* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download page 1 of 5 LECTURE OUTLINE: CTP
Monoclonal antibody wikipedia , lookup
Embryonic stem cell wikipedia , lookup
Cell culture wikipedia , lookup
Organ-on-a-chip wikipedia , lookup
Dictyostelium discoideum wikipedia , lookup
Induced pluripotent stem cell wikipedia , lookup
Chimera (genetics) wikipedia , lookup
State switching wikipedia , lookup
Nerve guidance conduit wikipedia , lookup
Hematopoietic stem cell wikipedia , lookup
Neuronal lineage marker wikipedia , lookup
Human embryogenesis wikipedia , lookup
Microbial cooperation wikipedia , lookup
Cell theory wikipedia , lookup
Developmental biology wikipedia , lookup
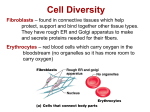
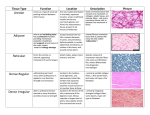
LECTURE OUTLINE & REVIEW QUESTIONS LECTURE OUTLINE: CTP (Connective Tissues Proper) (Ordinary Connective Tissues) General Definition: Tissues composed of cells embedded in an extracellular (intercellular) matrix, consisting of ground substance and protein fibers. General Functions: Structural Capsules & internal frameworks of soft organs Packing in spaces between organs Loose connections between structures Wrapping & bundling structures Tendons connecting muscles to bones Ligaments connecting bone to bone Transport of materials (nutrients, gases, vitamins, hormones, etc.) to and from cells. Bloodstream <-> Tissue fluids <-> Cells Defense Physical barrier against spread of microorganisms Removal of damaged cells & tissues Tissue repair Immunological reactions General Composition: 1. Matrix Ground substance Glycosaminoglycans (GAGS) Linear polysaccharides Proteoglycans GAGS (~90%) bound to a protein “core” (~10%) Hydrophilic (attract water) Structural Glycoproteins Proteins (predominate) + carbohydrates (not GAGS) Tissue fluid Filtrate of blood plasma. Pathway for materials moving between bloodstream & cells. Anatomy 25.mguthrie ANATOMY 25 - GUTHRIE Most water is hydrated to GAGS. Different connective tissues differ in their ground substance composition. Result: different functional characteristics. Protein Fibers Collagen Basic Structure: 3 polypeptide chains tropocollagen Linked tropocollagen molecules collagen fibril Collagen fibrils collagen fiber Collagen fibers collagen bundles Twelve types of collagen (I-XII) Differ in alpha chain amino acid composition I, II, III, IV most common In CTP: Type I: collagenous (white) fibers or bundles Type III: reticular fibers (massed fibrils) Elastin Structure: Fibrils embedded in periphery of amorphous core to form fibers. 2. Cells (“Resident Population”) Fibroblasts / Fibrocytes Most common CTP cell type Differentiate from mesenchymal cells Produce and maintain: Ground substance GAGS, proteoglycans, glycoproteins Protein fibers (collagenous, reticular, elastic) Cytological characteristics of protein secreting cells. Fibroblasts more active; fibrocytes less active. page 1 of 5 LECTURE OUTLINE & REVIEW QUESTIONS Tissue Macrophages Terminology: Resident / Elicited / Activated Functions: Phagocytosis of dead or damaged cells, tissue components, invasive microorganisms. Activation: chemical signal from damaged cells, extracellular tissues, invasive particulates. Chemotaxis & Amoeboid motion: Follows chemical trail to area of damage or invasion. Phagocytosis and Lysosomal Digestion APC (Antigen presenting cell) Function Phagocytosis of bacteria Activation: chemical signal from bacteria Chemotaxis & Amoeboid motion Opsonization Bacteria coated with complement & immunoglobulins. Complement & immunoglobulins lock onto macrophage plasmalemma receptors. Phagocytosis: phagosome intracellular digestion Presentation of bacterial components to other immune reaction cells Secretion Release a variety of factors affecting the activity of white blood cells, fibroblasts, and platelets. Mononuclear Phagocyte System (MPS) A body-wide system of phagocytic cells that meet the following requirements: Bone marrow stem cells differentiate into monocytes Monocytes transported through bloodstream Monocytes leave blood stream, enter tissues, and differentiate into phagocytic cells: CTP: tissue macrophages Liver: Kuppfer cells Lungs: alveolar macrophages Anatomy 25.mguthrie ANATOMY 25 - GUTHRIE Bone: osteoclasts Brain: microglia Skin: Langerhans cells Joints: type A cells Adipocytes (fat cells) Origin: mesenchymal cells adipoblasts unilocular (white) adipocytes