* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Eighth Grade Science
Tropical year wikipedia , lookup
Formation and evolution of the Solar System wikipedia , lookup
History of Solar System formation and evolution hypotheses wikipedia , lookup
Lunar theory wikipedia , lookup
Astrobiology wikipedia , lookup
Rare Earth hypothesis wikipedia , lookup
Astronomical unit wikipedia , lookup
Geocentric model wikipedia , lookup
Theoretical astronomy wikipedia , lookup
Late Heavy Bombardment wikipedia , lookup
Extraterrestrial life wikipedia , lookup
Timeline of astronomy wikipedia , lookup
Comparative planetary science wikipedia , lookup
Dialogue Concerning the Two Chief World Systems wikipedia , lookup
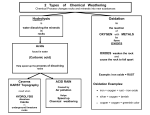
Eighth Grade Science First Six Weeks Lesson Objectives Know and demonstrate correct safety practices; Identify laboratory equipment; Evaluate the impact of research on scientific thought, society and the environment Identify and use the steps of the scientific method; Measure and calculate using the metric system; Differentiate between observation and inference using promotional materials Optional Extension: Read and interpret instructions to construct a model, then evaluate the steps taken Explain how scientists discovered subatomic particles; Explain how the atom model was developed; Describe the structure and properties of the atom Identify the number of protons, neutrons, and electrons for atoms and compare to isotopes; Describe process of radioactive decay and how these isotopes are used; Explain what is meant by half-life Describe the history of the periodic table; Interpret an element key for the periodic table; Explain how the periodic table is organized TEKS 8.1A; 8.3D 8.2A, B, D, E; 8.3B; 8.4A 8.3C 8.3D, E; 8.8A, B 8.8A, B 8.2E; 8.3C; 8.9B Second Six Weeks Lesson Objectives TEKS Recognize properties of some representative elements; Identify uses for the 8.9B, D representative elements; Recognize location of transition elements on the periodic table; Recognize properties of some transition elements Determine the difference between physical and chemical changes; 8.9A, C; 8.10C Determine the number of atoms for a chemical formula; Determine how to read and understand a chemical equation; Examine that some chemical reactions release energy and some absorb energy; Describe the chemical composition of water and identify its use as a solvent Determine how to describe and measure the speed of a chemical reaction; Identify factor that cause chemical reactions to speed up or slow down 8.9A, C Recognize that matter is made of particles in constant motion; Relate the three states of matter to the arrangement of particles within them; Explore viscosity and surface tension Compare Thermal Energy and Temperature; Relate changes in thermal 8.10A, B energy to changes of state; Explore energy and temperature changes on a graph Explain why some things float and others sink; Describe how pressure is transferred through fluids 8.7A Third Six Weeks Lesson Objectives Contrast distance and displacement; Define speed and acceleration; Calculate speed and acceleration Define force; Describe Newton's first law of motion; Predict changes in motion using Newton's second law of motion; Contrast balanced and unbalanced forces; Contrast different types of friction; Interpret motion using Newton's third law of motion Interpret motion using Newton's third law; Analyze motion using all three of Newton's laws Describe characteristics that all minerals share; Describe physical properties used to identify minerals; Identify minerals using physical properties; Describe characteristics of gems that make them more valuable; Identify some uses of minerals Recognize that igneous rocks form from magma and lava that cools; Contrast the formations of intrusive and extrusive igneous rocks; Describe conditions that form metamorphic rocks; Classify metamorphic rocks as foliated or non-foliated Explain how sedimentary rocks form; Classify sedimentary rocks as detrital, chemical or as organic in origin; Describe the difference between a rock and a mineral; Analyze and predict the sequence of events in the rock cycle TEKS 8.7A 8.7A 8.7A 8.12A 8.12A Fourth Six Weeks Lesson Objectives Describe the hypothesis of continental drift; Identify evidence of continental drift; Explain a sea floor spreading; Recognize that rock age and magnetic stripes support sea floor spreading Compare and