* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Mod 3 - Aim #2 - Manhasset Public Schools
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
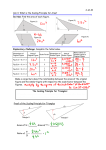
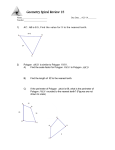
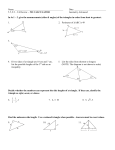
CC Geometry H Aim #2: What is the Scaling Principle for Area? Do Now: Find the area of each figure. Figure (1) Figure (2) Figure (4) Figure (3) Exploratory Challenge: Complete the table below. Dimensions of Original Figure Area of Dimensions of Area of Scale Factor Original Figure Similar Figure Similar Figure Fig.(1) b = 8, h = 3 3 Fig.(2) b = 5, h = 3 2 Ratio of Area of Similar Figure to Original Figure Fig.(3) b = 5, h = 4 Fig.(4) b = 3, h = 2 Make a conjecture about the relationship between the areas of the original figure and the similar figure with respect to the scale factor between the figures. The Scaling Principle for Triangles: If similar triangles S and T are related by a scale factor of r, then the 2 respective areas are related by a factor of r . Proof of the Scaling Principle for Triangles Triangle S Triangle T Area of S =_________ Area of T = __________ Ratio of = = The Scaling Principle for Polygons: If similar polygons P and Q are related by a scale factor of r, then the 2 respective areas are related by a factor of r . Polygon Q Polygon P Polygon Q is the image of Polygon P under a similarity transformation with scale factor r. How can we compute the area of a polygon like this? Proof of the Scaling Principle for Polygons Any polygon can be subdivided into non-overlapping triangles. Polygon Q Polygon P Each of the side lengths in polygon Q is r times the corresponding lengths in polygon P. Polygon P is divided into triangles T1, T2,T3, T4,T5 Polygon Q Polygon P By the Scaling Principle for Triangles, the areas of each of the triangles in Q is r times the areas of the corresponding triangles in P. 2 Area (Q) = r T1 + ______ + _______ + _______ + _________ 2 =r( 2 Area (Q) = r ( + + ) + + ) 2 The Scaling Principle for Area: If similar figures A and B are related by a scale factor of r, then their 2 respective areas are related by a factor of r . 1) Rectangles A and B are smilar and are drawn to scale. If the area of rectangle 2 A is 88 mm , what is the area of rectangle B? 2) If the scale factor between two similar figures is 1.2, what is the scale factor of their respective areas? 3) If the scale factor between two similar figures is , what is the scale factor of their respective areas? 4) In the following figure: a) Why is ΔABC ~ ΔEDC? b) What is the scale factor of the similarity transformation that takes ΔABC to ΔEDC? c) What is the value of the ratio of the area of ΔABC to the area of ΔEDC? Justify your answer. 2 2 d) If the area of ΔABC is 30 cm , what is the area of ΔEDC? (nearest cm ) 5) In ΔABC, DE connects two sides of the triangle and is parallel to BC. If the 2 area of ΔABC is 54 units and BC = 3DE, find the area of ΔADE. Horizontal and Vertical Scaling • By what scale factor was the unit square scaled horizontally? _____ How does the area of the resulting rectangle compare to the area of the unit square? • What is happening between the second and third image? • How are the two directions of the scaling related to each other?_________ • How does the area of the third image relate to the two scale factors that were applied? Summary: When a figure is scaled by factors a and b in two perpendicular directions, then its area is multiplied by a factor of ab. • The sides of a 1 x 1 square are scaled horizontally and vertically by factors a and b, respectively. The new area is ____ 1 1 Area =1 • The triangle with base 1 and height 1 is scaled by factors a and b, respectively. The area of the scaled triangle is ______ 1 1 Area = • What would be the effect on the original figure if a scale factor is between 0 and 1? 1) The small star has an area of 5. The large star is obtained from the small star by stretching by a factor of 2 in the horizontal direction and by a factor of 3 in the vertical direction. Find the area of the large star. 2) Figure T' is the image of figure T that has been scaled horizontally by a scale 2 factor of 4, and vertically by a scale factor of 1/3, If the area of T' is 24 units , what is the area of figure T? Let's Sum it Up! • The Scaling Principle for Area: If similar figures and are related by a scale 2 factor of r, then their respective areas are related by a factor of r . Name ______________________ Date ______________________ CC Geometry H HW #2 1. Figures E and F are similar and are drawn to scale. If the area of Figure E is 2 120 mm , what is the area of figure F? Determine the scale factor first. 2. Find the ratio of the scale fctor and the ratio of the areas of each pair of similar figures below. The lengths of corresponding line segments are shown. Consider the image on the left to be the pre-image. b. a. c. 3. An isosceles trapezoid has base lengths of 12 in. and 18 in. If the area of the 2 larger shaded triangle is 72 in , find the area of the smaller shaded triangle. 12 inches 18 inches 4. If the areas of two unique rectangles are the same, x, and both figures are dilated by the same scale factor r, what can we conclude about the areas of the dilated images? 5. In ΔABO, A'B' ll AB, OA' = 3, A'A = 6, OB' = 4, and B'B = 8. a) Determine the scale factor that was applied to ΔOAB to get ΔOA'B'. ______ O b) The area of ΔOA'B' is _____ the area of ΔOAB. 3 A' c) The area of quadrilateral ABB'A' is _______ the area of ΔOAB. 6 4 B' 8 A B 6. What is the effect on the area of a rectangle if... a) its height is doubled and base left unchanged? ________________________ b) its base and height are both doubled? ______________________________ c) its base were doubled and height cut in half? __________________________ Mixed Review: 1) Find PS and PR. Q T 8 6 P x+7 S x1 R 2) In parallelogram ABCD, diagonals AC and BD intersect at E. If ≮BAE = 5x – 5, ≮ABE = 3x + 23 and ≮BDC = 2x + 32: a) Is ABCD a rhombus? Justify your answer. b) Is ABCD a square? Justify your answer.