* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Chapter 20 Notes
Consequences of Nazism wikipedia , lookup
Axis powers wikipedia , lookup
Allied plans for German industry after World War II wikipedia , lookup
Anglo-German Naval Agreement wikipedia , lookup
Nazi views on Catholicism wikipedia , lookup
Naval history of World War II wikipedia , lookup
German–Soviet Axis talks wikipedia , lookup
Swedish iron-ore mining during World War II wikipedia , lookup
World War II by country wikipedia , lookup
End of World War II in Europe wikipedia , lookup
Nazi Germany wikipedia , lookup
Technology during World War II wikipedia , lookup
British propaganda during World War II wikipedia , lookup
Home front during World War II wikipedia , lookup
Consequences of the attack on Pearl Harbor wikipedia , lookup
New Order (Nazism) wikipedia , lookup
American Theater (World War II) wikipedia , lookup
Foreign relations of the Axis powers wikipedia , lookup
Economy of Nazi Germany wikipedia , lookup
Allies of World War II wikipedia , lookup
European theatre of World War II wikipedia , lookup
Western betrayal wikipedia , lookup
Appeasement wikipedia , lookup
Diplomatic history of World War II wikipedia , lookup
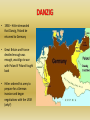
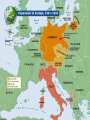
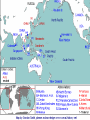
CHAPTER 20 A WORLD IN FLAMES (1931 - 1941) 20.1 – AMERICA AND THE WAR • See 20.1 packet DICTATORS OF WORLD WOR II Benito Mussolini Adolf Hitler Joseph Stalin 20.2 – WORLD WAR II BEGINS • In 1935 Hitler began to violate the Treaty of Versailles: a. Germany began building a new air force b. Began a draft to increase the size of the army • Why didn’t the European nations stop him at this time? ANSCHLUSS • In 1937 Hitler called for the unification of all German speaking peoples, including those in Austria and Czechoslovakia • 1938 – Hitler sent troops into Austria and announces the Anschluss (unification) of Austria and Germany MUNICH CONFERENCE SUDETENLAND • 1938 – Hitler announced German claims to the Sudetenland – German-speaking area in Czechoslovakia • At the Munich Conference G.B. and France agreed to Hitler’s demands – Appeasement? Why did G.B. and France do this? DANZIG • 1938 – Hitler demanded that Danzig, Poland be returned to Germany • Great Britain and France decided enough was enough, would go to war with Poland if Poland fought back • Hitler ordered his army to prepare for a German invasion and began negotiations with the USSR (why?) NAZI-SOVIET PACT • 1939 – Germany and the USSR sign the pact, world was shocked – Germany was now free or its Eastern Front concerns – Secret deal to divide Poland between Germany and the USSR – Why would the USSR agree to this? STALIN WORLD WAR II BEGINS • Sept. 1, 1939 – Germany invades Poland – Blitzkrieg tactics overwhelm Poland in 1 month • Sept. 3, 1939 – GB and France declare war on Germany WORLD WAR II BEGINS • W. Europe was quiet as British and French troops waited behind the Maginot Line – Defensive along Fr./Ger. border - Big mistake, why? • Germans went around the ML into Luxembourg and Belgium; F and B troops were trapped in Belgium MIRACLE AT DUNKIRK • 338,000 British and French troops were evacuated from the port at Dunkirk and sent across the English Channel in early June, 1940 GERMANY CONQUERS FRANCE • June 22, 1940 – Germany conquers northern and western France • Vichy France – established as puppet gov’t under Petain to govern France – De Gaulle challenged the legitimacy of the Vichy gov’t BRITISH RESISTANCE TO GERMANY • GB was led by Prime Minister Winston Churchill • Germany bombs London, hoping to break the will of the people and force a surrender • Battle of Britain (summer – fall of 1940) – massive air battle between GB and Germany – Both sides bombed civilians in cities – British used radar – Hitler called off the invasion of GB BEGINNING OF WORLD WAR 2 TIMELINE 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. Anschluss Munich Conference/Sudetenland Nazi-Soviet Pact Invasion of Poland/War Begins Miracle at Dunkirk Fall of France Battle of Britain 20.3 – THE HOLOCAUST • We will do this after the test 20.4 – AMERICA ENTERS THE WAR • As the war began the U.S. was “officially” neutral but helped Great Britain • Japan’s expansion in the Pacific increased tension with the U.S. Or Not? DEBATE ABOUT JOINING THE WAR IN America First Committee to Defend America Fight for Freedom Strongly opposed to Called for increased Repeal all neutrality any American American aid to the laws and take intervention or aid Allies but no armed stronger action to the Allies intervention against Germany WAYS FDR AIDED G.B. WHILE KEEPING U.S. “NEUTRAL” NEUTRALITY ACT OF 1939 • Allowed countries in war to buy weapons from the U.S. if they paid for them in cash and transported the weapons on their own ships DESTROYERS FOR BASES • America gave the British old American destroyers in exchange fro the right to build U.S. defense bases in British controlled areas such as Bermuda and the Caribbean islands – Got around the “loophole” of the neutrality act because there was no actual “sale” of anything LEND LEASE ACT • Allowed the U.S. to lend or lease arms/weapons to any country “vital to the defense of the United States HEMISPHERIC DEFENSE ZONE • FDR developed the idea that the entire western Atlantic half of the Atlantic Ocean was neutral • He ordered the U.S. Navy to patrol it and tell the British the location of any German submarines ATLANTIC CHARTER • August 1941 – FDR and Winston Churchill meet on warships near Newfoundland to agree on the content of the Atlantic Charter – Commits U.S. and G.B. to a postwar world of democracy, nonaggression, free trade, and freedom of the seas PEARL HARBOR – DEC.7, 1941 AMERICA & JAPAN • As Britain moved more of its warships from Asia to Europe to fight Germany they needed help against a possible Japanese attack against their colonial possessions • To slow down/prevent Japanese aggression FDR began applying economic pressure AMERICA’S ACTIONS TOWARDS JAPAN • July 1940 – Congress gives FDR power to restrict the sale of strategic materials to Japan – Airplane fuel, scrap iron JAPAN • 1941 – Lend-Lease is extended to China, which Japan had invaded in 1937 • 1941 – After Japan invaded Indochina, FDR…. – froze all Japanese assets in the U.S. – Reduced amount of oil being shipped to Japan (oil embargo would only end if Japan withdrew from Indochina and made peace with China) – Sent MacArthur to the Philippines to build up American defenses JAPAN ATTACKS PEARL HARBOR • Negotiations between Japan and the U.S. were ongoing • U.S. was wary of an attack but didn’t think Hawaii was a target • Attack on December 7, 1941 sank 8 battleships, 3 cruisers, 4 destroyers, and 6 other vessels, and 188 airplanes • 2,403 were killed and 1,178 wounded • FDR asked Congress to declare war against Japan on December 8