* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Electrical Resistance and Ohm`s Law
Cavity magnetron wikipedia , lookup
Switched-mode power supply wikipedia , lookup
Giant magnetoresistance wikipedia , lookup
Power MOSFET wikipedia , lookup
Nanofluidic circuitry wikipedia , lookup
Rectiverter wikipedia , lookup
Nanogenerator wikipedia , lookup
Current mirror wikipedia , lookup
Surge protector wikipedia , lookup
Resistive opto-isolator wikipedia , lookup
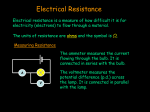
Georg Simon Ohm 1789-1854 German Physicist HIGH SCHOOL TEACHER!!!! Using equipment he built himself Determined there was a direct proportionality between voltage applied across a conductor and the resultant current (OHM’s LAW) Good conductors easily allow electrons to move through their atoms In a good conductor little energy is lost as the electrons pass along the conductor’s atoms In other materials such as a light bulb the electrons do not move as easily. This ability of a substance to impede the flow of electrons is called electrical resistance In other materials such as a light bulb the electrons do not move as easily. This ability of a substance to impede the flow of electrons is called electrical resistance Different loads have different resistances to achieve the desired conversion of energy e.g. : light bulb filament = high resistance (produces light) toaster = lower resistance (produces heat) The symbol for electrical resistance is R The standard unit is (SI) is the Ohm (Ω) The symbol for electrical resistance is R The standard unit (SI) is the Ohm (Ω) When electrons flow through different materials, the electrical resistance causes a loss of voltage There is a difference in the amount of voltage (electric potential) that an electron has after it has flowed through the material This is known as potential difference or voltage drop e.g. After electrons flow through a light bulb, they have less energy than before they went through it (some is used) e.g. After electrons flow through a light bulb, they have less energy than before they went through it (some is used) Ohm’s Law Ohm’s Law describes the relationship between potential difference and current in a conductor Potential difference = electric current x Electrical Resistance (voltage drop) V = Voltage (Potential Difference) I = electric current (measured in Amps) R = electrical resistance (measured in Ω) V = IxR (units for V are Volts) V/I = R or R = V/I (Units for R are Ω) V/R = I or I = V/R (Units for I are Amps) Sample problem: What is the voltage drop across the tungsten filament in a 100W light bulb? The resistance of the filament is 144 Ω and the current is 0.833A. V = ? I = 0.833A R = 144 Ω V = I x R V = 0.833A x 144 Ω = 120V Therefore the voltage drop at the light bulb is 120V