* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Fungi, plants, etc target packet questions - APBio09-10
Plant stress measurement wikipedia , lookup
Gartons Agricultural Plant Breeders wikipedia , lookup
Plant nutrition wikipedia , lookup
History of herbalism wikipedia , lookup
Plant defense against herbivory wikipedia , lookup
Plant secondary metabolism wikipedia , lookup
History of botany wikipedia , lookup
Ornamental bulbous plant wikipedia , lookup
Historia Plantarum (Theophrastus) wikipedia , lookup
Plant breeding wikipedia , lookup
Plant physiology wikipedia , lookup
Perovskia atriplicifolia wikipedia , lookup
Plant evolutionary developmental biology wikipedia , lookup
Pollination wikipedia , lookup
Plant ecology wikipedia , lookup
Plant use of endophytic fungi in defense wikipedia , lookup
Plant morphology wikipedia , lookup
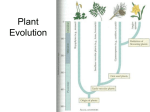
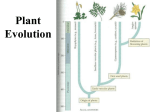
Evolutionary history of plants wikipedia , lookup
Fertilisation wikipedia , lookup
Flowering plant wikipedia , lookup
TARGET 1- MASTERY OF FUNGI DIVERSITY & CLASSIFICATION
ZYGOMYCETES
Order the steps of growth and reproduction
in zygomycotes from 1 to 5.
1. Hyphae called rhizoids penetrate
the food, anchor the mycelium, and absorb
nutrients.
2. An asexual spore germinates on a food source and hyphae begin to grow.
3. Spores are released and another asexual cycle begins.
4. Hyphae called stolons grow across the surface of the food source and form
a mycelium.
5. Special hyphae grow upward to form sporangia that are filled with asexual
spores.
____
____
____
____
____
Use each of the terms below just once to complete the passage.
yeasts
('SaC fungi
conidia
ascospores
multicellular
unicellular
yeast cells
ascus
conidiophores
vaccine
Ascomycotes are also called (6)
because they produce sexual
'./
spores,
called (7)
(8)
. During asexual reproduction,
called a(n)
ascomycotes
produce spores called
in chains or clusters at the tips of
_. These asexual spores are produced
(9)
structures
, in a saclike structure,
called
(10)
, which are elongated hyphae.
Morels and truffles are
(11)
ascomycetes that are edible. Yeasts are
(12)
ascomycotes.
are used to make
(13)
beer} wine} and bread. They are also used in genetic research. A(n)
(14)
for the disease hepatitis B is produced
(15)
, which contain spliced human genes.
from rapidly growing
BASIDIOMYCETES
Answer the following questions
about the life of a mushroom.
16. What are basidia and where are they found?
17. What happens when mycelia of two different mating strains meet?
18. What does a mycelium with two nuclei in its cells form'{
19 What does a diploid cell inside a basidium produce
t
25
a resuleofmetosis?
Plant Diversity
Practice Activities:
Target II
TARGET II - 4
Use each of the terms below just once to complete the passage.
diploid
gametes
generations
haploid
meiosis
sporophyte
The lives of all plants consist of two alternating
The gametophyte
stages, or (1)
'
generation of a plant is responsible for the development of (2)
_________
. All seeds of the gametophyte,
__________
including the gametes, are (3)
--'. The (4)
generation is responsible
for the production of spores. All cells of the sporophyte
plant body by (6)
The spores are produced by the sporophyte
and are, therefore,
are (5)
'
_
haploid.
TARGET II - 4
Circle the letter that best completes the statement:
7. The lives of
plants include two generations that alternate.
Q. non-seed producing
b. seed
c. all
d. most
8. The generation of a plant responsible for producing gametes is the
Q. alternation
of generations.
b. gametophyte generation.
c. sporophyte generation.
d. seed-producing generation.
9. All gametophyte spores are
and all sporophyte
b. diploid/haploid.
d. diploid/diploid.
haploid/diploid.
c. haploid/haploid.
Q.'
10. Non-seed plants
Q.
that grow into gametophytes.
'release soores into the environment
i
c. release seeds into the environment
i:
<
tissue cells are
b. retain snores in the parent
olcnt
'f
d. retain seeds in the parent plant
,
Nonvascular plants are not as common or as widespread as vascular picnrs because
a. nonvascuiar piants are small.
b. the life functions of nonvascular piants require a close association with water.
co nonvascular plants are limited to dry habitats.
d none of the above.
