* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Student Activity: To investigate how to solve f(x) = (x
Survey
Document related concepts
Unification (computer science) wikipedia , lookup
Two-body problem in general relativity wikipedia , lookup
BKL singularity wikipedia , lookup
Equations of motion wikipedia , lookup
Debye–Hückel equation wikipedia , lookup
Perturbation theory wikipedia , lookup
Euler equations (fluid dynamics) wikipedia , lookup
Schrödinger equation wikipedia , lookup
Differential equation wikipedia , lookup
Dirac equation wikipedia , lookup
Van der Waals equation wikipedia , lookup
Derivation of the Navier–Stokes equations wikipedia , lookup
Exact solutions in general relativity wikipedia , lookup
Partial differential equation wikipedia , lookup
Transcript
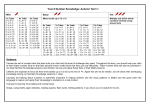
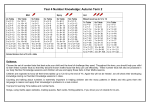
Student Activity: To investigate how to solve f(x) = (x - a) (x - b) Use in connection with the Interactive file, ‘ (x - a) (x - b)’, on the Student’s CD. Note: Solving the equation (x - a) (x - b) = 0 is the same as solving f(x) = 0. So we can find the roots of the equation (x - a) (x - b) = 0 by taking the x-values of the points where f(x) cuts the x-axis. 1. a. Using the interactive file, find where the function f(x) = (x - 2) (x - 5) cuts the x axis. _____________________________________________________________________ b. Hence solve the equation (x 2) (x 5)=0. _____________________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________________ c. By substituting your solution(s) for x into f(x), check that f(x) is equal to 0 at these point(s). _____________________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________________ Draft 01 © Project Maths Development Team 2011 (x –a) (x –b) Page 1 of 5 2. a. Using the interactive file, find where the function f(x) = (x 1) (x 5) cuts the x axis. _____________________________________________________________________ b. Hence solve the equation (x 1) (x 5) = 0. _____________________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________________ c. By substituting your solution(s) for x into f(x), check that f(x) is equal to 0 at these point(s). _____________________________________________________________________ 3. a. Using the interactive file, find where the function f(x) = (x + 1) (x 5) cuts the x axis. _____________________________________________________________________ b. Hence solve the equation (x + 1) (x 5) = 0. _____________________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________________ c. By substituting your solution(s) for x into f(x), check that f(x) is equal to 0 at these point(s). _____________________________________________________________________ Draft 01 © Project Maths Development Team 2011 (x –a) (x –b) Page 2 of 5 4. a. Using the interactive file, find where the function f(x) = (x + 1) (x + 5) cuts the x axis. _____________________________________________________________________ b. Hence solve the equation (x+1) (x+5) =0. _____________________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________________ c. By substituting your solution(s) for x into f(x), check that f(x) is equal to 0 at these point(s). _____________________________________________________________________ 5. Find the solution(s) to the equation f(x) = 0 where f(x) is represented on the graph below. 6. Find the solution(s) to the equation f(x) = 0 where f(x) is represented on the graph below. Draft 01 © Project Maths Development Team 2011 (x –a) (x –b) Page 3 of 5 7. Find the solution(s) to the equation f(x) = 0 where f(x) is represented on the graph below. 8. Find the solution(s) to the equation f(x) =0 where f(x) is represented on the graph below. 9. When does an equation of the form f(x) = (x a) (x b) =0 have only one solution? _____________________________________________________________________ 10. Draw a rough sketch of the function f(x) = (x 2) (x 4). Solve the equation (x 2) (x 4) = 0. Use the interactive file to check your answers. ___________________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________________ Draft 01 © Project Maths Development Team 2011 (x –a) (x –b) Page 4 of 5 11. Draw a rough sketch of the function f(x) = (x +3) (x + 1). Solve the equation (x+3) (x+1) =0. Use the interactive file to check your answers. 12. Draw a rough graph of the function f(x) = (x 1) (x 1). Solve the equation (x 1) (x 1) =0. Use the interactive file to check your answers. 13. Draw a rough graph of the function f(x) = (x + 3) (x 3). Solve the equation (x + 3) (x 3) =0. Use the interactive file to check your answers. Draft 01 © Project Maths Development Team 2011 (x –a) (x –b) Page 5 of 5