* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Activity: Star Classification - d
Dyson sphere wikipedia , lookup
International Ultraviolet Explorer wikipedia , lookup
Auriga (constellation) wikipedia , lookup
Corona Borealis wikipedia , lookup
Corona Australis wikipedia , lookup
Cassiopeia (constellation) wikipedia , lookup
Star of Bethlehem wikipedia , lookup
Cygnus (constellation) wikipedia , lookup
Observational astronomy wikipedia , lookup
Type II supernova wikipedia , lookup
H II region wikipedia , lookup
Planetary habitability wikipedia , lookup
Canis Major wikipedia , lookup
Star catalogue wikipedia , lookup
Aquarius (constellation) wikipedia , lookup
Perseus (constellation) wikipedia , lookup
Stellar classification wikipedia , lookup
Malmquist bias wikipedia , lookup
Stellar kinematics wikipedia , lookup
Timeline of astronomy wikipedia , lookup
Corvus (constellation) wikipedia , lookup
Stellar evolution wikipedia , lookup
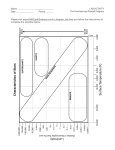
Activity: Star Classification Pre-Activity Notes: A star is an enormous, hot ball of gas held together by ________________. The gravity is so strong that it causes _____________________________ within the star. Stars are the only objects that heat & light the planets in a system. A star is a huge ball of ____________, usually made of ________________ (H) & _____________ (He). That ball of fire also gives off all kinds of light… There are __________________, ___________________, ___________________, & X-rays constantly emitted into space. Astronomers look at three main characteristics of stars. They study ______________________, ______________________, & ___________________ (size). Part 1: Exploring with Classification Each group will receive 1 set of 27 stars. Every star has: a color, name, temperature, size, & luminosity value o The luminosity is compared to the sun's luminosity. If a star has a luminosity value of 5, then it is 5 times brighter than our sun. If a star has a luminosity value of 0.1, than it is 1/10 the brightness of our sun. Explore the stars – spread them out on your table & create 3 different arrangements. Record the 3 different arrangements in each data table below. Arrangement #1 - We arranged our stars according to: List 3 observations about this arrangement: 1. 2. 3. Arrangement #2 - We arranged our stars according to: List 3 observations about this arrangement: 1. 2. 3. http://www.middleschoolscience.com 2003. Modified by E. Schumacher, 2009 Arrangement #3 - We arranged our stars according to: List 3 observations about this arrangement: 1. 2. 3. Part 2: Classification Challenge Is there a master way to organize the stars using ALL of this information? Using the large whiteboard, try to plot all of your stars. You choose the Y- and X- axis. Y Axis: Draw what you came up with in the box, but only draw circles & dots to represent the stars. DO NOT write the names of every star!! X Axis: Analysis & Conclusion: Color & Temperature 1. What do you think color tells us about temperature? ____________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________________ 2. A star’s color depends on its temperature. Color in the boxes below to show what color a star burns at each http://www.middleschoolscience.com 2003. Modified by E. Schumacher, 2009 temperature: Very Hot Hot Warm Cool Very Cool Size 3. What can we say about medium sized stars? __________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________________ 4. What can we say about large stars? _________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________________ Luminosity 5. What is the difference between luminosity & brightness? ________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________________ 6. What do you think temperature tells us about luminosity? _______________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________________ 7. What do you think size tells us about luminosity? ______________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________________ Special Stars 8. Name one star that is cool & dim: _____________________________ What is its temperature? __________________ Luminosity value? __________________ 9. Name one star that is cool & bright: _____________________________ What is its temperature? __________________ Luminosity value? __________________ 10. Name one star that is hot & dim: _____________________________ What is its temperature? __________________ Luminosity value? __________________ 11. Name one star that is hot & bright: _____________________________ What is its temperature? __________________ Luminosity value? __________________ 12. Complete the table below. The first row is done for you. You may need a textbook! Name of Special Star Size Temperature Luminosity Example Blue Giant Massive Really Hot Really Bright Naos Small Hot Dim Red Giant Supergiant Blue Dwarf Red Dwarf http://www.middleschoolscience.com 2003. Modified by E. Schumacher, 2009