<
.
TARGET II - 4
Use each of the terms below to complete
antheridia
leaves
pro thallus
strobilus
zygote
fertilization
the passage.
sporophyte
archegonia
reproductive cells
egg
sperm
Unlike nonvascular plants, the spore-producing
(23)
is the
dominant generation in vascular plants. A major advance in vascular plants was the
adaptation
of (24)
that protect
to form structures
developing (25)
the
. In some non-seed vascular plants, spore-
bearing leaves form a compact cluster called o(n) (26)
I,
Spores are
--'.
released from this compact cluster. These spores then grow to form the gametophyte,
called o(n) (27)
. This structure
on soil. The prcthcllus then forms (28), male reproductive
_________
is relatively small and lives in or
and (29)
structures,
, female reproductive structures.
(30)
_
are released from the cnrheridium and swim through a film of water to the (31)
__________
in the archegonium. (32)
large, dominant sporophyte
plant develops from the fertilized
TARGET II - 3
34. The most recognized generation
35. The
1:
occurs and a
(33)
'
of ferns is the
generation.
in most ferns is a thin, flat structure.
36. In most ferns, the main stem, called a
contains many stcrch-filled cells for
, is underground.
It
_
37. The leaves of a fern are eel led
and grow upward from the
rhizome.
38. fronds are often divided into leaflets celled
__
--'-
I
which are
attached to a central sripe.
39. Ferns were the first vascular plants to evolve leaves with branching
of vascular tissue.
_
Unit VII: Diversity of Life - Fungi, Non-Vascular Plants, Vascular Seedless Plants, & Vascular Seed Plants
TARGET PRACTICE PACKET ANSWERS
TARGET I - Mastery of Fungi Diversity & Classification
ZYGOMYCETES
1. step 3
2. step I
3. step 5
BASIDIOMYCETES
16. Structures in a mushroom that make basidiospores via meiosis
17. Plasmogamy
18. Dikaryon or heterokaryon
4. step 2
19. basidiospore
5. step 4
6. sac fungi
7. ascospores
8. ascus
9. conidiospores
10. conidia
11. multi-cellular
12. unicellular
13. Yeasts
14. vaccine
20. NOT ACCURATE ANYMORE Cd)
21. A
22.G
23.B
24.F
25.C
26.E
27. A
15. water
16. gametophyte
17. antheridia & archegonia
18. rhizoids
19. a waxy cuticle
20. & 21: SKIP - don't need to know abouthomworts
22. mosses, liverworts, and homworts (respectively)
TARGET II- 4 (again)
23. sporophyte
24. leaves
25. reproductive cells [(?) not sure about this one]
26. strobilus
27. prothallus
TARGETII-3
34. sporophyte
35. gametophyte
36. rhizome, energy storage
37. fronds
38. pinnae
39. bundles (?)
28. antheridia (sorry, I forgot to make the
)
29. archegonia
30. sperm
31. egg
32. fertilization
33. zygote (delete the word "fertilized" before the
TARGET II - 4 (3ed time is the charm, right?)
40. sporophyte, gametophyte
41. diploid
42. egg, sperm
43. vegetative reproduction
44. (the) dominant
45. protonema
46. mitosis
47. meiosis
48.
49.
50.
51.
52.
53.
54.
step
step
step
step
step
step
step
2
4
5
3
7
6
1
TARGET II - 5,6
55. sporophyte
56. pollen cones & ovulate cones (sporangia)
57. Megaspores are spores that will become the female gametophyte; haploid (see text p. 613 - yellow boxes)
58. Microspores are spores that will become the male gametophyte; haploid (see text p. 613 - yellow boxes)
59. Microspores become the male gametophyte enclosed in sporopollenin wall ~ pollen; pollen moves by
wind to other gymnosperms' ovulate cones
60. A micropyle is a hole in the integument of an ovule where pollen enters the female gametophyte
61. Pollen lands on and germinates a pollen tube in the female (ovulate) cone. The pollen tube grows towards
the female gametophyte and sperm swim through pollen tube to fertilize eggs in archegonium. (see :figure
30.6)
62. ovule ~ SEED
63. Seeds germinate to form 'baby' sporophyte conifer plants OR are eaten by heterotrophs (birds, squirrels)
64. Seedlings become sporophyte plant (very slowly, though)
TARGET II - 4
Use each of the terms below just once to complete the following statement?
dtploll:!
sporophyte
egg
vegetative reproduction
dominant
mitosis
qameropttyre
protanema
meiosis
sperm
40. The two phases of the plant life are the
___________
stage.
