* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Ophthalmic emergencies, Mr K Lett
Survey
Document related concepts
Contact lens wikipedia , lookup
Visual impairment wikipedia , lookup
Eyeglass prescription wikipedia , lookup
Keratoconus wikipedia , lookup
Idiopathic intracranial hypertension wikipedia , lookup
Vision therapy wikipedia , lookup
Retinal waves wikipedia , lookup
Visual impairment due to intracranial pressure wikipedia , lookup
Mitochondrial optic neuropathies wikipedia , lookup
Retinitis pigmentosa wikipedia , lookup
Blast-related ocular trauma wikipedia , lookup
Macular degeneration wikipedia , lookup
Transcript
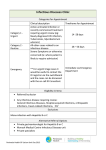
Mr. Kim Son Lett Consultant Ophthalmologist & Vitreo-Retinal Surgeon Birmingham & Midland Eye Centre & BMI The Priory Pre-Triage System Red Need to be seen within a few hrs, further triaging. Amber Need to be seen within 72 hrs, diverted to UCC slots. Green No need for urgent assessment, referred to GP, optometrist or to OPD (via GP). v Red – Very Urgent Penetrating eye injury Acute post-op endophthalmitis Severe chemical injury Orbital cellulitis GCA with visual symptoms Sudden loss of vision <6hrs v Red - Urgent Painful red eye with visual loss Retinal detachment with good VA Corneal ulcer, esp. with CL wear Blunt trauma with hyphaema & ↑ IOP Corneal graft rejection Painful diplopia v Amber Flashes & floaters, no loss of vision Red eye without pain or visual loss Retinal vein occlusions (OPD 4-6/52) Diabetic retinopathy with vitreous haemorrhage Wet AMD (preferably refer to Fast Track Macular Clinic) v Green – GP / Optometrist Mx Bacterial & viral conjunctivitis Allergic conjunctivitis Blepharitis Dry eyes Lid lumps and bumps v Green – OPD Referral Cataract Chronic / gradual visual loss (months) Open angle glaucoma, ocular hypertension Watery eyes Ectropion, entropion Lid lumps & bumps v Non-acute diplopia Trauma Burns Acid, alkali, thermal, arc eye Abrasions & lacerations Lid, corneal and conjunctival, Penetrating Eye Injuries Foreign bodies Corneal, conjunctival, sub-tarsal, intra-ocular Blunt trauma v Sub-conjunctival haemorrhage, hyphaema, choroidal rupture Orbital Blowout Fracture, Traumatic Optic Neuropathy Chemical Injury Emergency Alkali or Acid pH check Immediate irrigation v May result in limbal stem cell failure Corneal Abrasion History provides diagnosis & indication of severity Mostly doesn’t require A & E Oc. Chloramphenicol qid 5/7 v Foreign Bodies Can be removed if confident g. Chlor qid 5/7 Refer (PEARS?) if unable to remove or rust rings Always check for subtarsal FB v as well Sub-conjunctival Haemorrhage Spontaneous vs traumatic Self limiting No treatment No referral required v Blow Out Fracture Assess for globe damage, Traumatic Optic Neuropathy Orbital surgery only if tissue entrapment Normally performed within 4/52 v Cornea Dry eye Recurrent erosion syndrome Ulcers CL related Acanthamoeba Dendritic Shingles v Dry Eyes Lubricants Look for blepharitis Refer OPD only if unable to improve symptoms v Recurrent Corneal Erosion H/O Index injury Typically pain on waking / opening eyes Oc. Simple / Lacrilube nocte 3/12 Refer OPD if no improvement v Bacterial Keratitis Esp in CL wearers Excess wear, poor hygiene Urgent referral Differentiate from marginal keratitis v Dendritic Ulcer Typically HSV 1, as with cold sores Self limiting Treat with topical Acyclovir / Valgancyclovir 5x/d, 7/7 UCC referral v Herpes Zoster Ophthalmicus Oral antiviral Rx if started within 72hrs onset of rash Not always eye involvement Hutchinson’s sign 70% chance eye involvement Most eye involvement doesn’t require specialist Rx v Conjunctiva Conjunctivitis Bacterial, viral, allergic Episcleritis Scleritis v Bacterial Conjunctivitis Purulent / mucopurulent discharge Self limiting OTC g. Chlor qid 1/52 No referral required v Viral Conjunctivitis Watery discharge Follicular reaction Self limiting No referral required unless corneal involvement v Allergic Conjunctivitis Identification and avoidance of trigger allergen Topical Sodium cromoglycate Oral anti-histamines No referral required unless persistent problem v Episcleritis