* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Convection Currents Activity - Mamanakis
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
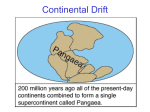
Convection Currents Activity Name Class DIRECTIONS: Teacher Demo: 1. Pour very hot water into a large beaker. 2. Add one or two deep blue ice cubes. 3. Record observations below and draw in beaker. ANALYSIS AND CONCLUSIONS: 1. What happened to the blue ice water? Why? 2. Relate your observations to the way convection currents work in the Mantle: How do you think the Mantle moves if it is cooler? Why? AND: How do you think the Mantle moves if it is hotter? Why? 3. How do the plates sitting on top of the Mantle move where convection currents are sinking? (See diagram below.) How do plates sitting on top of the Mantle move where convection currents are rising? (See diagram below.) 4. Study this diagram. a. What has to happen for convection currents to stop rising and sink back toward the core? What causes that to happen? b. What has to happen for convection currents to stop sinking and rise back toward the surface? What causes that to happen? CONVECTION CURRENTS WS OR: WHAT MAKES THE PLATES MOVE? Name Class 1. List four evidences Wegener used t support his Drifting Continents Theory: a. b. c. d. 2. Was Wegener’s Theory accepted during his lifetime? Why or why not? 3. What was discovered after World War II that caused scientists to eventually accept Wegener’s Theory of Continental Drift? 4. What is the mechanism called that moves or drives the tectonic plates across the surface of the Earth? 5. Color and label this diagram of the Earth’s Convection Currents. Color the arrows of the mantle RED that are HOT. Color the arrows of the mantle BLUE that are COOLER. Label the features formed by rising and falling CONVECTION CURRENTS. Add arrows to show the direction of movement of each plate. Words to Use: rift valley ridge volcanic mountain folded mountain trench convection currents Image by MJKrech SUMMARY QUESTIONS: 1. What does hot rock do? Why does hot rock rise? 2. What does cooler rock do? Why does cooler rock sink? 3. Hot rock and cooler rock . These moving columns of molten rock are called . 4. If a plate boundary is located directly above a rising column of hot rock, what do the plates do? What features are formed in this area? What type of boundary is this called? Give one example: 5. If a plate boundary is located directly above a sinking column of cooer rock, what do the plates do? What features are formed in this area? What type of boundary is this called? CONVERGENT: Give one example: What other type of features are formed in this area? What type of boundary is this called? CONVERGENT: Give one example: 6. How do plates move when CONVECTION CURRENTS are rising? How do plates move when CONVECTION CURRENTS are sinking? 7. What happens to the rock at A in the diagram as it moves right below the surface of the Earth? 8. What happens to the rock at B in the diagram as it moves right above the Core of the Earth? **9. Why wasn’t Wegener’s Theory of Continental Drift accepted in his lifetime? **10. What do YOU know that Wegener didn’t know? In other words, what is today’s accepted explanation for why continents can move around the world?