contrast different types of plate techtonics; Explain how heat inside the Earth causes plate techtonics; Recognize features formed by plate techtonics Explain how earthquakes are caused by a buildup of strain; Compare and contrast types of faults; Compare and contrast types of seismic waves; Recognize earthquake hazards and how to prepare for them Explain how volcanoes can affect people; Describe types of materials that are produced by earthquakes; Compare how three types of volcanoes form TEKS 8.3A; 8.14A 8.14A 8.7B 8.3C; 8.14A Explain howthe locations of volcanoes and earthquake epicenters are related to techtonic plate boundaries; Explain how heat within the Earth causes Earth's plates to move Compare and contrast phenotype and genotype; Describe some effects the environment has on traits Differentiate between genetics and heredity; Explain the results of Mendel's pea plant experiments; Identify the results shown by a Punnett Square Explain how living and nonliving factors may influence evolution; Describe how natural selection occurs in a species; Compare selective breeding and natural selection 8.7A; 8.14A 8.11A, B 8.11C 8.11A, B Fifth Six Weeks Lesson Objectives Identify the gases in the Earth's atmosphere; Describe the structure of Earth's atmosphere; Explain what causes air pressure Describe what happens to energy the Earth receives from the Sun; Compare and contrast radiation, conduction and convection; Explain the water cycle Explain why different latitudes on Earth receive different amounts of solar energy; Describe the Coriolis Effect; Locate doldrums, prevailing westerlies, polar easterlies, and jet streams State the importance of Earth's oceans; Discuss the origin of Earth's oceans; Describe the composition of sea water; Explain how temperature and pressure vary with depth State how wind and the rotation of the Earth influence surface currents; Discuss how ocean currents affect weather and climate; Describe the causes and effects of density currents; Explain how an upwelling occurs Describe how wind can form ocean waves; Explain the movement of particles in a wave; Describe how the Moon and Sun cause Earth's tides; List the forces that cause shoreline erosion Describe the characteristics of plankton, nekton, and bottom dwelling organisms; Distinguish among producers, consumers and decomposers; Explain how organisms in the ocean interact in food chains Describe organic and inorganic substances; Identify minerals that your body requires; Describe the basic structure and function of a typical human cell; Describe the levels of organization in the body Describe how body systems work together to carry out important life functions; Compare negative feedback mechanisms and positive feedback mechanisms TEKS 8.10B 8.10B 8.10B 8.10B 8.10B; 8.12B 8.7B; 8.10B; 8.14A 8.6C; 8.12C 8.6A 8.6A, B Examine Earth's Physical Characteristics; Use models to differentiate between rotation and revolution; Demonstrate what causes seasons to change using models Identify the phases of the moon and their causes; Explain why solar and lunar eclipes occur; Infer what the moon's surface may reveal about its history Examine facts about the moon that might influence future space travel 8.3C; 8.13A 8.3C, D; 8.12A; 8.13A 8.13A Sixth Six Weeks Lesson Objectives Compare the Sun-centered and Earth-centered models of the Solar System; Describe current models of the formation of the Solar System List the inner planets in order from the Sun; Describe important characteristics of each inner planet; Compare and contrast Venus and Earth; Describe the major characteristics of Jupiter, Saturn, Uranus and Neptune; Explain how Pluto differs from the outer planets Describe where comets come from and how a comet develops as it approaches the Sun; Distinguish among comets, meteoroids, and asteroids TEKS 8.3E; 8.13A, C Explain why the positions of the constellations change throughout the year; Distinguish between absolute magnitude and apparent magnitude; Describe how parallax is used to determine distance Describe the structure of the Sun; Explain how sunspots, solar flares and prominences are related; Explain why the Sun is considered an average star and how it differs from stars in binary systems Describe how stars are classified; Explain how the temperature of a star relates to its color; Describe how a star evolves Diffentiate between chemical and mechanical erosion 8.13A, B 8.13A 8.13A 8.10B; 8.13A 8.13A, C 8.14A