Self limiting Mild – Moderate discomfort Oral NSAIDs, eg ibuprofen No referral required unless persistence Steroid dependency v Scleritis Severe dull boring pain Brawny red appearance Strong association with autoimmune and connective tissue disease Urgent referral Needs extensive management v Lids Blepharitis Anterior, posterior Chalazion, stye Ectropion, entropion Pre-septal cellulitis v Anterior & Posterior Blepharitis Lid hygiene Hot compresses Treat associated dry eye No referral required v Chalazion Hot compresses I&C if refractory Prescribe oral Abx if infected No referral to A & E v Senile Ectropion & Entropion Ensure lubrication of ocular surface No acute management in A&E Refer routinely v Pre-Septal Cellulitis Need to differentiate with orbital cellulitis Pt not systemically unwell No orbital signs Needs oral Abx (GP) Refer if in doubt v Orbital Cellulitis Potentially sight / life threatening condition Pt systemically unwell, pyrexial Orbital signs Emergency referral Need admission and IV ABx v Neuro-ophthalmology IIIrd, IVth, VIth nerve palsies Optic neuritis Papilloedema Giant cell arteritis v 3rd, 4th, 6th Palsy Majority will be microvascular in elderly diabetic hypertensive population Consider duration Beware of painful nerve palsy esp 3rd PCA aneurysm Beware of assoc headache esp 6th GCA v Disc Swelling Physiological Hypermetropes Optic cup SVP Vessel changes Exudates Haemorrhages Hyperaemia Retinal folds VISUAL SYMPTOMS? v Optic Neuritis Mostly due to demyelination Unilateral vs bilateral Child vs adult 2/52 ↓, 2/52 ↔, 2/52 ↑ Reduced vision, colour vision, RAPD Uhtoff’s phenomenon Pain esp ocular movement Haemorrhages Hyperaemia Venous distension Swelling Or no physical signs v Papilloedema Due to raised ICP Bilateral Reduced vision Obscurations Blind spot enlargement Haems Hyperaemia Tortuous congested vessels Exudates Cup obliteration Retinal folds v Giant Cell Arteritis Temporal headache and tenderness Blurred vision Jaw claudication Polymyalgia Associated with RAOs Emergency referral to Eye Cas ONLY if visual symptoms eg. v Amaurosis Otherwise refer urgently to Rheumatology / Physicians Glaucoma Open vs Closed angle 1̊ vs 2̊ Neovascular What IOP is urgent? <30mmHg refer to outpatients >30mmHg D/W on call team v Acute Angle Closure Glaucoma Typically presents midday onwards Fixed, semi-dilated pupil High pressure, corneal oedema Closed angle – may need to examine fellow eye Emergency referral Needs medical treatment then laser iridotomy More extensive surgery may be necessary v Vitreo & Medical Retina Posterior Vitreous Detachment Vitreous haemorrhage Retinal tears and holes Retinal detachment Wet AMD Vascular occlusions v Proliferative diabetic retinopathy Posterior Vitreous Detachment Only 30-50% PVD symptomatic Symptomatic PVD refer to UCC, depending on duration Most are not associated with retinal detachment v Vitreous Haemorrhage Check for systemic associations eg. DM, HT, Sickle Examine fellow eye If present, UCC referral (duration dependent) In absence of systemic disease, PVD with VH has 70% incidence of retinal tear Urgent referral to Eye Cas v Retinal Detachment Is the macula on or off? VA Clinical exam If on, emergency referral If off, Eye Cas, UCC or clinic depending on duration Check for symptoms of chronicity NOT ALL DETACHMENTS ARE AN EMERGENCY! v Wet Macular Degeneration Sudden onset reduction of vision, distortion H/O dry AMD Optician can diagnose Fast track macular service v Venous Occlusions No emergency treatment available Refer via fast track system Need long term treatment v Arterial Occlusions Irreversible retinal damage from 4hrs of onset Immediate emergency treatment up to 8hrs from onset Aspirin ocular massage rebreathing into bag Beyond this time no heroic measures Check for GCA symptoms Stroke/TIA pathway v Proliferative Retinopathy Most commonly diabetics Also Sickle, prior RVOs and rarely RAOs Refer to UCC unless also VH v The Future 6-9% annual increase in demand <30% of attenders are genuine 4hr cases PEARS / MECS Rapid access clinics Allied professionals in house Nurses Optometrists Orthoptists v GP surgeries open all hours!