or multilocular (brown) adipocytes Functions: White fat cells Lipid storage Packing & cushioning Insulation Secretion Brown fat cells Heat production Hormones secretion ? Mast Cells Origin: bone marrow precursor cells bloodstream tissues mast cells Cytoplasmic granules: histamine (vasodilator); heparin (anticoagulant); trypsin & chymase (enzymes); eosinophilic chemotactic factor; leukotrienes Functions: Hypersensitivity Reactions Allergic reactions, asthma, anaphylactic shock Initial exposure to an antigen: Antigen B-lymphocytes plasma cells antigen specific antibody Antigen-antibody complex Plasma cells antigen specific IgE mast cell plasmalemma IgE receptors page 2 of 5 LECTURE OUTLINE & REVIEW QUESTIONS Subsequent exposures Antigen plasma cells antibody Antigen mast cells degranulation Leukotrienes bronchiolar constriction Heparin anticoagulant Histamine capillary dilation & bronchiolar constriction ECF attracts eosinophils 3. Cells (“Wandering Population”) Plasma cells Antigen B-lymphocyte plasma cells + memory cells. Plasma cells antigen specific antibody Neutrophils (neutrophilic leukocytes) “Specialists” in bacterial phagocytosis Eosinophils (eosinophilic leukocytes) Modulate inflammatory reactions Phagocytize antigen-antibody complexes Combat some parasites Classification: Types of CTP Loose CT (Areolar Tissue) “Tossed salad” of collagenous, reticular and elastic fibers + fibrocytes, macrophages, mast cells, fat cells + plasma cells, neutrophils and eosinophils as necessary ANATOMY 25 - GUTHRIE Adipose Tissue White fat Masses of unilocular fat cells with some loose ct between. Each cell supported by a “girdle” of reticular fibers Brown fat Masses of multilocular fat cells. Highly vascularized. Dense Irregular CT Essentially a compacted loose ct. Fibers appear to be randomly oritented, but actually reflect stresses imposed on them. Dense Regular CT Parallel bundles of collagenous fibers wrapped with loose ct. Fibrocytes - only cells present – squeezed in rows between bundles. Forms ligaments & tendons Elastic Tissue Dense bundles or sheets of elastic fibers Examples: ligamentum nuchae; elastic laminae of blood vessels Mucous Tissue A “primitive” connective tissue. Example: Wharton’s jelly in umbilical cord. Contains stem cells (mesenchymal cells) Reticular Tissue Interlacing network of reticular fibrils + fibrocytes (sometimes called reticulocytes) and macrophages. Forms a scaffolding for some soft organs. Example: lymph nodes Anatomy 25.mguthrie page 3 of 5 LECTURE OUTLINE & REVIEW QUESTIONS 1. CTP matrix consists of _?_. (a) cells and protein fibers (b) cells and tissue fluid (c) ground substance and protein fibers (d) tissue fluids and protein fibers (e) none of these 2. The ground substance of CTP is a chemical solution that contains _?_. (a) glycosaminoglycans: polysaccharides (b) proteoglycans: GAGS bonded to a protein core (c) glycoproteins: proteins + non-GAG carbohydrates (d) water: mostly solvated to proteoglycans (e) all of these 3. Select the incorrect statement about collagen. (a) All collagen molecules are identical. (b) Collagen fibers are bundles of collagen fibrils. (c) Collagen fibrils are arrays of tropocollagen molecules. (d) Tropocollagen molecules consist of three intertwined polypeptide chains. (e) Collagen is a protein. 4. Select the correct statement about the matrix protein fibers of CTP. (a) Collagenous or white fibers are bundles of type I collagen fibrils. (b) Reticular or argyrophilic fibers are bundles of type III collagen fibrils. (c) Elastic or yellow fibers consist of a core of the protein elastin and associated microfibrils. (d) All of these are correct. (e) None of these is correct. 5. Select the incorrect statement. Fibroblasts or fibrocytes _?_. (a) are the least common cell type in CTP (b) are derived from mesenchymal cells (c) produce the gags, proteoglycans, and glycoproteins of the ground substance. (d) produce collagenous, reticular, and elastic fibers. (e) have the cytological characteristics of protein secreting cells. ANATOMY 25 - GUTHRIE part of the mononuclear phagocyte system (e) All of these are incorrect. 8. Activated macrophages do not _?