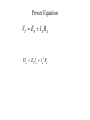* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Dc motors - WordPress.com
Electrical substation wikipedia , lookup
Current source wikipedia , lookup
Pulse-width modulation wikipedia , lookup
History of electric power transmission wikipedia , lookup
Switched-mode power supply wikipedia , lookup
Buck converter wikipedia , lookup
Stray voltage wikipedia , lookup
Power engineering wikipedia , lookup
Three-phase electric power wikipedia , lookup
Rectiverter wikipedia , lookup
Dynamometer wikipedia , lookup
Electrification wikipedia , lookup
Mains electricity wikipedia , lookup
Alternating current wikipedia , lookup
Voltage optimisation wikipedia , lookup
Commutator (electric) wikipedia , lookup
Electric machine wikipedia , lookup
Brushless DC electric motor wikipedia , lookup
Electric motor wikipedia , lookup
Induction motor wikipedia , lookup
Variable-frequency drive wikipedia , lookup
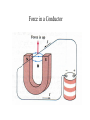
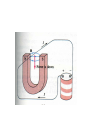
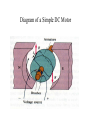
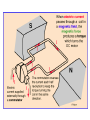
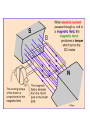
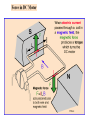
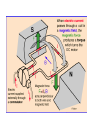
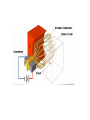
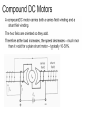
II UNIT D.C MOTORS UNIT-II D.C. MOTORS : Principle of operation of DC Motor, Types of Motors, Back EMF Equation, Characteristics of DC motor, Torque Equation, DC Motor Starter (Three Point starter), Efficiency Calculation, Swinburne's Test and speed control of armature and field. DC Machines DC Motor DC Generator DC motor Force in a Conductor Diagram of a Simple DC Motor Eb and it is indicated by Eb ZNP 60 A Net voltage across armature circuit = If Ra is the armature resistance , then Eb V Eb V Eb Ia Ra ZNP 60 A This back e.m.f is also called as counter e.m.f and indicated by Eb Significance of Back E.M.F The presence of back e.m.f makes the dc motor a self regulating machine i.e. it makes the motor to draw as much armature current as is sufficient to develop the torque required by the load . V Eb Ia Ra Terminal Voltage Equation VT Eb I A RA VT = voltage at motor terminals E = Back EMF induced in armature (V) IA = armature current (A) RA RA = armature resistance + + Eb VT - - Power Equation VT Eb I A RA VI a Eb I a I a Ra 2 VI a is the electrical input to the motor 2 I a Ra represents the copper losses in the motor Eb I a is the electrical equivalent mechanical power developed in armature of Electric Motor TYPES OF D.C MOTORS (i) Shunt wound motors : in which the field winding is connected in parallel with the armature. (ii) Series –wound Motor : in which the field winding is connected in series with the armature (iii) Compound Wound Motor : which has two field windings ,one connected in parallel with the armature and the other in series with it Torque of a dc motor • The turning or twisting moment of a force about an axis. • It is measured as the product of force and radius at which it acts. • T=F*r N-m • Work done by force= F*2*3.14*r N-m • Power developed=F*2*3.14*r *N • P=T*W watts (since T=F*r) • P=(2*3.14)NT/60 watts • P=NT/9.55 watts Armature Torque • If Ta is the torque developed by armature and N is speed in rps • • • • P=Ta*2*3.14*N watts Electrical power: Eb*Ia Eb*Ia =Ta*(2*3.14*N) Ta=(Eb*Ia)/(2*3.14*N) • Eb=ZNP/A • Ta= (ZP/A)*(Ia/(2*3.14)) • Ta=0.159* ZIa(P/A) N-m • Ta is proportional to (Ia) SPEED CONTROL OF DC MOTORS 1. Vary the voltage supplied to the armature circuit while holding the field constant. 2. Vary the field current while holding the armature supply voltage constant. 3. Insert resistance in series with the armature circuit.