* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Electrical Potential
Quantum potential wikipedia , lookup
Electrical resistivity and conductivity wikipedia , lookup
Work (physics) wikipedia , lookup
Internal energy wikipedia , lookup
Gibbs free energy wikipedia , lookup
Conservation of energy wikipedia , lookup
Electric charge wikipedia , lookup
Aharonov–Bohm effect wikipedia , lookup
Chemical potential wikipedia , lookup
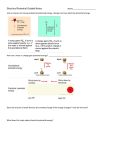
January 2012 Electrical Potential Energy Just as masses can have gravitational potential energy, charges can have electrical potential energy Electrical potential energy A mass gains PEg if work is done against gravity (i.e., if the mass is moved against the gravitational field) E A charge gains PEe if work is done against electric force (i.e., if the field is moved against the electric field) Electrical Potential Energy Just as masses can have gravitational potential energy, charges can have electrical potential energy Electrical potential energy In both cases, PE is determined by the position of an object within a field. In both cases, ΔPE = W = Fdcosθ E Electrical Potential Energy & Charge Does the amount of work done by the monkey change if the charge changes? What does that imply about Pee? Yes! Stronger charge = more work = greater increase in Pee Electrical Potential Energy & Electrical Potential Two different things that sound alike! Introducing … Electrical Potential (V) … a measure that doesn’t depend on charge. electric potential The SI unit of electric potential is the volt. electric potential energy charge 1J 1V 1C Electrical Potential Energy vs Electrical Potential A Two positive charges, A and B, are placed at equal distances from a positively charged sphere. +++++ + + ++++ + A has a larger charge than B. 0.5 m ++ + + + +++ B ++ + ++ 0.5 m Which has greater potential energy (PE)? 1) A 2) B 3) They have the same PE Which has greater electrical potential (V)? 1) A 2) B 3) They have the same V Electrical Potential Energy vs Electrical Potential The quantity electric potential is defined as the amount of _____. 1. electric potential energy 2. force acting upon a charge 3. potential energy per charge 4. force per charge Electrical Potential Energy vs Electrical Potential What happens if a positive charge is moved from point A to point B? In the first case no applied force is needed to move positive charge along electric field. In the second one, there has to be applied force to move the charge from A to B. Potential Difference (ΔV) The change in electric potential energy between two points equals the work done per unit of positive charge in order to move it from one point to the other. ∆𝑃𝐸 W VB − VA = ∆V= = q q Charge (the positive one) will naturally move from areas of high potential to areas of low potential. Work / an input of energy is needed to move charge up from low potential to high Potential Difference (ΔV) & Circuits What is the role of a battery in a circuit? Batteries supply energy to maintain a potential difference across the circuit. 1) A 12V battery means that the + terminal has an electric potential that is 12V higher than the – terminal. 2) Charges flow through the external circuit (the wire) from high to low potential. 3) As the charges flow through the circuit, they ‘lose’ energy to circuit elements such as lights and motors 4) By the time the charges get to the end terminal, they have used up 12 V of potential 5) The battery supplies the energy necessary to ‘push’ the charges back to high potential Potential Difference (ΔV) & Circuits As charges ‘lose’ energy to different circuit elements, the electric potential decreases. This is known as voltage drop. All of the electric potential difference– i.e. all of the voltage -- is used up by the end of the circuit. 1. The variable we use for potential, potential difference, and the unit for potential difference (volts) is V. 2. Don't let that confuse you when you see V = 1.5V 3. Electric potential energy is not the same as electrical potential. 4. Electrical potential can also be described by the terms, potential difference, voltage, potential drop, potential rise, electromotive force, and EMF. These terms may differ slightly in meaning depending on the situation. Check your understanding Compare an electric circuit to a roller coaster ride. What is the difference in height from the top to the bottom of a rollercoaster analogous to in a circuit? potential difference What is the motor that pulls the rollercoaster up the hill analogous to in circuit? battery Check your understanding If a battery provides a high voltage, it can ____. 1. 2. 3. 4. do a lot of work over the course of its lifetime do a lot of work on each charge it encounters push a lot of charge through a circuit last a long time Check your understanding Compared to point D, point A has … 1. 12 V higher potential energy 2. 12 V lower potential energy 3. Exactly the same potential energy The electrical potential energy is 0 at … 1. A 2. B 3. C 4. D Check your understanding The energy required to move +2C of charge from D to A is 1. 0.167 J 2. 2 J 3. 6 J 4. 24 J