* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download File
Management of acute coronary syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Coronary artery disease wikipedia , lookup
Quantium Medical Cardiac Output wikipedia , lookup
Cardiac surgery wikipedia , lookup
Mitral insufficiency wikipedia , lookup
Myocardial infarction wikipedia , lookup
Artificial heart valve wikipedia , lookup
Antihypertensive drug wikipedia , lookup
Atrial septal defect wikipedia , lookup
Lutembacher's syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Dextro-Transposition of the great arteries wikipedia , lookup
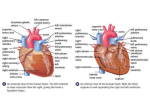
6.2.1 Draw and label a diagram of the heart showing the four chambers, associated blood vessels, valves and the route of the blood through the heart Some terms and functions ventricles – pump blood through the body or to the lungs atria – pump blood to the ventricles valves – prevent blood from going the wrong direction (backflow) arteries – carry blood away from the heart (the aorta is the main artery) veins – carry blood to the heart (the superior and inferior vena cava are the main veins) 6.2.2 State that the coronary arteries supply the heart muscle with oxygen and nutrients The heart muscle is very active and needs a lot of oxygen, glucose and other nutrients It would be impossible for the heart to obtain these nutrients from the fast flowing blood that travels through the chambers The walls of the heart are covered with a network of coronary arteries and capillaries 6.2.3 Explain the action of the heart in terms of collecting blood, pumping blood, and opening and closing of valves Right Side The right atrium collects blood from the body from the vena cava The muscle of the right atrium contracts which pushes the blood past the tricuspid valve into the right ventricle The right atrium muscle relaxes 6.2.3 Explain the action of the heart in terms of collecting blood, pumping blood, and opening and closing of valves Right Side The right ventricle muscle contracts increasing the blood pressure in that chamber This causes the tricuspid valve to close and semilunar valve opens 6.2.3 Explain the action of the heart in terms of collecting blood, pumping blood, and opening and closing of valves Right Side Blood flows into the pulmonary arteries and the pressure causes the semilunar valve to close Blood travels to the lungs and then back to the left atrium 6.2.3 Explain the action of the heart in terms of collecting blood, pumping blood, and opening and closing of valves Left Side The left atrium collects blood from the lungs from the pulmonary vein The muscle of the left atrium contracts which pushes the blood past the mitral (bicuspid) valve into the left ventricle The left atrium muscle relaxes 6.2.3 Explain the action of the heart in terms of collecting blood, pumping blood, and opening and closing of valves Left Side The left ventricle muscle contracts increasing the blood pressure in that chamber This causes the mitral valve to close The semilunar valve to opens 6.2.3 Explain the action of the heart in terms of collecting blood, pumping blood, and opening and closing of valves Left Side Blood flows into the aorta and the pressure causes the semilunar valve to close Blood travels through the body and returns to the right atrium The process is repeated 6.2.3 Explain the action of the heart in terms of collecting blood, pumping blood, and opening and closing of valves This type of circulatory system is called double circulation because the blood goes from the heart to the lungs back to the heart and then to the body. All mammals have this type of transport system Important to remember: • The walls of the left ventricle are thicker than the right ventricle. • This is because the left ventricle must pump the blood through the entire body and the right ventricle needs only to pump the blood to the lungs