* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Faraday`s Law of Induction
Current source wikipedia , lookup
Brushed DC electric motor wikipedia , lookup
Stray voltage wikipedia , lookup
History of electromagnetic theory wikipedia , lookup
Induction motor wikipedia , lookup
Alternating current wikipedia , lookup
Electric machine wikipedia , lookup
Skin effect wikipedia , lookup
Magnetic core wikipedia , lookup
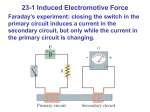
Faraday’s Law of Induction Faraday discovered that a moving conductor (perpendicularly) in a magnetic field has a current induced to flow in it. (Faraday’s Law of Induction relates to this, but in more detail). The conductor disturbs the magnetic field lines which forces the electrons to move in the wire. Lenz applied the energy of conservation concept that you can’t get something for nothing: the induced current flows in such a way as to oppose the changing magnetic field that produced the current. (Lenz’s Law) This allows for built in resistance/friction that must exist as the electrons can’t flow freely by themselves. (No such thing as perpetual motion). The induced current only exists when the magnetic field changes. A good example is to have a fixed coil, not connected to any external battery source, with a changing magnetic field nearby: Ex1) A North pole of a bar magnet is physically pushed by a keen physics student into a coil. Determine the direction of the induced current in the coil, using the laws of induction. N Step 1: Use Lenz’s law to predict the induced poles in the coil that would oppose the changing magnetic field: the end closest to the magnet becomes ______. Step 2: Use the hand rule for coils (left hand for electron current) to determine the current direction on the front of the coil as _______. Ex 2) S Ex 3) The coil is rotated (by wind in a windmill) around a fixed axis. S N Ex 4) A conducting rod is moved West through a magnetic field directed down. X X X X X X X X X X X X X X X X X X X X Lenz’s law predicts that the induced current will flow to generate a magnetic field that will oppose the motion of the rod. Therefore, a force on the rod is experienced ________. Use the 3D hand rule to predict that the current in the rod is ________. Induced Voltage: the current flow that is induced implies that energy is given to the charges and therefore a voltage. (Induced voltage is referred to as a EMF (electro-motive force).) V = LvB V is the induced voltage, L is the length of the conductor, v is the velocity of the conductor and B is the magnetic field strength. In example 4, if v = 12 cm/s, B = 3.0 mT and L = 5.0 cm, what is the induced EMF? V = LvB = (0.05 m)(0.12 m/s)(0.003 T) = 1.8 x 10-5 V