* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Traits and Alleles Laboratory
Genetically modified crops wikipedia , lookup
Population genetics wikipedia , lookup
Heritability of IQ wikipedia , lookup
Dual inheritance theory wikipedia , lookup
Microevolution wikipedia , lookup
Behavioural genetics wikipedia , lookup
Genetic drift wikipedia , lookup
Hardy–Weinberg principle wikipedia , lookup
Designer baby wikipedia , lookup
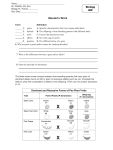
Title: Traits and Alleles 1. Introduction 1.1. The Problem: Are traits controlled by dominant alleles more common than traits controlled by recessive alleles? 1.2. Background Information: Vocabulary: Trait: A characteristic passed on from parent to offspring through its genes. Gene: A segment of DNA on a chromosome that controls a trait. Alleles: Are the different forms of a gene. Dominant allele: An allele whose trait will always show up in the organism as long as its present. Recessive allele: An allele that is always masked and never shows up in the organism when a dominant allele is present. Heterozygous: Having two different alleles for a trait. (one recessive and one dominant). Traits that will be looked at in this experiment: (pictures on the top row portray traits controlled by dominant alleles and pictures on the bottom row portray traits controlled by recessive alleles.) 1.3. Hypothesis: If........then........because........ If one looks at the traits of a group of people, then the data will show that the traits controlled by dominant alleles are seen more commonly than traits controlled by Page 1 Camila Saravia Monday, May 30, 2011 4:43:54 PM Hong Kong SAR China Time recessive alleles, because the dominant allele will always mask the recessive allele and shine through. Therefore, all that is required for a trait to be controlled by a dominant allele is for there to be at least one in the pair, giving this a 75% chance of being the case. On the other hand, a trait controlled by a recessive allele must have a combination of two recessive alleles, which has only 25% chance of occurring. 1.4. Variables: · 1.3.1 Independent: The independent variable in this experiment are the different people being surveyed. · 1.3.2 Dependent: The dependent variable in this experiment is the number of people with various traits controlled by the different alleles. · 1.3.3 Constants: The variables that will be held constant during this experiment are the traits being looked at, which means the chart being used to survey must stay the same when surveying every person. In addition, the species being surveyed must stay the same as only human beings will be surveyed. 1.5. Materials: • a mirror (optional) •subjects • the wheel Page 1 Camila Saravia Monday, May 30, 2011 4:43:54 PM Hong Kong SAR China Time 1.6. Method: Part 1: 1. Copy the data table below. Traits Possessed Total Number of Participants: Trait 1 Number Trait 2 A Free ear lobes Attached ear lobes B Hair on fingers No hair on fingers C Widowʼs peak No widowʼs peak D Curly hair Straight hair E Cleft chin Smooth chin F Smile dimples No smile dimples Number 2. Count the total number of participants and record this on the data table. 3. Call out Trait 1a. 4. Optionally, one can use the the mirror to see if they posses the trait that was called and raise their hand if they do. 5. Carefully count the number of hands seen up for the trait, including one’s own, and record this number in the Number column for the trait. 6. Repeat steps 4-10 for all traits changing the red part correspondently. (Tip: To make sure the numbers are accurate make sure the Numbers of Trait xa and Trait xb add up to the total number of participants.) Part 2: 1. Place a finger on the half of the small inner circle on the wheel according to the trait one posses. (free ear lobes or attached ear lobes). 2. Move the fingertip to the next description that applies to one. 3. Continue using a fingertip to trace the traits until a number on the outside rim of the circle is reached. 4. Record this number and share with the other participants. 2. Data 2.1 Tables: Page 1 Camila Saravia Monday, May 30, 2011 4:43:54 PM Hong Kong SAR China Time Traits Possessed Total Number of Participants: 11 Trait 1 Number Trait 2 Number A Free ear lobes 8 Attached ear lobes 3 B Hair on fingers 11 No hair on fingers 0 C Widowʼs peak 3 No widowʼs peak 8 D Curly hair 3 Straight hair 8 E Cleft chin 4 Smooth chin 7 F Smile dimples 4 No smile dimples 7 Circle of Traits Results Name Number Lucy 62 Stasia 56 Georgia 51 Irene 54 Santi 60 Nicholas 30 Paul 29 Alan 62 Khalid 60 Malte 62 Camila 25 2.2 Graphs: Page 1 Camila Saravia Monday, May 30, 2011 4:43:54 PM Hong Kong SAR China Time Circle of Traits Results Number from Circle of Traits 70 62 52.5 62 60 56 51 60 62 54 35 30 29 25 17.5 0 Lucy Stasia Georgia Irene Santi Nicholas Paul Alan Khalid Malte Person 3. Results and Analysis The data gathered from the data table and graphed on the double bar graph clearly shows that traits