. sound voltage current heat 47. Insulators ________________ the flow of electric current. A. B. C. D. increase decrease reverse do not change 48. The wires used to connect bulbs and batteries _______________ A. B. C. D. are good insulators are good conductors are bad conductors are not conductors or insulators 49. The base of a light bulb is made of metal so that _____________ A. B. C. D. It can break a circuit. It can be an insulator. It can conduct electric current. It can be an electric cell. Short Circuits Station J Schematic Diagram 50-55. (Note this question is worth 5 points) Draw a schematic diagram of a circuit that can be used to light two bulbs, such that if one bulb goes out, the other bulb remains lit. Short Circuits Station L Ohms Law (Bonus and 1st Tie Breaker) Complete the following table to demonstrate your understanding of Ohm’s Law and the rules for two resistors connected in series to a 12 volt battery. (Note – this is a challenging question and requires that you explored and practiced Ohms Law and you have a very good understanding of how current and voltages are related in a series circuit. Ohms Law is a mathematical relation between these three variables ( V – voltage, I – current, and R – resistance). The equation is V = I R. Voltage (volts) Current (amperes) Resistance (ohms) R1 2 R2 4 Total 12