* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Basic Electric Circuits Series Circuits
Negative resistance wikipedia , lookup
Electronic engineering wikipedia , lookup
Printed circuit board wikipedia , lookup
Radio transmitter design wikipedia , lookup
Integrating ADC wikipedia , lookup
Transistor–transistor logic wikipedia , lookup
Josephson voltage standard wikipedia , lookup
Regenerative circuit wikipedia , lookup
Power electronics wikipedia , lookup
Operational amplifier wikipedia , lookup
Surface-mount technology wikipedia , lookup
Valve RF amplifier wikipedia , lookup
Voltage regulator wikipedia , lookup
Switched-mode power supply wikipedia , lookup
Power MOSFET wikipedia , lookup
Current source wikipedia , lookup
Schmitt trigger wikipedia , lookup
Two-port network wikipedia , lookup
Rectiverter wikipedia , lookup
Surge protector wikipedia , lookup
RLC circuit wikipedia , lookup
Current mirror wikipedia , lookup
Integrated circuit wikipedia , lookup
Resistive opto-isolator wikipedia , lookup
Flexible electronics wikipedia , lookup
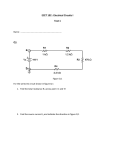
Basic Electric Circuits Series Circuits ET 150 Series Circuit Learning Objectives In this lesson you will: learn the characteristics of a series electric circuit. solve a series electric circuit using a voltmeter and Ohm’s Law see how a series circuit can be used as a voltage divider solve example problems find the equivalent resistance for a series-connected string of resistors Series Circuits Series Circuit Characteristics Components connected end-to-end Current only follows one path Voltage of source divides between components according to their value Sum of component voltage values must equal source value R2 R1 + + VR1 I VR2 + VR3 Es R3 Es = VR1+VR2+VR3 Kirchhoff’s Voltage Law Series Circuits Solving series circuits using Ohm’s law and a voltmeter VR1=6.5 V VR2=8.5 V I=? + R1=65 Ω + R2=85 Ω + R3=50 Ω Es=20V VR3=5.0 V Es = VR1 + VR2 +VR3 = 6.5+8.5+5 = 20V I= VR1 6.5 V = = 0.1 A R1 65 Ω I= VR 2 8.5 V = = 0.1 A R2 85 Ω I= VR 3 5.0 V = = 0.1 A R3 50 Ω Current, I same in all resistors Series Circuits The Voltage Divider Circuit The voltage divider circuit is a series circuit with two resistors Design Formula R1 Es ⎛ R2 ⎞ ⎟⎟ E s Vout = ⎜⎜ ⎝ R1 + R 2 ⎠ R2 Voltage across resistor, R2, is considered the output of the circuit. Vout Series Circuits Example: A 120 V dc source is series connected to a 50 kΩ and a 100 kΩ resistor. (See the figure.) What is the voltage output read by the meter? ⎛ R2 ⎞ ⎟⎟ E s Vout = ⎜⎜ ⎝ R1 + R 2 ⎠ R1=50 kΩ R2=100 kΩ Es=120 V Vo=? V 100 kΩ ⎛ ⎞ Vo = ⎜ ⎟ 120 V ⎝ 50 kΩ + 100 kΩ ⎠ ⎛ 100 kΩ ⎞ Vo = ⎜ ⎟ 120 V ⎝ 150 kΩ ⎠ ⎛2⎞ Vo = ⎜ ⎟ 120 V = 80 V ⎝3⎠ Series Resistors Simplifying series resistors Equivalent Circuit RT Voltage source will supply the same current, I, to RT as to R1+R2+R3 . RT RT = R1 + R2 +R3 RT is the equivalent value of the series resistors This formula works for any number of resistors Simplifying Series Resistors Example Find the equivalent resistance, RT, for the circuit below. 120 Ω 68 Ω RT =R1+R2+R3 RT=120 Ω +68 Ω + 47 Ω 47 Ω RT=235 Ω RT=235 Ω ET 150 Coming Next: Parallel Electric Circuits BASIC ELECTRIC CIRCUITS SERIES CIRCUITS