* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download ECOSYSTEMS
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
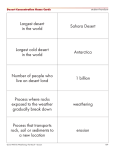
December, 2009: Ecosystem Newsletter* based in Spfld, IL EC O S Y S TEMS By Chris Crawford and Brandon Staley Table of Contents// Page 1: Saltwater Page 2: Desert Page 3: Grasslands Ecosystems Ecosystems Ecosystem SALTWATER BODIES ON EARTH Earth’s saltwater bodies contain areas such as Oceans, seas, inland lakes such as the Great Salt Lake in Utah, Estuaries, and Coastal Inlets. The moon and sun, to a lesser extent, control the tides that provide homes for many organisms such as plankton, eels, and fish. The ecosystems controlled by the rising tides are more diverse, and usually live in the darkened zone of the sea. An extremely diverse saltwater ecosystem is the coral reef. They are formed over long periods of time, from Calcium Carbonate scattered by animals called corals. Over time, coral reefs are formed. Coral Saltwater Body Facts *About 95% of earth’s surface water is salt water. *Average salinity of oceans is 35g of salt per 1000g of water *Scientists divide the ocean into zones based on the distance which lights penetrates the water. The lighted zone is the upper 200m, while the lower areas are the dark zones. reefs do not adapt well to long term stress. Runoff from fields, increased sedimentation, and increased sewage damage rates are all causes of coral reef pollution, and the death of corals. Inside coral reefs live many species of animals. Sponges, Anemones, Bryozoans, Sea Stars, Urchins, and Sea Turtles all live in reefs. Ecosystems Newsletter*2300 E. Jackson Street*Springfield, IL*62702*U.S.A December, 2009: Ecosystem Newsletter* based in Spfld, IL EC O S Y S TEMS : D ES ERT EC O S Y S TEMS Desert Life Desert plants are adapted for survival in the extreme dryness, and hot and cold temperatures of this biome. Most plants are able to store water in their bodies for long periods of time (up to several years at a time.) Cactus are the most recognizable desert plants in the western hemisphere, and are often portrayed as the desert’s most identifiable characteristic. Weather Conditions and environmental facts Deserts receive less than 25 centimeters of rain each year. Some deserts never receive rain at all. Soil contains very little organic matter. Much of the ground is bare. Wind blown sand dunes are characteristics of the driest desert. (Oryx Antelope on dunes) Animals also have special adaptations to survive in this extreme environment. One of these animals is the Kangaroo Rat. It has the ability to take water from it’s food when it is in it’s digestional track. Large animals are not often found in the desert. Another animal adapted to the desert is the Giant Hairy Scorpion. It has a venomous sting, and it is protected from predators. Desert Geology A desert biome The geology of each desert is unique. Some deserts have sand dunes - great waves of sand weathered from rock, that move over time as wind blows the sediment. Other deserts have no dunes but instead have unique rock formations carved by wind and streams that only flow at times when there is moisture. Ecosystems Newsletter*2300 E. Jackson Street*Springfield, IL*62702*U.S.A December, 2009: Ecosystem Newsletter* based in Spfld, IL TH E G RA S S LA ND EC O S Y S TEM Grassland Life Grasslands usually house large mammals, ranging from Kangaroos to Bison to Zebra. Some common animals in the grasslands are Coyotes, Eagles, Bobcats, the Gray Wolf, Wild Turkey, Fly Catcher, Canadian Geese, Crickets, Dung Beetle, Bison, and Prairie Chicken. Grasslands provide a home to many different species of plant; Wheat, Rye, Oats, Barley, Corn are all examples. There are two different types of grasslands; tall-grass type, which are humid and wet, and short-grass, which are dry, and have hotter summers and colder winters than the tall-grass type. In the North American Grasslands, it rains quite often and it is very humid. As you travel further west and approached the Rocky Mountains, the grass becomes shorter. There is less rain in the summer and the winters got colder. These are the short-grass prairies. Region Facts The grassland is a temperate and tropical biome, and it receives 25 centimeters of rain each year. Grasslands have a dry season where there is no rain, and rivers go dry, and all grasslands have these. Grassland Names • • • • Prairies Panes Savannas Steppe Grasslands are normally used to raise livestock such as cattle, or sheep. Overgrazing can cause lack of topsoil. Ecosystems Newsletter*2300 E. Jackson Street*Springfield, IL*62702*U.S.A