* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Module 2 / Endocrine System
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
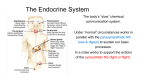
5/8/13 Endocrine System - [ S IGN IN ] Anatomy & Physiology (Open + Free) Unit 1:: Introduction to Anatomy and Physiology Introduction Module 2 / Introduction of Sy stem s Sy lla bu s | Ou t lin e | Help | Mor e This course is not led by an instructor Search this course Endocrine System 25 Describe the endocrine sy stem : list the m ajor organs and structures, describe the m ajor functions, and use anatom ical planes and directional term s to identify organs and their relationships to each other. Endocrine System - Function The endocrine system is an equally important method of sending messages within the body for control and coordination of multiple body systems. The functional unit of the endocrine system is a gland, or a group of cells that secrete chemicals called hormones. Hormones circulate throughout the body within the bloodstream and act as long-term messengers. In comparison with neurotransmitters, hormones act over long distances for a longer time. Endocrine System - Organs and Structures The major organs of the endocrine system are: 1. hypothalamus 2. pituitary gland 3. pineal gland 4. thyroid and parathyroid glands 5. thymus (note that this gland is also part of the lymphatic system) 6. adrenal glands https://oli.cmu.edu/jcourse/workbook/activity/page?context=b880ecea80020ca6014ec505c060d014 1/5 5/8/13 Endocrine System 7. pancreas (note that this gland is also part of the digestive system) 8. gonads (that is, ovaries or testes—note that these glands are also part of the reproductive system) As a specialized part of the brain, the hypothalamus is an endocrine gland that produces hormones that regulate many basic functions such as hunger, thirst and sleep through control of the pituitary gland. The hypothalamus receives sensory input from receptors and perceptual information from the brain, such as changes in emotional state, temperature, and lighting. The pituitary gland is sometimes called the master gland, because it controls the release of hormones from many other endocrine glands. The pineal gland secretes the hormone melatonin, which is important for transmitting information about environmental lighting and inducing sleep. The thyroid glands and parathyroid gland are located together in the neck. The thyroid glands secrete hormones that regulate metabolism and calcium levels. The parathyroid gland also secretes hormones that regulate calcium levels. https://oli.cmu.edu/jcourse/workbook/activity/page?context=b880ecea80020ca6014ec505c060d014 2/5 5/8/13 Endocrine System The thymus gland secrets the hormones thymosin and thymopoietin that stimulate the production of special lymphocytes (white blood cells) called T-cells, which play an important role in the immune system by attacking foreign or abnormal cells. The adrenal glands produce steroid hormones that regulate metabolic functions during stress, kidney function, and sexual function. The adrenal glands also secrete epinephrine (adrenaline) when stimulated by the autonomic nervous system. The pancreas secretes insulin, to lower blood sugar levels, and glucagon to raise blood sugar levels. Therefore, the pancreas is an important endocrine organ for regulating the fuels available for energy production by cells. The gonads, or sex organs (ovaries and testes) secrete sex hormones which control production of sperm and eggs as well as other secondary sex characteristics that are different for males and females. The secretion of sex hormones by the gonads is under the control of pituitary gland hormones. learn by doing learn by doing did I get this https://oli.cmu.edu/jcourse/workbook/activity/page?context=b880ecea80020ca6014ec505c060d014 3/5 5/8/13 Endocrine System did I get this Endocrine System - Anatomy and Direction The hypothalamus is found deep inside the brain and lies inferior to the thalamus. The pituitary gland is located at the base of the brain, inferior to the hypothalamus. The pineal gland is a small gland on the midline at the posterior of the brain. The thyroid and parathyroid glands lie inferior to the larynx, around the trachea. The parathyroid gland lies on the posterior surface of the thyroid gland. The adrenal glands are located superior to each kidney. The pancreas is located posterior to the stomach and is connected to the part of the small intestine called the duodenum. The ovaries are located in the pelvic cavity lateral to the uterus, while the testes are held external to the abdominopelvic cavity inside the scrotum. learn by doing https://oli.cmu.edu/jcourse/workbook/activity/page?context=b880ecea80020ca6014ec505c060d014 4/5 5/8/13 Endocrine System Open Learning Initiativ e 25 Unless otherwise noted this work is licensed under a Creativ e Com m ons Attribution 3 .0 Unported License. https://oli.cmu.edu/jcourse/workbook/activity/page?context=b880ecea80020ca6014ec505c060d014 5/5