41. The cells of the sporophyte
stage and the
are all
_
42. The female gamete is the
, and the male gamete is the
------_.'
v-...,-~- -
I., ~which a new plant is produced from an existing vegetativedstructure.
43. Some plants reproduce csexuclly
44. Mosses belong to one of the
___
by a process called
few
-'---
(J
plcnt divisions in which the gametophyte
plant is
generation.
45. A small, green filament of moss cells that develops into either a maie or female moss
game:tophyte is known as a(tt)
_
46. The moss diploid zygote divides by _----!!;;...,'._., ••••.
'>'-, __
to form a new
.--'='--
sporophyte in the form of a stalk and capsule.
47. Spores are produced by
sporophyte.
in the capsule of the moss
TARGET II - 4
Number eoch description to order the stages
of a fern, from 1 (start) to 7 (last).
48. A spore germinates
of spore release
in the life cycle
and grows into a heart-shaped
gametophyte
celled
a prcthcllus.
49. After fertilization,
the diploid zygote gr<Jws into a sporophyte.
50. As the sporoohvte qrows, roots and fronds qrow out from the rhizome.
~,
51
Sperm swim
fertilize
_
through
J
a
film of
water on
the oro+hallus 1'0 reach and
en egg in the crcheqonium.
52. In each sporcnqium, spores are produced by meiosis, and the cycle
,.J."
th
.
f
oeg!ns ogaln as the spores ore orspersec ov rne wmc.
r'
;;;;':1
------~......,:~
•
f
f
12. The life cycle of nonvosculor plants includes an alternation
a. diploid sporophyte and a diploid gametophyte.
b. haploid sporophyte and a haploid gametophyte.,
c. diploid sporophyte and a haploid gametophyte.
d. haploid sporophyte and a diploid gametophyte.
of generations
between a
TARGET II - 2,3
Answer the following short answer questions and FITB (fill in the blank).
13. Identify three similarities and three differences between vascular and nonvascular
plants?
14. Some land plants produce seeds. What is the function of a seed? How does a seed
differ from a spore?
TARGET II - 2
15. Nonvascular plants are successful
16. The
with adequate
in habitats
_
generation is dominant in nonvascular plants.
17. Sperm are produced in male reproductive structures celled
and e99s are produced in female reproductive structures called
_
-_._------18. Mosses have colorless multi-cellular structures
help anchor the stem to the soil.
celled
19. N\ost liverworts have
, which
that helps reduce;
evaporation of water from the plant's tissues.
2Q. Liverworts occur in many environments and include two groups: the;
iiverwor-rs.
------------------- liverworts and +he
21. One unique feature of hornworrs is the. presence of c(n)
_________________
in each cell.
22.. The common names ;-0;" the nonvcsculcr pkmts. Br'yophyta, HepaTophytc., and
Anrhoceroohvto
arc~ ------------'.
,
-------------" . tone:
DEUTEROMYCETES,the mutualistic relationships of mycorrnizae and lichens,
and the origins of fungi.
In each blank fill in the letter of the best answer.
20.
is an example of a deuteromycote.
21. A mycorrhiza is a mutualistic
fungus and a(n)
_
22.
deueero
ill
ycote
relationship
is an antibiotic produced
_
23. Plants that have
roots grow larger.
between a
by a
associated
with their
24.
make up a division of fungi that have
no known sexual stage.
25. A lichen is a mutualistic relationship
aln]
or cyanobacterium.
26. Lichens are
between a fungus and
in all parts of the world.
27. Scientists think that ascomycotes
evolved from a common ancestor.
and
_
COMPARE AND CONTRAST
List 3 similarities
Similarities
and 3 differences
between fungi and plants.
Differences
1.
2.
3,
2.
a. basidiomycetes
b. mycorrhizae
c. alga
d. Penicillium
e. pioneer species
1'. deuteromycotes
g. penicillin
h. plant
.--.