controlled by recessive alleles were more commonly seen in the 11 people who part took in this laboratory. This is because as determined by looking at the data, more than half of the 11 students had 2 traits controlled by dominant alleles (free Page 1 Camila Saravia Monday, May 30, 2011 4:43:54 PM Hong Kong SAR China Time Camila ear lobes and hair on fingers). However, the remaining four traits people most commonly possessed where those controlled by recessive alleles including: no widow’s peak, straight hair, smooth chin and no smile dimples. Thus, based on this one can infer that in a small group of people traits controlled by dominant alleles aren’t necessarily more commonly possessed by people as in this case it was traits controlled by recessive alleles that were more commonly seen. Overall, based on the data one can infer that most of the people who part took in this lab inherited two recessive genes from their parents on the four traits that were most commonly controlled by the recessive trait. Thus, traits controlled by recessive alleles were more common in this specific crowd of people. 4. Conclusion 4.1 Conclusion: In conclusion, during this laboratory the traits of 11 people were looked upon to see weather traits controlled by dominant alleles were more common than traits controlled by recessive alleles. The significance behind conducting this lab was to gain a better understanding on why people look the way they do and if there were common trends in which traits were seen more commonly. At the end of this experiment the results showed that the in the group of 11 people, most traits possessed were controlled by recessive alleles. Therefore, these results do no support the initial hypothesis that stated that if this experiment was conducted, it would prove that most traits possessed by a group of people would be controlled by dominant alleles. Also, in part 2 of this laboratory as the graph 2 shows there were only 2 patterns and trends. This is because there were only two groups of people that had the same numbers. Firstly, the data shows that Lucy, Alan and Malte all had 62 as their final number. Santi and Khalid also ended up with the same number on the circle of traits, both getting a 60. This shows that Lucy, Alan and Malte have similar traits, suggesting that the traits possessed by these people are not as unique. The same applies to Santi and Khalid who have the same number, and thus similar traits. The other 6 people all had different numbers, which suggests that these people posses unique traits as the exact traits they posses is possessed by nobody else. 4.2 Error Analysis / Improvements: Looking back at the results it is evident they are not completely accurate. This is because according to the probability behind the inheritance of traits from parent to offspring, traits are most commonly controlled by dominant alleles. This is because if both parents are heterozygous then the probability of the offspring’s traits being controlled by the dominant allele is 75% as the possible combinations for this to be true include Rr, rR, or RR. On the other hand there is only a 25% chance the offspring’s traits will be controlled by the recessive allele as the only combination for this to be the case would be rr. Of course there are many other combinations of alleles that parents can have, however the majority of them have a higher probability of the offspring’s trait being controlled by a dominant allele. (e.g. RR and RR or RR, rr or Rr all have higher Page 1 Camila Saravia Monday, May 30, 2011 4:43:54 PM Hong Kong SAR China Time chances that the offspring’s traits will be controlled by dominant alleles). Likewise, there are combinations of alleles parents can posses that will most likely result in the offspring’s traits being controlled by recessive alleles, although these combinations are fewer and the only combination the offspring can inherit for the trait to be controlled by recessive alleles is rr. Therefore, because the probability of genetics suggest it is most likely for traits controlled by dominant traits to be more common this experiment’s data is inaccurate and it needs to be improved. Due to the many many factors that can determine what trait is inherited, for maximum accuracy it is best to have a bigger sample space. The sample space in this experiment consisting of only 11 people was too small. Since weather or not the trait is controlled by the dominant or recessive allele varies according to the many different allele combinations possible the bigger the sample space the more accurate representation you will have on the several different cases that exist--the more accurate your results. Therefore, to improve this experiment for next time it would be better to have a bigger sample space, where instead of surveying just a classroom one may reach out to the entire school community and collect data from more people. Page 1 Camila Saravia Monday, May 30, 2011 4:43:54 PM Hong Kong SAR China Time