_. (a) phagocytize damaged cells and tissue components (b) phagocytize bacteria and particulate foreign materials (c) process and present antigens to lymphocytes (d) secrete substances that affect white blood cells and fibroblasts (e) produce circulating antibodies 9. Which is the second step in the macrophage processing of an invading bacterium ? (a) opsonization of the bacteria (b) phagocytosis and phagosome formation (c) binding of the bacterium to C3 complement and Fc receptors on the macrophage membrane (d) lysosomal breakdown and processing of the bacterium (e) presentation of bacterial breakdown products on the macrophage plasmalemma to lymphocytes 10. Connective tissue mast cells _?_. (a) originate from bone marrow stem cells (b) contain cytoplasmic granules of histamine, heparin, enzymes, and ECF (c) are involved in inflammatory reactions, allergies, and anaphylactic shock (d) interact with plasma cells (e) all of these 11. Which mast cell factor do you think is most responsible for the swelling (edema), redness (erythema), and increased warmth (heat) characteristic of inflammatory reactions ? (a) heparin (b) histamine (c) eosinophilic chemotactic factor (d) antigenspecific IgE receptors (e) none of these 12. Lipoblasts _?_. (a) are undifferentiated adipocytes (b) are 6. Which cell type do you think is responsible for scar formation ? (a) macrophage (b) white adipocyte (c) mast cell (d) fibroblast (e) neutrophils. 7. Select the incorrect statement about CTP macrophages. (a) Like fibroblasts, they develop from mesenchymal cells. (b) They are activated by chemical signals indicating cell damage, tissue damage or the presence of invasive organisms (c) They exhibit chemotaxis, amoeboid motion, and phagocytosis. (d) They are derived from mesenchymal cells (c) differentiate into either brown or white fat cells (d) all of these (e) none of these 13. White fat cells _?_. (a) are more common than brown fat cells Anatomy 25.mguthrie (b) are unilocular (c)are usually surrounded by a thin girdle of reticular and collagenous fibers (d) all of these (e) none of these 14. Brown fat cells _?_. (a) are multilocular (b) are more numerous in infants than in adults (c) have more mitochondria and page 4 of 5 LECTURE OUTLINE & REVIEW QUESTIONS produce more heat than white fat cells (d) all of these (e) none of these 15. Plasma cells _?_. (a) are derived from B-lymphocytes (b) are derived from mast cells (c) produce circulating antibodies (d) a & c (e) b & c 16. Which white blood cell enters the connective tissues to phagocytize antigen-antibody complexes ? (a) monocyte (b) neutrophil (c) eosinophil (d) B-lymphocyte (e) none of these ANATOMY 25 - GUTHRIE 24. Dense regular connective tissue _?_. (a) contains closely packed, parallel bundles of collagenous fibers (b) contains only fibrocytes (c) makes up tendons, ligaments, and aponeuroses (d) all of these (e) none of these. 25. Select the incorrect statement about most of the adipose tissue in the body. (a) It consists of closely packed multilocular adipocytes (b) It is white fat. (c) It is a storage depot for lipids, a source of energy and raw materials. (d) It packs spaces around organs, provides protection to various structures, and absorbs shocks. (e) It provides insulation and helps to conserve body heat. 17. Which white blood cell is a “specialist” in the phagocytosis of bacteria ? (a) monocyte (b) neutrophil (c) eosinophil (d) Blymphocyte (e) none of these 26. Which CTP is found in the umbilical cord ? (a) areolar (b) mucous (c) elastic (d) adipose (e) reticular 18. Loose c.t. usually contains _?_. (a) fibroblasts & fibrocytes (b) mast cells (c) fat cells (d) macrophages (e) all of these 19. Loose c.t. contains _?_. (a) collagenous fibers (type 1 collagen) (b) reticular fibers (type III collagen) (c) elastic fibers (d) all of these (e) none of these 20. Loose c.t. is also called _?_ . (a) reticular tissue (b) mesenchymal tissue (c) elastic tissue (d) areolar tissue (e) mucous tissue 21. _?_ tissue consists of reticular fibers, fibrocytes and macrophages that form a supporting meshwork for some soft organs. (a) areolar (b) mucous (c) reticular (d) dense irregular (e) dense regular 22. Dense irregular c.t. is most similar in its composition to a compacted _?_. (a) reticular tissue (b) dense regular c.t. (c) loose c.t. (d) elastic tissue (e) adipose tissue 23. Which connective tissue proper forms capsules and supporting frameworks for soft organs, fasciae, and most of the dermis of the skin ? (a) areolar (b) dense regular (c) dense irregular (d) reticular (e) elastic. Anatomy 25.mguthrie page 5 of 5