* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Forces and Motion
Inertial frame of reference wikipedia , lookup
Coriolis force wikipedia , lookup
Classical mechanics wikipedia , lookup
Newton's theorem of revolving orbits wikipedia , lookup
Seismometer wikipedia , lookup
Length contraction wikipedia , lookup
Fictitious force wikipedia , lookup
Hunting oscillation wikipedia , lookup
Equations of motion wikipedia , lookup
Rigid body dynamics wikipedia , lookup
Mass versus weight wikipedia , lookup
Classical central-force problem wikipedia , lookup
Centrifugal force wikipedia , lookup
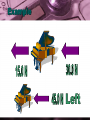
Motion and Forces What makes us move and why we move in that particular way… What Is Motion? • Motion: when an object changes position over time when compared with a reference point Object In Motion Reference Point How Can We Describe Motion? • 3 Ways To Categorize Motion 1. Position 2. Direction of Motion 3. Speed Which way did he go, which way did he go??? Follow The Directions!!!! The direction of the objects motion is dependent on the reference point If the reference point changes, the direction of the object can also be looked at differently What Makes An Object Move? • Force: a push or pull on an object Characteristics of Forces 1. Have size 2. Direction 3. Units = Newtons 40.0 Newtons Forces Control The Motion of an Object • If an object is in moving or even if it is sitting still, there are still forces acting upon it If the forces acting on the object are balanced, or equal to one another but in opposite directions…then the object doesn’t move. If one of the forces is larger, it will move the object in the direction of that force All Forces Control The Motion of the Object • We can use something called a Force Diagram Net Force • Easy Calculation 2 Scenarios 1. If the forces are moving in the same direction, add them together 2. If the forces are moving in the opposite direction, subtract them, leaving the object to move in the direction of the greater force Example Newton’s Laws 1. An object in motion tends to stay in motion unless acted upon by an outside force 2. Force = mass x acceleration 3. For every action, there is an equal and opposite reaction One Force Calculation Example 5.0 m/s2 Force = mass x acceleration Force = 500.0 kg x 5.0 m/s2 Force = 2500.0 N to the left